444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
The global sharing economy market has experienced significant growth in recent years, revolutionizing traditional industries and transforming the way people consume goods and services. This market is characterized by the sharing, renting, or exchanging of resources, assets, and services between individuals or organizations, facilitated by digital platforms.
The sharing economy refers to a socio-economic system where individuals or businesses share their underutilized resources, such as vehicles, accommodation, or skills, with others in exchange for monetary or non-monetary benefits. This concept promotes efficient resource allocation, sustainability, and cost savings, leading to increased convenience and access for consumers.
Executive Summary
The global sharing economy market has witnessed rapid expansion due to the proliferation of digital platforms and the increasing adoption of sharing practices across various sectors. Key players in the market are capitalizing on the growing demand for shared services and the shift in consumer preferences towards more sustainable and cost-effective solutions.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities

Market Dynamics
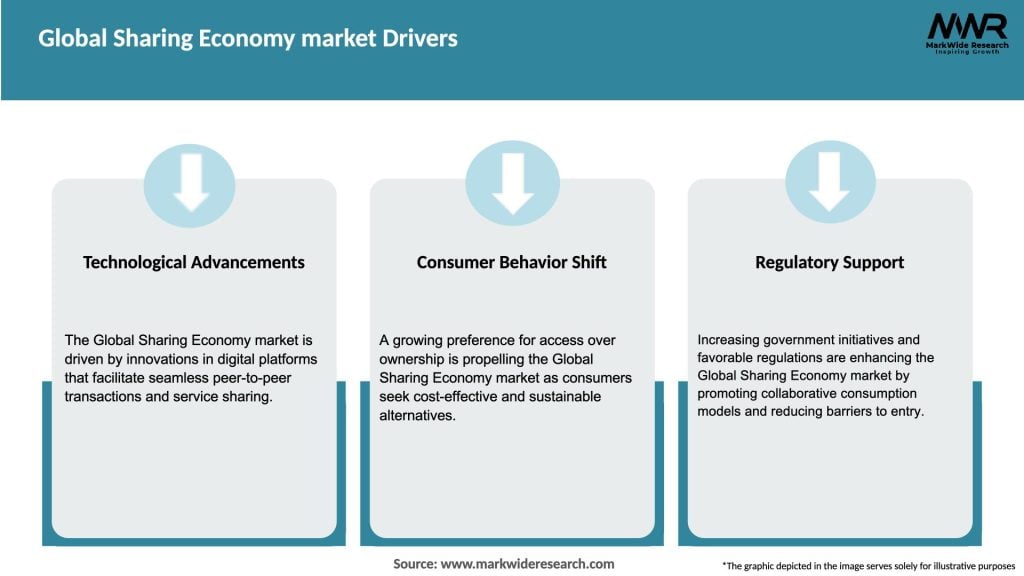
The sharing economy market is driven by a combination of socio-economic, technological, and environmental factors. As consumer behavior continues to evolve and technology advances, the market dynamics are expected to transform further, creating new opportunities and challenges for market participants.
Regional Analysis
The sharing economy market exhibits regional variations due to cultural, economic, and regulatory factors. North America and Europe have witnessed significant adoption of sharing practices across various sectors, including transportation and accommodation. Emerging economies in Asia Pacific and Latin America are also experiencing rapid growth in the sharing economy, driven by increasing internet penetration and the need for affordable services.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Global Sharing Economy Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
The sharing economy market can be segmented based on the type of shared resources or services. Common segments include transportation, accommodation, peer-to-peer lending, co-working spaces, and skill-sharing platforms. Each segment presents unique opportunities and challenges, catering to different consumer needs and preferences.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic had a mixed impact on the sharing economy. While certain sectors such as ride-hailing and short-term accommodation experienced a downturn due to travel restrictions and safety concerns, other segments like online marketplaces for essential goods and remote work platforms witnessed increased demand. The pandemic has also highlighted the importance of hygiene and safety measures within the sharing economy.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future of the sharing economy looks promising, with continued growth expected across various sectors. Technological advancements, changing consumer behavior, and increased environmental consciousness will drive further innovation and expansion in the market. However, overcoming regulatory challenges, building trust, and ensuring sustainable practices will be key to long-term success.
Conclusion
The global sharing economy market has disrupted traditional industries and transformed the way resources and services are consumed. It offers cost savings, convenience, and sustainability benefits to individuals and businesses. However, the market faces regulatory challenges, trust concerns, and market fragmentation. By embracing collaboration, integrating technology, and addressing user safety, the sharing economy can continue to thrive and reshape industries in the years to come.
What is Sharing Economy?
The Sharing Economy refers to an economic model where individuals share access to goods and services, often facilitated by a third-party platform. This model includes various sectors such as transportation, accommodation, and peer-to-peer lending.
What are the key players in the Global Sharing Economy market?
Key players in the Global Sharing Economy market include companies like Airbnb, Uber, and TaskRabbit, which provide platforms for sharing services and resources. These companies have transformed traditional industries by enabling peer-to-peer transactions, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Global Sharing Economy market?
The main drivers of growth in the Global Sharing Economy market include the increasing demand for cost-effective services, the rise of digital platforms, and changing consumer behaviors favoring access over ownership. Additionally, urbanization and sustainability concerns are also contributing factors.
What challenges does the Global Sharing Economy market face?
The Global Sharing Economy market faces challenges such as regulatory hurdles, safety concerns, and competition from traditional businesses. These issues can hinder growth and create barriers for new entrants in the market.
What opportunities exist in the Global Sharing Economy market?
Opportunities in the Global Sharing Economy market include the expansion into emerging markets, the development of niche platforms catering to specific needs, and the integration of advanced technologies like blockchain for enhanced security and transparency.
What trends are shaping the Global Sharing Economy market?
Trends shaping the Global Sharing Economy market include the increasing use of mobile applications for service access, a growing focus on sustainability, and the rise of collaborative consumption models. These trends are influencing how consumers engage with shared services.
Global Sharing Economy market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Service Type | Ride Sharing, Home Sharing, Food Delivery, Equipment Rental |
| Customer Type | Individuals, Small Businesses, Corporations, Nonprofits |
| Platform Type | Mobile Apps, Web Platforms, Social Media, Marketplaces |
| Transaction Model | Subscription, Commission-Based, Freemium, Direct Sales |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Global Sharing Economy Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at