444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The GMO (Genetically Modified Organism) testing market is experiencing significant growth due to the increasing adoption of genetically modified crops, rising consumer awareness about GMOs, and the need for regulatory compliance in the food and agriculture industry. GMO testing refers to the process of detecting and analyzing genetically modified traits in various agricultural products, including crops, seeds, and processed foods. This market plays a crucial role in ensuring transparency, safety, and compliance with labeling regulations in the global food supply chain.
Meaning
GMO testing involves the analysis and detection of genetically modified traits in agricultural products. Genetically modified organisms are organisms whose genetic material has been altered through genetic engineering techniques. In the context of the GMO testing market, the focus is on the identification and quantification of genetically modified traits, such as specific DNA sequences or proteins, in crops, seeds, and food products. GMO testing is essential for verifying product authenticity, ensuring regulatory compliance, and providing consumers with accurate information about genetically modified ingredients.
Executive Summary
The GMO testing market is witnessing robust growth, driven by factors such as the increasing adoption of genetically modified crops, growing consumer demand for GMO-free products, and stringent regulations governing GMO labeling and traceability. The market is characterized by the presence of both established players and emerging companies offering a wide range of testing services and technologies. The COVID-19 pandemic has also had a notable impact on the market, with a heightened focus on food safety and supply chain resilience.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The GMO testing market is characterized by intense competition among key players, the presence of regulatory frameworks governing GMO labeling, and a growing consumer demand for transparency and choice. Key dynamics include:
Regional Analysis
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the GMO Testing Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
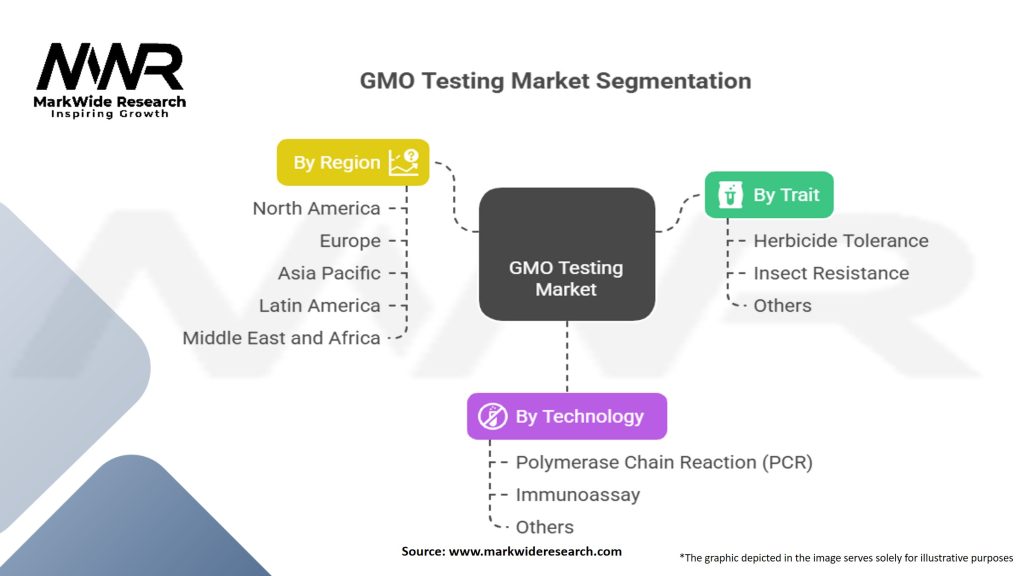
Segmentation
The GMO testing market can be segmented based on the following factors:
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of food safety and supply chain resilience. The heightened focus on hygiene practices and food traceability has increased the demand for GMO testing to ensure the safety and transparency of genetically modified ingredients in the global food supply chain.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The GMO testing market is expected to witness continued growth in the coming years, driven by the increasing adoption of genetically modified crops, growing consumer demand for GMO labeling transparency, and stringent regulatory requirements. Technological advancements, including the development of high-throughput testing methods and rapid detection technologies, will further enhance the market’s growth potential.
Conclusion
The GMO testing market plays a crucial role in ensuring transparency, safety, and compliance with GMO labeling regulations in the food and agriculture industry. It addresses the growing consumer demand for GMO-free products, supports regulatory compliance, and promotes informed consumer choices. The market is driven by the adoption of genetically modified crops, rising consumer awareness, and stringent regulations. Technological advancements and collaborations will shape the future of the GMO testing market, ensuring the integrity of the food supply chain and promoting consumer confidence.
What is GMO Testing?
GMO Testing refers to the methods and processes used to detect genetically modified organisms in food, crops, and other products. This testing is crucial for ensuring food safety, regulatory compliance, and consumer transparency.
What are the key companies in the GMO Testing Market?
Key companies in the GMO Testing Market include Eurofins Scientific, SGS SA, and Intertek Group, which provide a range of testing services for food and agricultural products, among others.
What are the drivers of growth in the GMO Testing Market?
The growth of the GMO Testing Market is driven by increasing consumer demand for non-GMO products, stringent regulations on food labeling, and advancements in testing technologies that enhance accuracy and efficiency.
What challenges does the GMO Testing Market face?
Challenges in the GMO Testing Market include the high costs associated with testing procedures, the complexity of testing multiple GMO traits, and varying regulations across different regions that can complicate compliance.
What opportunities exist in the GMO Testing Market?
Opportunities in the GMO Testing Market include the expansion of organic farming, the development of rapid testing methods, and increasing partnerships between testing laboratories and food manufacturers to ensure product integrity.
What trends are shaping the GMO Testing Market?
Trends in the GMO Testing Market include the rise of consumer awareness regarding food sources, the integration of digital technologies for data management, and the growing emphasis on sustainability in agricultural practices.
GMO Testing Market
| Segmentation | Details |
|---|---|
| By Trait | Herbicide Tolerance, Insect Resistance, Others |
| By Technology | Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), Immunoassay, Others |
| By Region | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the GMO Testing Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at