444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
The high power charger for electric vehicle market has witnessed significant growth in recent years. With the increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) across the globe, the demand for high-power charging infrastructure has surged. High power chargers provide fast and efficient charging solutions, reducing the charging time and enabling longer travel distances for EV owners. This market overview will delve into the key aspects of the high power charger for electric vehicle market, including its meaning, executive summary, key market insights, market drivers, market restraints, market opportunities, market dynamics, regional analysis, competitive landscape, segmentation, category-wise insights, key benefits for industry participants and stakeholders, SWOT analysis, market key trends, Covid-19 impact, key industry developments, analyst suggestions, future outlook, and conclusion.
High power chargers for electric vehicles refer to charging stations capable of delivering a substantial amount of power to EV batteries. These chargers typically have power outputs ranging from 50 kW to 350 kW or even higher, enabling rapid charging of electric vehicles. Unlike standard chargers, high power chargers significantly reduce the charging time, allowing EV users to conveniently charge their vehicles and continue their journeys without long waiting periods.
Executive Summary:
The executive summary of the high power charger for electric vehicle market provides a concise overview of the market’s key highlights and trends. It encompasses the market size, growth rate, major players, and emerging opportunities. This summary acts as a snapshot of the market’s current state and sets the foundation for a comprehensive understanding of the following sections.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
The High Power Charger for Electric Vehicle Market is influenced by several critical factors:
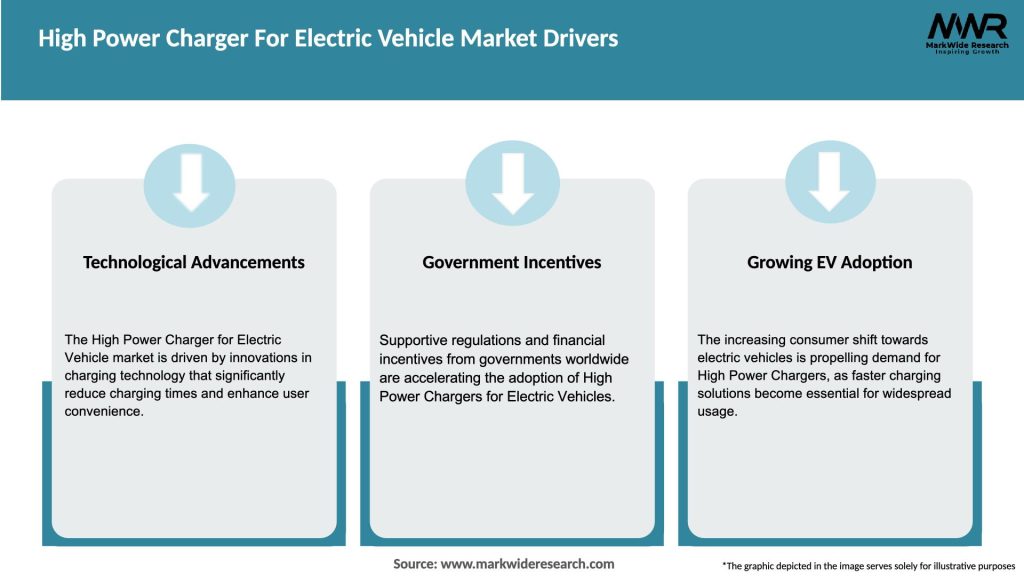
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The dynamics of the High Power Charger for Electric Vehicle Market are influenced by several key factors:
Regional Analysis
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the High Power Charger for Electric Vehicle Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
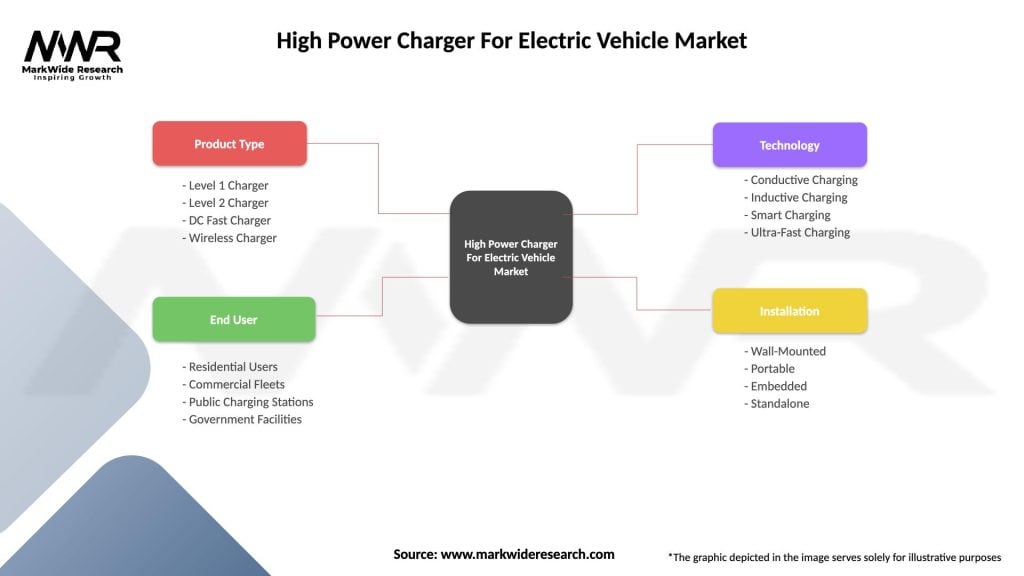
Segmentation
The High Power Charger for Electric Vehicle Market can be segmented by:
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic led to a temporary slowdown in the installation of high power chargers due to supply chain disruptions and economic uncertainty. However, the pandemic highlighted the importance of clean energy solutions, accelerating the transition to electric vehicles and their supporting infrastructure.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook:
The future outlook section offers a glimpse into the anticipated trajectory of the high power charger for electric vehicle market. It includes forecasts, growth opportunities, and emerging technologies that are expected to shape the market in the coming years. This outlook assists businesses in making informed decisions and formulating long-term strategies.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the high power charger for electric vehicle market is experiencing robust growth due to the increasing adoption of electric vehicles and the need for efficient charging infrastructure. With a focus on fast charging and reducing range anxiety, high power chargers are revolutionizing the EV charging experience. However, challenges such as infrastructure costs and interoperability need to be addressed. By capitalizing on market opportunities, embracing technological advancements, and addressing key challenges, industry participants and stakeholders can position themselves for success in this rapidly evolving market.
What is High Power Charger For Electric Vehicle?
A High Power Charger for Electric Vehicles is a charging station designed to deliver a significant amount of electrical power to electric vehicles, enabling faster charging times compared to standard chargers. These chargers are essential for supporting the growing adoption of electric vehicles by providing efficient and convenient charging solutions.
What are the key players in the High Power Charger For Electric Vehicle Market?
Key players in the High Power Charger for Electric Vehicle Market include companies like Tesla, ABB, and ChargePoint, which are known for their innovative charging solutions and infrastructure development. These companies are actively contributing to the expansion of charging networks and enhancing charging technology, among others.
What are the main drivers of the High Power Charger For Electric Vehicle Market?
The main drivers of the High Power Charger for Electric Vehicle Market include the increasing adoption of electric vehicles, government incentives for EV infrastructure, and advancements in charging technology. Additionally, the growing demand for sustainable transportation solutions is propelling market growth.
What challenges does the High Power Charger For Electric Vehicle Market face?
The High Power Charger for Electric Vehicle Market faces challenges such as the high cost of installation and maintenance of charging stations, limited availability of charging infrastructure in certain regions, and concerns regarding grid capacity. These factors can hinder the widespread adoption of high power charging solutions.
What opportunities exist in the High Power Charger For Electric Vehicle Market?
Opportunities in the High Power Charger for Electric Vehicle Market include the potential for partnerships between charging station providers and automotive manufacturers, as well as the development of smart charging solutions. Additionally, the expansion of renewable energy sources for charging can enhance sustainability and attract more users.
What trends are shaping the High Power Charger For Electric Vehicle Market?
Trends shaping the High Power Charger for Electric Vehicle Market include the integration of fast charging technology, the rise of ultra-fast charging stations, and the implementation of mobile charging solutions. Furthermore, the focus on user-friendly interfaces and payment systems is enhancing the overall charging experience.
High Power Charger For Electric Vehicle Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Level 1 Charger, Level 2 Charger, DC Fast Charger, Wireless Charger |
| End User | Residential Users, Commercial Fleets, Public Charging Stations, Government Facilities |
| Technology | Conductive Charging, Inductive Charging, Smart Charging, Ultra-Fast Charging |
| Installation | Wall-Mounted, Portable, Embedded, Standalone |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the High Power Charger for Electric Vehicle Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at