444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The global temporary labor market is a dynamic and evolving sector that plays a vital role in various industries across the world. Temporary labor refers to the employment of workers on a short-term basis to meet specific demands or fill gaps in the workforce. It offers flexibility for businesses and provides job opportunities for individuals seeking temporary employment. This market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by various factors such as globalization, changing work patterns, and the need for cost-effective solutions.
Meaning
Temporary labor refers to the hiring of workers for a fixed duration or until a specific project is completed. It is a flexible arrangement that allows businesses to scale their workforce up or down based on their needs. Temporary workers are typically employed through staffing agencies or directly by companies for positions ranging from entry-level to highly skilled roles. This temporary employment arrangement offers advantages to both employers and employees, such as reduced administrative burden, access to specialized skills, and the ability to test potential permanent hires.
Executive Summary
The global temporary labor market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by factors such as increased globalization, changing work patterns, and the need for cost-effective solutions. This market provides businesses with the flexibility to scale their workforce according to demand, while also offering job opportunities for individuals seeking temporary employment. However, the market also faces challenges, including regulatory complexities, competition from the gig economy, and concerns about worker rights and protections. Despite these challenges, the temporary labor market is expected to continue expanding in the coming years, driven by evolving work dynamics and the need for agile staffing solutions.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The global temporary labor market is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including economic conditions, regulatory frameworks, technological advancements, and shifting work patterns. Changes in labor laws and regulations, such as those related to worker rights, immigration policies, and employment contracts, can have a significant impact on the market. Additionally, advancements in technology, such as AI-powered talent matching platforms and mobile applications, are reshaping how temporary labor is sourced, managed, and deployed.
Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on the temporary labor market. The outbreak resulted in widespread business disruptions, shifting demand patterns, and increased reliance on remote work. While the pandemic initially led to a decline in temporary labor demand in some sectors, the subsequent recovery and reopening efforts have fueled the market’s resurgence.
Regional Analysis
The temporary labor market exhibits regional variations due to differences in labor laws, cultural norms, economic conditions, and industry landscapes. Developed economies, such as the United States, the United Kingdom, and Germany, have well-established temporary labor markets supported by robust staffing agency networks. These regions benefit from strong regulatory frameworks and higher demand for specialized skills in industries like technology, finance, and healthcare.
In emerging economies, such as India, Brazil, and China, the temporary labor market is rapidly expanding due to factors such as economic growth, increasing globalization, and the demand for cost-effective staffing solutions. These regions present significant opportunities for staffing agencies and companies looking to leverage a large pool of skilled workers and tap into growing industries.
Competitive Landscape
Leading companies in the Global Temporary Labor Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.

Segmentation
The global temporary labor market can be segmented based on various factors, including industry, skill level, and duration of employment.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic had a significant impact on the temporary labor market. In the initial stages of the pandemic, many industries faced disruptions, leading to a decline in temporary labor demand. Businesses across sectors implemented cost-cutting measures, including reduced hiring and layoffs, affecting both permanent and temporary workers.
However, as the world adapted to the new normal, the temporary labor market began to recover. Certain industries, such as healthcare, logistics, and e-commerce, experienced increased demand for temporary workers to meet the surge in essential services. As vaccination efforts progressed and restrictions eased, businesses started reopening and resuming operations, further fueling the demand for temporary labor.
The pandemic also accelerated certain trends in the temporary labor market. Remote work became more prevalent, allowing businesses to hire temporary workers from different locations. Virtual collaboration tools and online platforms facilitated the remote hiring and management of temporary workers, creating new opportunities for staffing agencies and businesses.
Nevertheless, the pandemic highlighted the importance of worker safety and welfare. Businesses implemented stringent health and safety protocols to protect both permanent and temporary workers. Adequate personal protective equipment (PPE), sanitization measures, and remote work arrangements became crucial considerations in the temporary labor market.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The global temporary labor market is expected to continue growing in the coming years, driven by factors such as the need for flexibility in workforce management, evolving work patterns, and cost-effective staffing solutions. The integration of technology will play a crucial role in shaping the market, with advancements in AI, automation, and data analytics further optimizing the temporary labor hiring process.
The post-pandemic recovery is expected to contribute to increased demand for temporary labor as businesses rebuild and adapt to changing market conditions. The healthcare, technology, e-commerce, and logistics sectors are likely to remain key drivers of temporary labor demand.
Regulatory changes and the focus on worker well-being are expected to shape the market’s future landscape. Stricter regulations governing temporary labor, increased worker protections, and initiatives promoting fair labor practices will influence the operations of businesses and staffing agencies.
As the gig economy continues to expand, the temporary labor market may witness a closer integration between traditional staffing agencies and gig platforms. Hybrid models that combine the benefits of traditional temporary labor with the flexibility and convenience of digital platforms are likely to emerge.
Conclusion
The global temporary labor market is a dynamic and evolving sector that plays a crucial role in various industries worldwide. It offers businesses the flexibility to adjust their workforce according to demand, providing cost-effective staffing solutions and access to specialized skills. Temporary labor also creates job opportunities for individuals seeking short-term employment or looking to gain experience in specific industries.
While the market faces challenges such as regulatory complexities, job insecurity, and competition from the gig economy, it continues to grow and adapt. Technological advancements, such as AI-powered talent matching platforms and mobile applications, have streamlined the hiring process and improved operational efficiency. Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated certain trends in the market, including remote work and the integration of gig economy platforms.
What is Temporary Labor?
Temporary labor refers to a workforce that is hired for a limited period to meet specific needs, such as seasonal demands or project-based work. This type of labor is commonly utilized in industries like hospitality, construction, and retail.
What are the key players in the Global Temporary Labor market?
Key players in the Global Temporary Labor market include Adecco Group, Randstad, ManpowerGroup, and Kelly Services, among others. These companies provide staffing solutions across various sectors, including healthcare, IT, and manufacturing.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Global Temporary Labor market?
The Global Temporary Labor market is driven by factors such as the increasing demand for flexible work arrangements, the rise of the gig economy, and the need for companies to quickly adapt to changing market conditions. Additionally, businesses are increasingly relying on temporary labor to manage costs and enhance operational efficiency.
What challenges does the Global Temporary Labor market face?
The Global Temporary Labor market faces challenges such as regulatory compliance, fluctuating demand for temporary workers, and competition from automation and technology. These factors can impact the availability and stability of temporary labor across various industries.
What opportunities exist in the Global Temporary Labor market?
Opportunities in the Global Temporary Labor market include the expansion of remote work options, the growth of specialized staffing services, and the increasing acceptance of temporary roles among job seekers. These trends can lead to innovative solutions for workforce management.
What trends are shaping the Global Temporary Labor market?
Trends shaping the Global Temporary Labor market include the integration of technology in recruitment processes, the rise of on-demand staffing platforms, and a focus on employee well-being and engagement. These trends are transforming how companies approach temporary labor solutions.
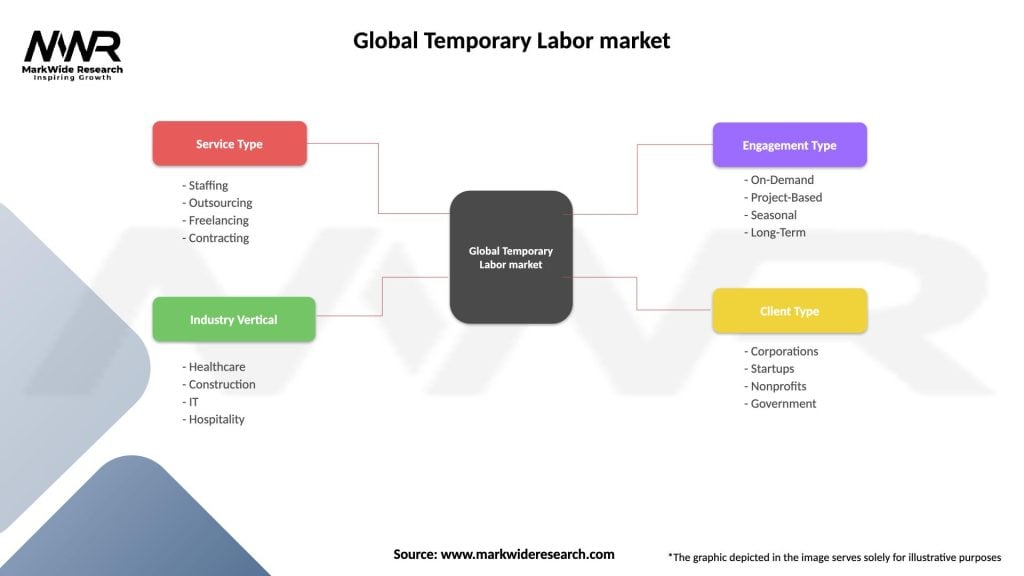
Global Temporary Labor market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Service Type | Staffing, Outsourcing, Freelancing, Contracting |
| Industry Vertical | Healthcare, Construction, IT, Hospitality |
| Engagement Type | On-Demand, Project-Based, Seasonal, Long-Term |
| Client Type | Corporations, Startups, Nonprofits, Government |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Global Temporary Labor Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at