444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
Market Overview
Cloud seeding, a weather modification technique, has gained traction in India as a potential solution to mitigate drought conditions, enhance rainfall, and address water scarcity issues. The Indian cloud seeding market holds promise in augmenting precipitation levels through the introduction of seeding agents into clouds, stimulating the formation of raindrops or snowflakes and promoting precipitation in targeted regions. As India grapples with erratic monsoon patterns and uneven distribution of rainfall across different regions, cloud seeding emerges as a strategic intervention to enhance water resources and agricultural productivity.
Meaning
Cloud seeding refers to the artificial process of inducing precipitation by dispersing seeding agents, such as silver iodide or potassium iodide, into clouds to stimulate the condensation and aggregation of water vapor particles, thereby triggering rainfall or snowfall. This technique aims to modify atmospheric conditions and enhance precipitation levels in regions experiencing water scarcity or drought conditions. In India, cloud seeding initiatives are implemented to augment rainfall during the monsoon season, replenish reservoirs, and support agricultural activities.
Executive Summary
The India cloud seeding market presents opportunities for stakeholders to leverage innovative weather modification technologies and collaborative partnerships to address water management challenges, mitigate drought risks, and enhance environmental sustainability. Cloud seeding projects, supported by government agencies, research institutions, and private enterprises, aim to optimize rainfall patterns, replenish water resources, and promote socio-economic development in drought-prone regions. As India intensifies efforts to combat water scarcity and climate change impacts, cloud seeding emerges as a viable strategy to harness atmospheric moisture and augment precipitation levels through scientific interventions and operational deployments.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The India cloud seeding market operates within a dynamic ecosystem shaped by evolving climatic trends, technological innovations, regulatory frameworks, and stakeholder engagements. The interplay of market dynamics, including scientific advancements, policy interventions, socio-economic considerations, and environmental impacts, influences the trajectory and impact of cloud seeding initiatives on water resources management, agricultural sustainability, and climate resilience in India.
Regional Analysis
The India cloud seeding market exhibits regional variations in meteorological conditions, hydrological landscapes, and socio-economic factors, necessitating tailored approaches to cloud seeding deployment, target identification, and outcome evaluation across diverse regions, including arid zones, coastal areas, mountainous terrains, and agricultural hinterlands.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in India Cloud Seeding Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
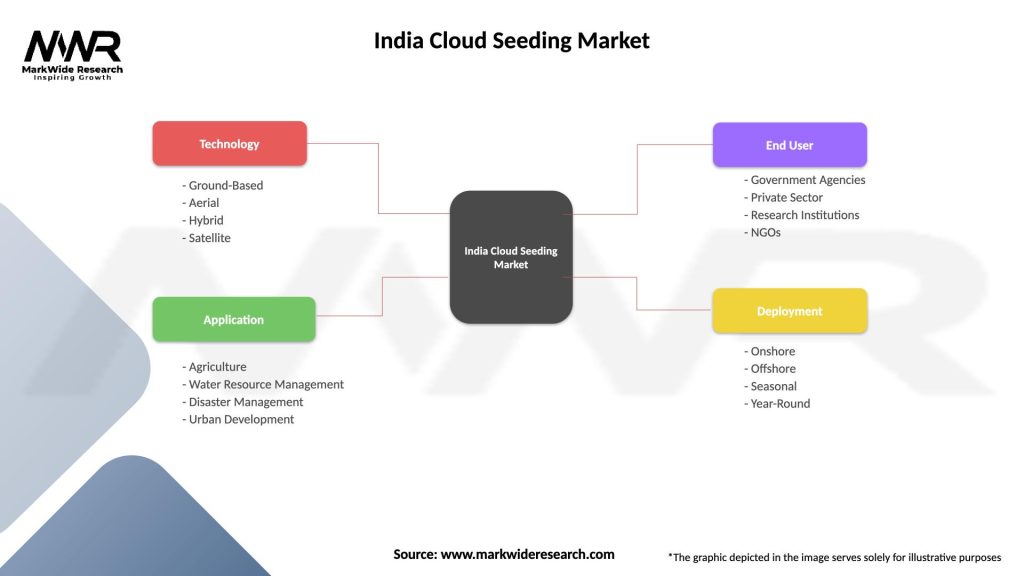
Segmentation
The India cloud seeding market can be segmented based on various factors, including geographical regions, climatic zones, target applications, seeding methodologies, and outcome metrics, facilitating nuanced analyses, customized interventions, and performance evaluations tailored to specific contexts and objectives in India.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
The India cloud seeding market offers several benefits for industry participants and stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis provides insights into the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats associated with cloud seeding interventions in India:
Understanding these factors through a comprehensive SWOT analysis helps stakeholders strategize, plan, and implement cloud seeding interventions effectively in India’s dynamic and evolving water management landscape.
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic has implications for cloud seeding operations in India:
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the India cloud seeding market is characterized by innovation, collaboration, and adaptive management strategies to address water management challenges, enhance climate resilience, and promote sustainable development outcomes across diverse regions and sectors. As India navigates complex socio-economic, environmental, and technological transitions, cloud seeding emerges as a strategic tool to harness atmospheric moisture, optimize precipitation patterns, and build resilience to climate change impacts in India’s water-stressed regions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the India cloud seeding market represents a dynamic nexus of science, technology, policy, and society aimed at addressing water scarcity, enhancing rainfall, and building climate resilience through innovative weather modification interventions. By leveraging scientific advancements, stakeholder partnerships, and community engagement, cloud seeding initiatives have the potential to transform India’s water management landscape, mitigate drought risks, and promote sustainable development outcomes for future generations. With careful planning, adaptive strategies, and ethical considerations, cloud seeding emerges as a valuable tool in India’s quest for water security, environmental sustainability, and inclusive growth in the face of climate change challenges.
What is Cloud Seeding?
Cloud seeding is a weather modification technique that aims to enhance precipitation by dispersing substances into the atmosphere. This process can be used to increase rainfall in arid regions, improve water supply, and mitigate drought conditions.
What are the key players in the India Cloud Seeding Market?
Key players in the India Cloud Seeding Market include companies like Weather Modification, Inc., and AgraWeather, which specialize in weather modification technologies and services. These companies focus on providing cloud seeding solutions for agricultural and water resource management, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the India Cloud Seeding Market?
The India Cloud Seeding Market is driven by factors such as increasing water scarcity, the need for enhanced agricultural productivity, and government initiatives to combat drought. Additionally, advancements in technology and growing awareness of weather modification benefits contribute to market growth.
What challenges does the India Cloud Seeding Market face?
Challenges in the India Cloud Seeding Market include regulatory hurdles, environmental concerns regarding the impact of seeding agents, and the unpredictability of weather patterns. These factors can hinder the widespread adoption and effectiveness of cloud seeding initiatives.
What opportunities exist in the India Cloud Seeding Market?
The India Cloud Seeding Market presents opportunities for innovation in technology and methods, as well as partnerships between government and private sectors. There is also potential for expanding applications in disaster management and climate resilience strategies.
What trends are shaping the India Cloud Seeding Market?
Trends in the India Cloud Seeding Market include the integration of advanced meteorological technologies, increased investment in research and development, and a growing focus on sustainable practices. These trends aim to enhance the effectiveness and acceptance of cloud seeding as a viable solution for water management.
India Cloud Seeding Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Technology | Ground-Based, Aerial, Hybrid, Satellite |
| Application | Agriculture, Water Resource Management, Disaster Management, Urban Development |
| End User | Government Agencies, Private Sector, Research Institutions, NGOs |
| Deployment | Onshore, Offshore, Seasonal, Year-Round |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in India Cloud Seeding Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at