444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The GPS jammer market plays a controversial yet significant role in disrupting satellite navigation systems by emitting signals that interfere with GPS (Global Positioning System) signals, disrupting communication and navigation capabilities. While GPS jammers have legitimate uses in military, law enforcement, and civilian applications such as privacy protection and security enforcement, their misuse poses risks to public safety, transportation, and critical infrastructure. This comprehensive analysis delves into the dynamics driving the GPS jammer market, highlighting key trends, drivers, challenges, and regulatory implications shaping the future of GPS interference technologies.
Meaning
GPS jammers, also known as GPS blockers or GPS disruptors, are electronic devices designed to emit radio frequency signals that interfere with GPS signals, preventing accurate positioning, navigation, and timing information from being received by GPS receivers. These devices operate across various frequency bands and power levels, disrupting GPS signals within their vicinity and potentially affecting a wide range of applications reliant on satellite navigation, including aviation, maritime, transportation, agriculture, and telecommunications.
Executive Summary
This executive summary provides a concise overview of the GPS jammer market, offering insights into market size, growth projections, key players, and emerging trends. By examining the strategic imperatives driving demand for GPS interference technologies and the regulatory challenges associated with their use, stakeholders can gain actionable intelligence to navigate the complexities of this disruptive market landscape.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The GPS jammer market is characterized by a complex interplay of technological innovation, regulatory oversight, and security concerns surrounding the use and misuse of GPS interference technologies. Adapting to these dynamics requires a balanced approach that addresses legitimate market needs while mitigating risks to public safety, critical infrastructure, and national security posed by malicious actors and unauthorized use of GPS jammers.
Regional Analysis
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the GPS Jammer Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
The GPS jammer market can be segmented based on device type, frequency band, power output, and application. Key segments include portable GPS jammers, vehicle-mounted jammers, stationary jammers, and handheld jammers, catering to diverse end-user requirements and operational scenarios.
Category-wise Insight
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic has led to increased concerns over cybersecurity, privacy, and digital infrastructure resilience, driving demand for GPS anti-jamming solutions and resilient positioning technologies to protect critical infrastructure, emergency services, and supply chain operations from disruption and sabotage.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future of the GPS jammer market is shaped by technological innovation, regulatory oversight, and security imperatives surrounding the responsible use and mitigation of GPS interference threats. As satellite navigation systems continue to evolve and proliferate across diverse applications and industries, opportunities abound for industry stakeholders to develop and deploy advanced GPS anti-jamming solutions and resilient positioning technologies that safeguard critical infrastructure, enhance security, and preserve the integrity of satellite navigation signals in an increasingly contested electromagnetic environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the GPS jammer market represents a complex and contentious segment of the global telecommunications and navigation industry, driven by technological innovation, regulatory oversight, and security concerns surrounding the use and misuse of GPS interference technologies. By understanding key market trends, drivers, challenges, and regulatory implications outlined in this analysis, stakeholders can navigate the complexities of the GPS jammer market landscape and develop strategies to address emerging threats, mitigate risks, and promote responsible use of GPS interference technologies in authorized applications while safeguarding public safety, transportation, and critical infrastructure from malicious interference activities.
What is GPS Jammer?
A GPS jammer is a device that interferes with the signals used by GPS receivers, preventing them from accurately determining their location. These devices are often used in various applications, including military operations, privacy protection, and anti-tracking measures.
What are the key companies in the GPS Jammer Market?
Key companies in the GPS Jammer Market include TechnoCom Corporation, Jammer Store, and GPS Jammers, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the GPS Jammer Market?
The growth of the GPS Jammer Market is driven by increasing concerns over privacy and security, the rise in anti-tracking technologies, and the demand for military applications. Additionally, the proliferation of GPS-enabled devices has heightened the need for jamming solutions.
What challenges does the GPS Jammer Market face?
The GPS Jammer Market faces challenges such as legal restrictions on the use of jamming devices, potential misuse for criminal activities, and technological advancements in GPS technology that may reduce the effectiveness of jammers. These factors can hinder market growth and adoption.
What opportunities exist in the GPS Jammer Market?
Opportunities in the GPS Jammer Market include the development of advanced jamming technologies, increasing demand from the automotive sector for anti-theft solutions, and potential applications in personal privacy protection. As awareness of these issues grows, the market may expand.
What trends are shaping the GPS Jammer Market?
Trends in the GPS Jammer Market include the integration of jamming devices with mobile technology, the rise of DIY jamming solutions, and increased focus on regulatory compliance. Additionally, innovations in signal processing are enhancing the effectiveness of jammers.
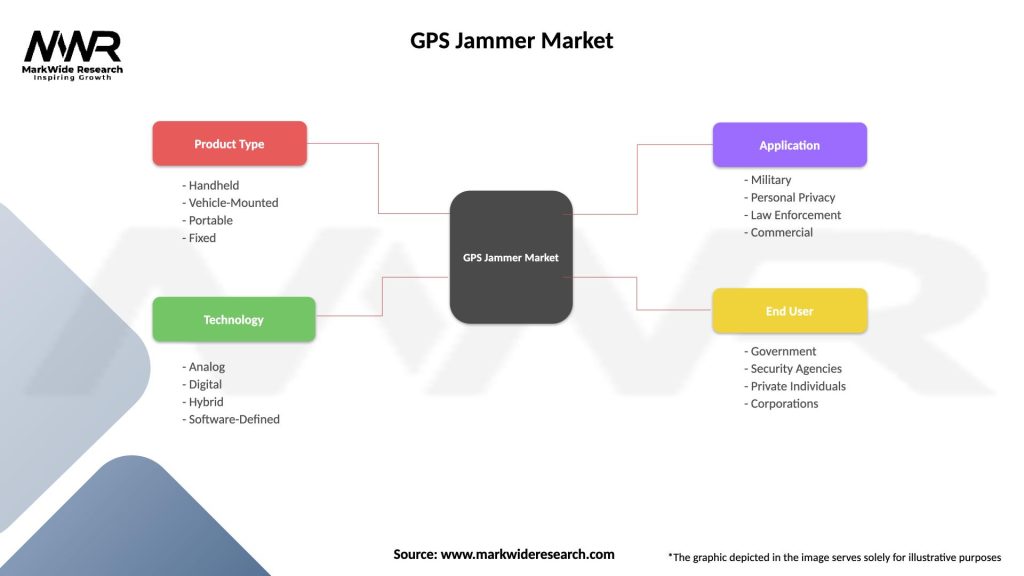
GPS Jammer Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Handheld, Vehicle-Mounted, Portable, Fixed |
| Technology | Analog, Digital, Hybrid, Software-Defined |
| Application | Military, Personal Privacy, Law Enforcement, Commercial |
| End User | Government, Security Agencies, Private Individuals, Corporations |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the GPS Jammer Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at