444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
High-speed cameras are the advanced imaging devices used to capture images at high frame rates with high resolutions. The high-speed cameras are typically used for scientific research, automotive, and aerospace applications. High-speed cameras have a high-speed image sensor that can capture images at speeds up to several thousand frames per second (fps), providing better image quality and more accurate results. In recent years, high-speed cameras have become more affordable and widely used in various industries, which has boosted the growth of the high-speed camera market.
A high-speed camera is a type of camera that is designed to capture fast-moving objects or processes. High-speed cameras are used in a wide range of applications, including scientific research, engineering, sports, entertainment, and defense. These cameras can capture images at speeds of up to thousands of frames per second, providing high-quality images that are used for analysis and research.
Executive Summary
The global high-speed camera market is projected to grow significantly in the coming years due to the increasing adoption of high-speed cameras in various industries. The high-speed camera market is expected to be driven by the growing demand for high-speed cameras in scientific research and the automotive industry. The high-speed camera market is also expected to be driven by the increasing use of high-speed cameras in the entertainment industry and the adoption of high-speed cameras in defense and aerospace applications.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Frame Rate vs. Resolution Trade-Offs: Systems offering ultra-high frame rates often compromise on resolution; manufacturers are balancing both through sensor innovation and FPGA-based real-time processing.
Emerging Industry 4.0 Use Cases: High-speed imaging integrated into production-line monitoring boosts early defect detection and process optimization.
Cross-Sector Demand: While automotive crash testing remains a major application, growth in sports analytics, biomedical research, and UAV-based inspections is accelerating.
Cloud-Enabled Workflows: Wireless connectivity and cloud storage options allow remote control and collaboration, expanding usage beyond dedicated labs.
Rising Entry of Compact Systems: Portable, high-speed cameras with built-in lighting and onboard storage are opening new field-deployable use cases.
Market Drivers
Quality Control in Manufacturing: Automated optical inspection of high-speed production lines requires high-speed imaging to detect microscopic defects without slowing throughput.
Automotive and Crash Test Demand: Regulatory safety standards and consumer expectations drive extensive crash testing and pedestrian safety research, leveraging high-speed videography.
Aerospace & Defense R&D: Ballistics testing, explosion analysis, and aerodynamic studies rely on detailed frame-by-frame data to validate designs and ensure safety.
Advancements in Sensor Technology: Improvements in CMOS sensor sensitivity and global shutter performance enable higher frame rates with lower noise and better dynamic range.
Growth of Digital Content Creation: Filmmakers and broadcasters increasingly use slow-motion footage to enhance visual storytelling, fueling demand for high-speed camera rentals and purchases.
Market Restraints
High Capital Costs: Premium high-speed cameras and their supporting infrastructure (high-bandwidth storage, specialized lighting) entail significant investment.
Data Management Challenges: Extremely high data rates require robust on-board processing, high-capacity storage, and efficient post-capture workflows.
Specialized Expertise Required: Effective deployment and interpretation demand trained operators and analysts, limiting adoption in smaller organizations.
Limited Portability of High-End Models: Ultra-high-frame-rate systems remain bulky and reliant on external power sources, constraining field use.
Competitive Alternatives: In certain applications, high-frame-rate photodiodes or laser-based sensors can substitute for imaging systems at lower cost.
Market Opportunities
Embedded AI Analytics: Real-time defect detection and event classification directly on camera hardware can reduce data volumes and speed decision making.
Hybrid Imaging Systems: Combining high-speed modules with multispectral or thermal sensors unlocks new diagnostic capabilities in research and industrial applications.
Modular, Scalable Platforms: Interchangeable sensor heads and lens mounts allow users to upgrade frame-rate or resolution without replacing entire systems.
Remote Monitoring Solutions: Cloud-connected high-speed cameras enable distributed teams to control experiments and analyze footage from any location.
Growing SME Adoption: Affordable entry-level high-speed cameras designed for small labs and educational institutions broaden the user base.
Market Dynamics
The high-speed camera market is dynamic and constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing market trends. The market is highly competitive, with several major players and a large number of smaller players. The high-speed camera market is characterized by rapid product development, with manufacturers constantly developing new and advanced high-speed camera systems to meet the growing demand from various industries.
The high-speed camera market is also driven by changing market trends, such as the increasing adoption of high-speed cameras in the healthcare and consumer electronics industries. The market is also influenced by various factors, such as government regulations, technological advancements, and the economic environment.
Regional Analysis
The global high-speed camera market is segmented into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East and Africa. North America is expected to be the largest market for high-speed cameras due to the presence of major players and the high adoption rate of high-speed cameras in various industries. The Asia Pacific is expected to be the fastest-growing market for high-speed cameras due to the increasing demand for high-speed cameras in the automotive, aerospace, and defense industries.
Competitive Landscape
Leading companies in the High-Speed Camera Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.

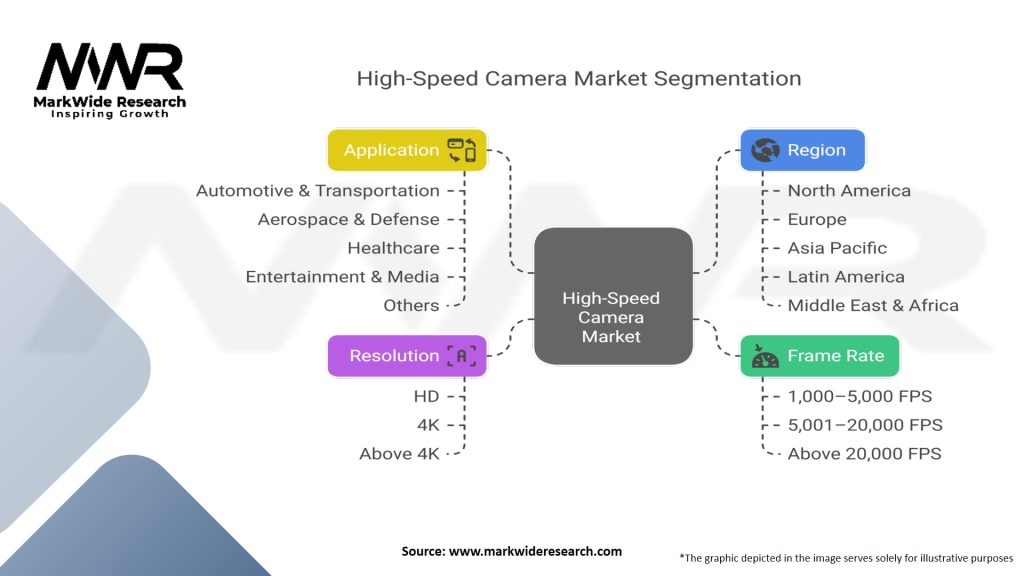
Segmentation
Frame Rate: Entry-Level (up to 5,000 fps), Mid-Range (5,000–100,000 fps), Ultra-High (above 100,000 fps).
Resolution: Standard Definition (<1 MP), High Definition (1–4 MP), Ultra-High Definition (>4 MP).
Application: Industrial Inspection, Automotive Testing, Defense & Ballistics, Scientific Research, Media & Entertainment, Sports Analytics.
Form Factor: Desktop/Lab-Mounted, Portable/Handheld, OEM/Module.
Category-wise Insights
Industrial Inspection: Cameras in this segment emphasize rugged build, compatibility with machine-vision interfaces, and synchronization capabilities for multi-camera setups.
Automotive Testing: Systems optimized for crash-test dummies, airbag deployment analysis, and NVH (noise-vibration-harshness) testing offer synchronized multi-camera control and high dynamic range.
Defense & Ballistics: Requires ultra-high frame rates, precise triggering, and often specialized housings to withstand blast and shock environments.
Scientific Research: Focuses on high resolution and sensitivity for low-light experiments in fluid mechanics, combustion studies, and droplet dynamics.
Media & Entertainment: Balances frame rate with color fidelity and output formats, often tied into existing post-production pipelines and lens ecosystems.
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
Enhanced Insight: Ability to visualize and quantify transient events leads to improved process design, product quality, and safety validation.
Time Savings: High-speed imaging replaces trial-and-error testing, accelerating R&D cycles and reducing development costs.
Risk Mitigation: Detailed analysis of failure modes and dynamic events helps prevent costly downtime and safety incidents.
Competitive Differentiation: Access to advanced imaging capabilities allows companies to innovate faster and demonstrate superior product performance.
Cross-Functional Applications: A single high-speed camera platform can serve diverse departments—engineering, quality, marketing—maximizing ROI.
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Unmatched temporal resolution for analyzing high-velocity phenomena.
Broad applicability across multiple high-value industries.
Ongoing innovation in sensor and processing technologies.
Weaknesses:
High initial investment and specialized infrastructure requirements.
Steep learning curve for effective operation and data interpretation.
Large data volumes demand robust IT infrastructure.
Opportunities:
Integration of AI-based event detection and automated annotation.
Expansion into emerging small-lab and educational markets with entry-level models.
Development of wireless, battery-operated systems for untethered field use.
Threats:
Alternative sensing technologies (e.g., LiDAR, high-speed photodiodes) eating into certain niche applications.
Economic downturns potentially delaying capital equipment purchases.
Supply chain disruptions affecting specialized components.
Market Key Trends
AI-Driven Analytics: On-camera edge computing for real-time anomaly detection and metadata tagging.
Miniaturization: Development of compact, lens-interchangeable cameras that fit on drones and robotic arms.
High Dynamic Range: New sensor designs that capture both low-light and bright-spark events without saturation.
Multi-Camera Synchronization: Seamless operation of large arrays for 3D reconstruction and volumetric analysis.
Cloud-Native Workflows: Direct streaming of high-speed data to cloud platforms for collaborative review and machine-learning training.
Covid-19 Impact
During the pandemic, supply chain disruptions and laboratory access restrictions briefly slowed deployments of new high-speed camera systems. However, increased emphasis on automated inspection in contactless manufacturing boosted demand in factory automation. R&D organizations pivoted toward remote access solutions, leading to rapid adoption of cloud-connected cameras and web-based control interfaces.
Key Industry Developments
Phantom VEO™ Series Launch: Vision Research introduced a new line of compact, AI-enabled cameras with integrated GPU acceleration for onboard processing.
Photron FASTCAM™ Nova: Unveiled a 12 MP global shutter sensor capable of 10,000 fps at full resolution, targeting scientific research applications.
Basler ace2 25 k: Entered the mid-range high-speed segment with a 25,000 fps camera priced competitively for machine-vision integration.
Analyst Suggestions
Bundle Offerings: OEMs should offer turnkey packages combining camera, lens, lighting, and software to simplify procurement and deployment.
Focus on Usability: Streamline user interfaces and provide automated setup wizards to lower the barrier for new users.
Expand Rental Programs: Flexible rental and time-share options can make high-speed imaging accessible to smaller organizations and short-term projects.
Develop Ecosystem Partnerships: Collaborate with lens, lighting, and analytics providers to create validated solutions for key verticals.
Future Outlook
The High-Speed Camera market is set for sustained growth as industries continue to demand deeper insights into fast-paced events. Advances in sensor materials, on-board processing, and connectivity will yield smaller, smarter, and more affordable systems. Adoption will broaden beyond specialized labs into mainstream production floors, field research, and even consumer-grade devices. As AI and cloud ecosystems mature, high-speed imaging will evolve from niche diagnostics into a ubiquitous tool for innovation, quality assurance, and storytelling alike.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the High-Speed Camera market stands at the intersection of cutting-edge imaging technology and diverse industry applications. Stakeholders—from OEMs and systems integrators to end-user engineers and content creators—can harness these powerful tools to unlock new possibilities in R&D, manufacturing, safety testing, and media production. By emphasizing usability, integration, and cost-effective deployment models, the industry can drive broader adoption and realize the full potential of high-frame-rate visualization in the years ahead.
What is a high-speed camera?
A high-speed camera is a specialized device designed to capture fast-moving objects with high temporal resolution, allowing for detailed analysis of motion in various applications such as sports, scientific research, and industrial processes.
Who are the key players in the high-speed camera market?
Key players in the high-speed camera market include Vision Research, Photron, and Olympus, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the high-speed camera market?
The growth of the high-speed camera market is driven by increasing demand in sectors such as automotive testing, entertainment, and scientific research, where detailed motion analysis is crucial.
What challenges does the high-speed camera market face?
Challenges in the high-speed camera market include high costs of advanced models, the need for specialized knowledge to operate these cameras, and competition from alternative imaging technologies.
What opportunities exist for the high-speed camera market in the future?
Opportunities in the high-speed camera market include advancements in camera technology, growing applications in virtual reality and augmented reality, and increasing use in medical imaging and diagnostics.
What trends are shaping the high-speed camera market?
Trends in the high-speed camera market include the integration of artificial intelligence for enhanced image processing, miniaturization of camera systems, and the development of more affordable models for broader consumer access.
High-Speed Camera Market
| Segmentation | Details |
|---|---|
| Frame Rate | 1,000–5,000 FPS, 5,001–20,000 FPS, Above 20,000 FPS |
| Resolution | HD, 4K, Above 4K |
| Application | Automotive & Transportation, Aerospace & Defense, Healthcare, Entertainment & Media, Others |
| Region | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the High-Speed Camera Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at