444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
Market Overview:
The India Connected Rail market represents a pivotal advancement in the railway sector, leveraging connectivity and technology to enhance efficiency, safety, and passenger experience. This comprehensive overview delves into the market’s growth drivers, challenges, opportunities, and transformative impact on the Indian railway system.
Meaning:
Connected Rail in India refers to the integration of digital technologies, communication systems, and data analytics within the railway infrastructure. This involves the deployment of smart sensors, connectivity solutions, and advanced analytics to optimize operations, improve safety, and provide an enhanced travel experience for passengers.
Executive Summary:
The India Connected Rail market is undergoing significant growth, driven by the government’s focus on modernizing railway infrastructure and improving overall efficiency. This executive summary provides a concise overview of key market trends, leading players, and the transformative impact of connected rail technologies on the Indian railway system.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights:
Market Drivers:
Market Restraints:
Market Opportunities:
Market Dynamics:
The India Connected Rail market operates in a dynamic environment influenced by technological advancements, regulatory changes, and the evolving expectations of passengers. Key dynamics include the integration of digital solutions into traditional rail systems, the role of data in decision-making, and the pursuit of a connected rail network that prioritizes safety and efficiency.
Regional Analysis:
Competitive Landscape:
Leading Companies in the India Connected Rail Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
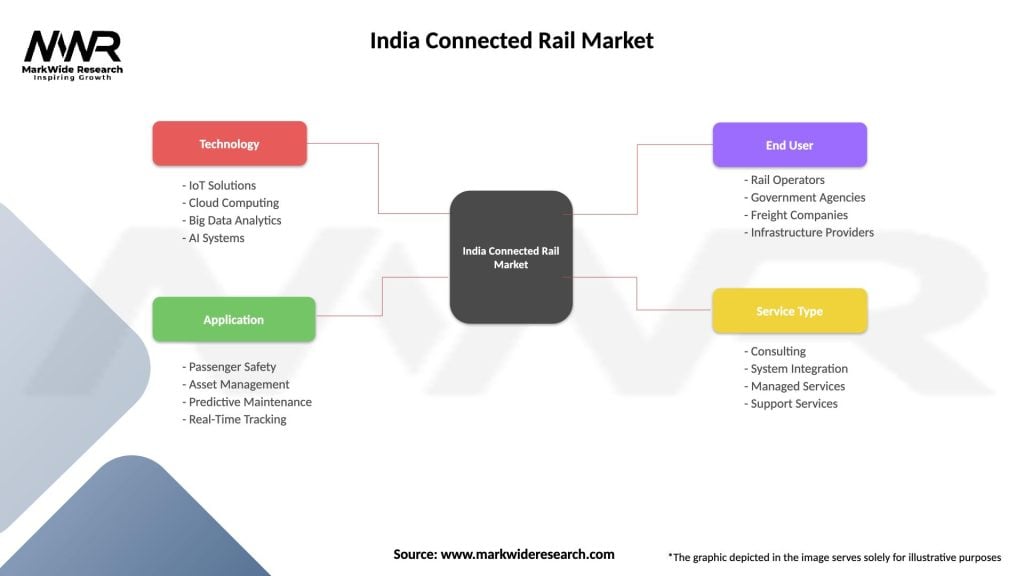
Segmentation:
Category-wise Insights:
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis:
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends:
Covid-19 Impact:
The Covid-19 pandemic has had notable implications for the India Connected Rail market:
Key Industry Developments:
Analyst Suggestions:
Future Outlook:
The future outlook for the India Connected Rail market is characterized by ongoing advancements, technological innovations, and a commitment to creating a modern, efficient, and passenger-friendly railway system. Considerations for the future include:
Conclusion:
The India Connected Rail market represents a transformative phase in the country’s railway sector, where connectivity and technology converge to create a modern and efficient transportation network. As the industry navigates challenges and capitalizes on opportunities, the strategic deployment of connected rail technologies is expected to redefine railway operations, ensuring safety, efficiency, and an enhanced experience for passengers. Stakeholders in this dynamic landscape are encouraged to embrace innovation, collaborate on solutions, and contribute to the realization of a connected and future-ready railway system in India.
What is Connected Rail?
Connected Rail refers to the integration of advanced technologies in railway systems to enhance operational efficiency, safety, and passenger experience. This includes the use of IoT, big data analytics, and real-time communication systems.
What are the key players in the India Connected Rail Market?
Key players in the India Connected Rail Market include Indian Railways, Siemens, Alstom, and Bombardier, among others. These companies are involved in various aspects of rail technology, including signaling, train control systems, and passenger information systems.
What are the growth factors driving the India Connected Rail Market?
The growth of the India Connected Rail Market is driven by increasing urbanization, the need for improved safety and efficiency in rail transport, and government initiatives aimed at modernizing railway infrastructure. Additionally, the rising demand for smart transportation solutions contributes to this growth.
What challenges does the India Connected Rail Market face?
Challenges in the India Connected Rail Market include high initial investment costs, the need for skilled workforce, and potential cybersecurity threats. These factors can hinder the implementation of advanced technologies in rail systems.
What opportunities exist in the India Connected Rail Market?
Opportunities in the India Connected Rail Market include the expansion of high-speed rail networks, the integration of smart city initiatives, and advancements in automation and AI technologies. These developments can enhance operational efficiency and passenger services.
What trends are shaping the India Connected Rail Market?
Trends in the India Connected Rail Market include the adoption of digital twin technology for infrastructure management, increased use of predictive maintenance, and the implementation of contactless ticketing solutions. These innovations aim to improve the overall efficiency and user experience in rail travel.
India Connected Rail Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Technology | IoT Solutions, Cloud Computing, Big Data Analytics, AI Systems |
| Application | Passenger Safety, Asset Management, Predictive Maintenance, Real-Time Tracking |
| End User | Rail Operators, Government Agencies, Freight Companies, Infrastructure Providers |
| Service Type | Consulting, System Integration, Managed Services, Support Services |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at