444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
The global zero emission vessel market has been witnessing significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing focus on sustainability and the transition towards cleaner energy sources in the maritime industry. Zero emission vessels (ZEVs) refer to ships that produce zero greenhouse gas emissions during their operation, utilizing renewable energy and advanced propulsion technologies. This market analysis provides valuable insights into the current state and future prospects of the global zero emission vessel market.
Zero emission vessels are a promising solution to address the environmental challenges posed by traditional maritime transportation. These vessels are designed to minimize or eliminate carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen oxide (NOx), sulfur oxide (SOx), and particulate matter (PM) emissions. By adopting renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydrogen fuel cells, ZEVs offer an eco-friendly alternative to conventional ships powered by fossil fuels.
Executive Summary
The global zero emission vessel market is experiencing rapid growth, driven by the increasing need for sustainable shipping solutions. The demand for ZEVs is fueled by stringent environmental regulations, rising awareness of climate change, and the growing preference for eco-friendly transportation options. This market analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the key trends, market drivers, restraints, and opportunities shaping the industry. Additionally, it explores the regional dynamics, competitive landscape, and market segmentation, along with offering insights into the impact of COVID-19 and future outlook.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
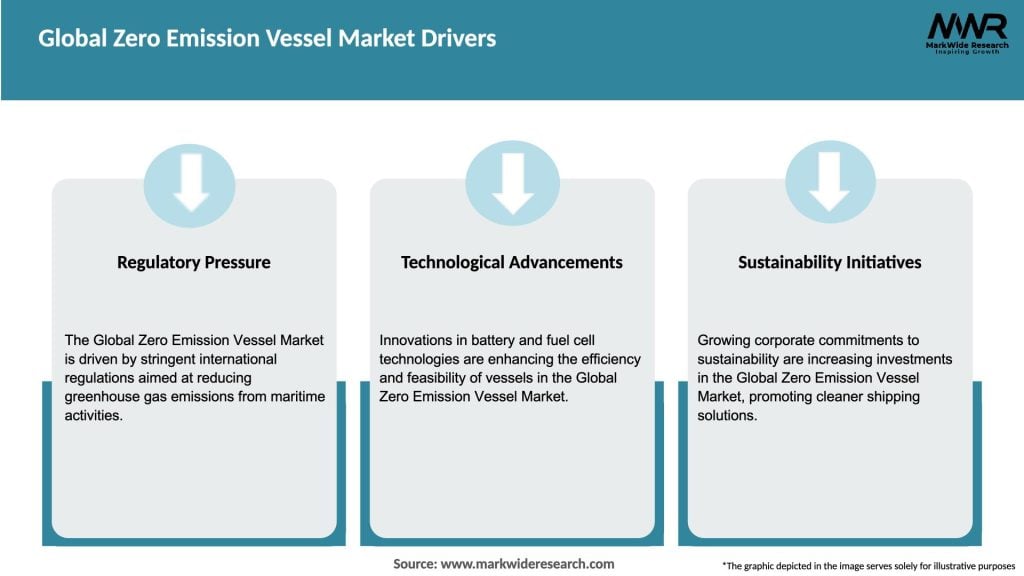
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities

Market Dynamics
The global zero emission vessel market is characterized by dynamic and evolving factors that impact its growth and development. The market dynamics are influenced by a combination of regulatory policies, technological advancements, market demand, and industry trends. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for stakeholders to make informed decisions and capitalize on emerging opportunities in the market.
Regional Analysis
The zero emission vessel market exhibits regional variations due to differences in regulatory frameworks, environmental priorities, and infrastructure development. The analysis provides an in-depth assessment of key regions, including North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and Rest of the World, highlighting their market size, growth potential, and key market players.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Global Zero Emission Vessel Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
The market analysis provides a comprehensive segmentation of the zero emission vessel market based on various factors such as vessel type, power source, and region. By segmenting the market, industry participants and stakeholders can gain valuable insights into specific market segments and tailor their strategies accordingly.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
The zero emission vessel market presents numerous benefits for industry participants and stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Environmental Compliance: Meets IMO decarbonization targets and reduces greenhouse-gas emissions.
Fuel Cost Savings: Electric and hydrogen propulsion can lower operating expenses over lifecycle.
Technological Innovation: Advances in battery energy density and fuel-cell efficiency drive performance.
Weaknesses:
High Upfront Costs: New hull designs, propulsion systems, and energy-storage add significant capex.
Range & Refueling Infrastructure: Limited charging/refueling ports restrict long-haul viability.
Weight & Space Constraints: Large battery or hydrogen tanks reduce payload capacity.
Opportunities:
Government Incentives: Subsidies and green finance programs accelerate vessel adoption.
Port Electrification: Shore-power infrastructure investments support zero-emission docking.
Short-Sea & Inland Waterways: Ferries and coastal vessels are ideal early adopters due to defined routes.
Threats:
Infrastructure Lag: Slow rollout of charging/refueling stations hampers market growth.
Alternative Green Fuels: Biofuels or synthetic fuels could compete with electric and hydrogen solutions.
Regulatory Uncertainty: Evolving international standards may create compliance complexity.
Market Key Trends
The market analysis identifies key trends shaping the global zero emission vessel market:
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic had a significant impact on the global zero emission vessel market. The analysis assesses the effects of the pandemic on the industry, including disruptions in the supply chain, project delays, and changes in market demand. It also explores the pandemic’s long-term implications and the measures taken by industry stakeholders to mitigate the impact.
Key Industry Developments
The analysis highlights key industry developments in the zero emission vessel market, such as:
Analyst Suggestions
Based on the market analysis, analysts suggest the following strategies for industry participants:
Future Outlook
The future of the global zero emission vessel market looks promising, with substantial growth opportunities on the horizon. The market is expected to witness increased adoption of zero emission vessels, driven by regulatory mandates, technological advancements, and shifting consumer preferences. Industry participants should stay abreast of market trends, invest in research and development, and capitalize on emerging opportunities to remain competitive in the evolving landscape.
Conclusion
The global zero emission vessel market is experiencing significant growth, driven by environmental concerns, stringent regulations, and technological advancements. The adoption of zero emission vessels offers numerous benefits, including reduced emissions, cost savings, and compliance with environmental regulations. However, challenges such as high initial investment and limited infrastructure need to be addressed. The market analysis provides valuable insights into the current state and future prospects of the global zero emission vessel market, helping industry participants and stakeholders make informed decisions and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
What is the Global Zero Emission Vessel?
The Global Zero Emission Vessel refers to ships designed to operate without emitting greenhouse gases, utilizing alternative fuels and technologies to achieve sustainability in maritime transport.
What are the key companies in the Global Zero Emission Vessel market?
Key companies in the Global Zero Emission Vessel market include Wärtsilä, MAN Energy Solutions, and Hyundai Heavy Industries, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Global Zero Emission Vessel market?
The main drivers of growth in the Global Zero Emission Vessel market include increasing regulatory pressure for emissions reduction, advancements in alternative fuel technologies, and rising demand for sustainable shipping solutions.
What challenges does the Global Zero Emission Vessel market face?
Challenges in the Global Zero Emission Vessel market include high initial investment costs, limited availability of alternative fuels, and the need for extensive infrastructure development.
What opportunities exist in the Global Zero Emission Vessel market?
Opportunities in the Global Zero Emission Vessel market include the potential for innovation in fuel cell technologies, partnerships for research and development, and growing interest from shipping companies in sustainable practices.
What trends are shaping the Global Zero Emission Vessel market?
Trends shaping the Global Zero Emission Vessel market include the increasing adoption of hydrogen and battery-powered vessels, the integration of digital technologies for efficiency, and a shift towards circular economy practices in shipbuilding.
Global Zero Emission Vessel Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Technology | Battery Electric, Fuel Cell, Hybrid Electric, Wind Powered, Solar Powered, Others |
| Ship Type | Passenger Ships, Cargo Ships, Ferries, Others |
| Power Range | Less than 1 MW, 1 MW to 5 MW, Above 5 MW |
| Region | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Global Zero Emission Vessel Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at