444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
The Global RFID Market is witnessing significant growth and is poised for further expansion in the coming years. RFID, which stands for Radio Frequency Identification, is a technology that uses radio waves to identify and track objects or individuals. It consists of tags or labels attached to the objects and readers or scanners that capture the information encoded in these tags.
RFID technology has gained prominence due to its ability to improve supply chain management, enhance operational efficiency, and provide real-time data visibility. The market is witnessing increasing adoption across various industries such as retail, healthcare, transportation, logistics, and manufacturing, among others. The global RFID market is expected to experience substantial growth, driven by factors such as increasing need for inventory management, rising demand for contactless payment systems, and growing emphasis on enhancing security and authentication processes.
RFID technology is based on the concept of using radio waves to wirelessly identify and track objects or individuals. It enables the automatic capture of data without the need for line-of-sight contact between the reader and the tag. The tags or labels consist of a microchip and an antenna, which stores and transmits information to the RFID reader. These tags can be either passive, active, or battery-assisted passive (BAP) depending on their power source and functionality.
RFID technology offers several advantages over traditional identification methods such as barcodes. It allows for faster and more accurate data capture, enables real-time visibility of assets, improves inventory management, enhances security and authentication processes, and enables contactless payment systems. With advancements in technology and decreasing costs, RFID is becoming more accessible and widely adopted across industries.
Executive Summary
The Global RFID Market is experiencing substantial growth and is expected to expand further in the coming years. The technology offers numerous benefits, including improved supply chain management, enhanced operational efficiency, and increased security. The market is being driven by factors such as the need for efficient inventory management, growing demand for contactless payment systems, and the emphasis on enhancing security and authentication processes.
However, there are also challenges and restraints that need to be addressed, such as concerns regarding privacy and data security, high implementation costs, and the lack of global standards. Despite these challenges, the market presents significant opportunities for RFID technology providers to innovate and cater to the evolving needs of industries worldwide.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
The Global RFID Market is characterized by the following key insights:
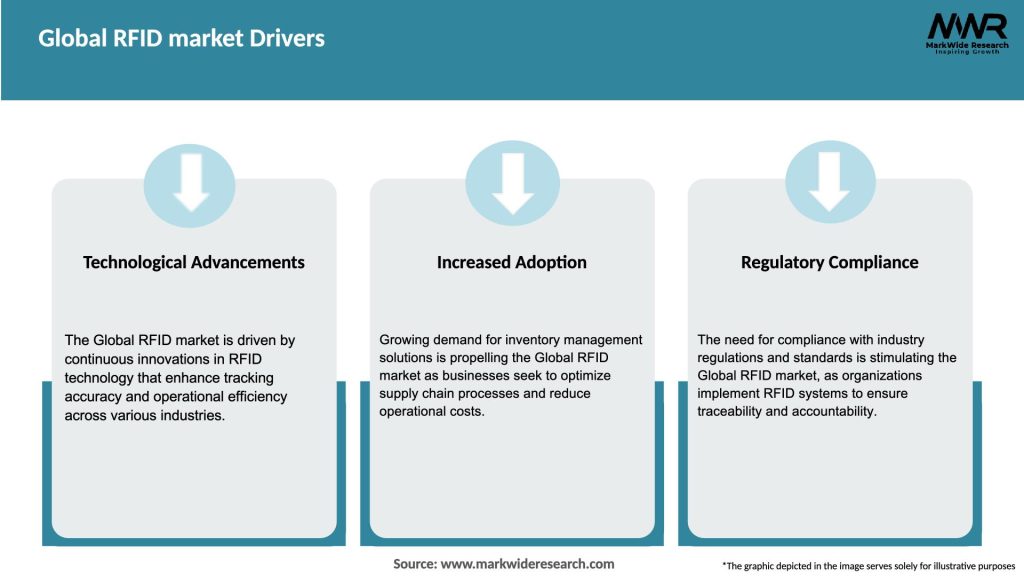
Market Drivers
The Global RFID Market is driven by the following factors:
Market Restraints
The Global RFID Market faces certain restraints, including:
Market Opportunities
The Global RFID Market presents several opportunities for growth and innovation, including:

Market Dynamics
The Global RFID Market is dynamic and influenced by various factors, including technological advancements, industry trends, regulatory changes, and market competition. Understanding these dynamics is essential for businesses operating in the RFID space to stay competitive and capitalize on opportunities.
Technological advancements, such as the miniaturization of RFID tags, increased read range, and improved battery life, continue to drive market growth. Integration with advanced technologies like IoT and AI further expands the capabilities of RFID systems. Industry trends, such as the rise of omnichannel retailing, e-commerce, and smart manufacturing, also contribute to the increased adoption of RFID technology.
Regulatory changes, including product traceability mandates, data privacy regulations, and standards development, shape the RFID landscape. Compliance with these regulations becomes a priority for businesses operating in regulated industries.
Market competition plays a crucial role in driving innovation and improving the affordability of RFID solutions. RFID technology providers strive to differentiate themselves through product features, cost-effectiveness, and industry-specific solutions.
Overall, the Global RFID Market is driven by a combination of technological advancements, industry trends, regulatory factors, and competitive dynamics. Businesses need to stay updated with these market dynamics to effectively leverage the opportunities and overcome challenges in this evolving landscape.
Regional Analysis
The Global RFID Market exhibits regional variations in terms of adoption, industry focus, and market dynamics. Key regions analyzed in this report include North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East and Africa.
North America:
North America is a prominent region in the Global RFID Market, driven by advanced technological infrastructure and the presence of major RFID solution providers. The United States, in particular, leads the market in terms of adoption and innovation. The region’s retail industry extensively utilizes RFID for inventory management, supply chain optimization, and theft prevention. Additionally, sectors like healthcare, transportation, and logistics are witnessing increased RFID adoption to improve operational efficiency and enhance patient safety.
Europe:
Europe is another significant market for RFID technology, with countries like Germany, the United Kingdom, and France at the forefront of adoption. The region’s strong emphasis on industrial automation, supply chain optimization, and e-commerce drives the demand for RFID solutions. The European retail sector extensively uses RFID technology for inventory management, ensuring product availability, and enhancing customer experience. The healthcare industry is also leveraging RFID for patient tracking, medication management, and asset tracking.
Asia Pacific:
The Asia Pacific region is experiencing rapid growth in the RFID market, driven by the presence of major manufacturing hubs, increasing e-commerce activities, and the emergence of smart cities. Countries like China, Japan, South Korea, and India are leading contributors to the market growth in this region. The retail sector in Asia Pacific is adopting RFID technology to improve inventory accuracy, reduce stockouts, and enhance the customer shopping experience. Additionally, the logistics and transportation sectors are deploying RFID solutions for supply chain visibility and efficient asset tracking.
Latin America:
Latin America is witnessing a gradual increase in RFID adoption across various industries. Countries like Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina are key players in this market. The retail sector in Latin America is embracing RFID technology to combat theft, improve inventory management, and enhance operational efficiency. The healthcare industry is also leveraging RFID for patient identification, asset tracking, and improving medication management.
Middle East and Africa:
The Middle East and Africa region show significant potential for RFID adoption, primarily driven by sectors such as retail, healthcare, and logistics. Countries like the United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, and South Africa are witnessing increased RFID implementation. The retail sector is utilizing RFID technology to streamline operations, reduce stock discrepancies, and enhance customer experience. In the healthcare sector, RFID is used for asset tracking, patient identification, and supply chain management.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Global RFID Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
The Global RFID Market can be segmented based on various factors, including technology, frequency, application, end-use industry, and geography.
Based on technology, the market can be categorized into:
Frequency-wise segmentation includes:
Applications of RFID technology span across various industries:
Geographically, the market can be divided into regions such as North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East and Africa.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
The adoption of RFID technology offers several key benefits for industry participants and stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis of the Global RFID Market provides a comprehensive understanding of its internal and external factors:
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the RFID market. While certain sectors experienced disruptions, others witnessed increased demand for RFID solutions. The key impacts of the pandemic include:
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Based on the analysis of the Global RFID Market, industry experts and analysts suggest the following strategies for businesses and stakeholders:
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the Global RFID Market is promising, with continued growth anticipated. Advancements in technology, increasing industry adoption, and the emergence of new applications will drive market expansion. Key trends such as integration with IoT and AI, enhanced data security, and the development of innovative RFID tags will shape the market landscape.
RFID technology will play a vital role in the digital transformation of industries, enabling real-time visibility, automation, and enhanced decision-making. The retail, healthcare, transportation, and logistics sectors will be significant drivers of RFID adoption, focusing on improving efficiency, reducing costs, and meeting regulatory requirements.
As RFID technology becomes more affordable and scalable, it will penetrate emerging markets and smaller businesses. The standardization of RFID systems will contribute to seamless interoperability, facilitating data exchange across supply chain partners.
Overall, the Global RFID Market is expected to witness steady growth in the coming years, driven by technological advancements, industry-specific requirements, and the increasing need for operational efficiency, security, and supply chain optimization.
Conclusion
The Global RFID Market is experiencing significant growth, driven by factors such as improved operational efficiency, supply chain visibility, and enhanced security and authentication. RFID technology finds applications across various industries, including retail, healthcare, transportation, manufacturing, and aerospace. While the market offers numerous opportunities, challenges such as high implementation costs, interoperability issues, and privacy concerns need to be addressed.
What is RFID?
RFID, or Radio-Frequency Identification, is a technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. These tags contain electronically stored information and are widely used in various applications such as inventory management, asset tracking, and supply chain logistics.
What are the key players in the Global RFID market?
Key players in the Global RFID market include companies like Zebra Technologies, Impinj, and NXP Semiconductors, which are known for their innovative RFID solutions. These companies focus on enhancing RFID technology for applications in retail, healthcare, and manufacturing, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Global RFID market?
The main drivers of growth in the Global RFID market include the increasing demand for automation in supply chain management, the need for real-time tracking of assets, and the growing adoption of RFID technology in retail for inventory management and loss prevention.
What challenges does the Global RFID market face?
The Global RFID market faces challenges such as high implementation costs, interoperability issues between different RFID systems, and concerns regarding data privacy and security. These factors can hinder widespread adoption in certain industries.
What opportunities exist in the Global RFID market?
Opportunities in the Global RFID market include the expansion of IoT applications, advancements in RFID technology such as passive and active tags, and the increasing use of RFID in emerging markets. These trends are expected to drive innovation and growth in various sectors.
What are the current trends in the Global RFID market?
Current trends in the Global RFID market include the integration of RFID with IoT for enhanced data analytics, the development of smaller and more efficient RFID tags, and the growing focus on sustainability in supply chain practices. These trends are shaping the future of RFID applications across industries.
Global RFID market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Active RFID, Passive RFID, Semi-Passive RFID, RFID Tags |
| End User | Healthcare, Retail, Manufacturing, Logistics |
| Technology | Near Field Communication, Ultra High Frequency, Low Frequency, High Frequency |
| Application | Inventory Management, Asset Tracking, Access Control, Supply Chain Management |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Global RFID Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at