444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
Nuclear fusion is a process that involves the combination of atomic nuclei to form a heavier nucleus, resulting in the release of a significant amount of energy. This clean and sustainable energy source has the potential to revolutionize the global energy landscape. The global nuclear fusion market is witnessing substantial growth as governments, research organizations, and private companies recognize the immense potential of this technology in addressing the world’s growing energy needs.
Meaning
Nuclear fusion refers to the process of combining atomic nuclei to produce energy. Unlike nuclear fission, which is currently used in nuclear power plants, fusion does not produce long-lived radioactive waste or carry the risk of a meltdown. It is a highly efficient and virtually limitless source of energy, as it relies on isotopes of hydrogen found abundantly in seawater. Harnessing nuclear fusion has the potential to provide a clean and sustainable energy solution for the future.
Executive Summary
The global nuclear fusion market is experiencing significant growth due to increasing investments and research initiatives aimed at developing fusion energy technologies. Governments and private entities worldwide are recognizing the potential of fusion as a long-term solution to meet rising energy demands while reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Despite the significant technical challenges involved, the progress made in recent years has been promising, and stakeholders in the fusion industry are optimistic about the commercialization of fusion energy in the coming decades.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The global nuclear fusion market is characterized by dynamic factors that impact its growth and development. These dynamics include technological advancements, government policies, private investments, and international collaborations. The market is driven by the growing demand for clean energy, environmental concerns, and the need to reduce carbon emissions. However, it faces challenges such as technical hurdles, high costs, and uncertain timelines. Despite these challenges, the market presents opportunities for energy transition, job creation, and the development of spin-off technologies.
Regional Analysis
The development and progress of the nuclear fusion market vary across regions. Key regions actively involved in fusion research and development include:
The regional analysis reflects the global nature of fusion research, with collaboration and knowledge sharing among countries driving advancements in the field.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Global Nuclear Fusion Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.

Segmentation
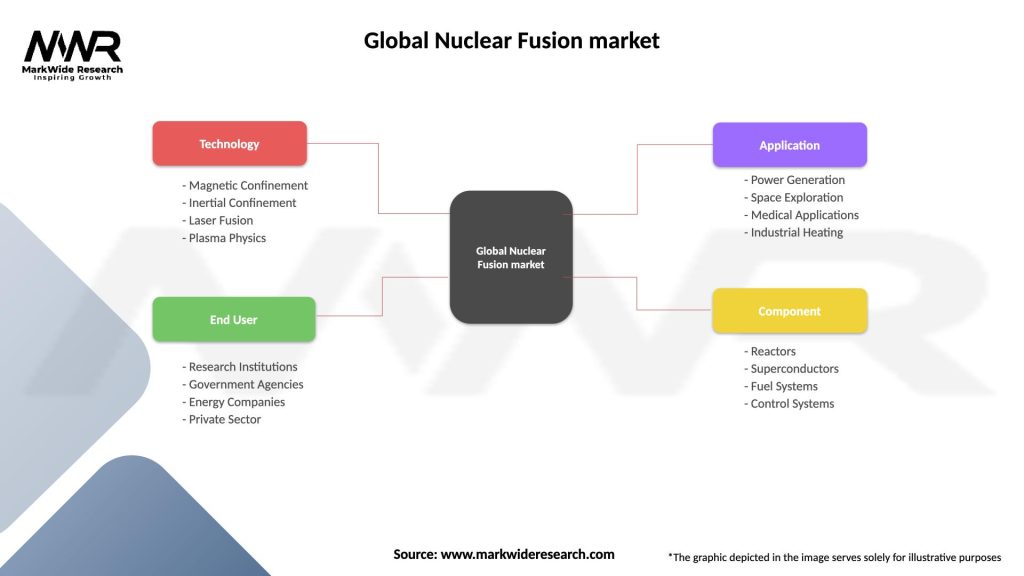
The nuclear fusion market can be segmented based on various factors, including:
Segmentation allows for a better understanding of the market dynamics, trends, and specific opportunities and challenges within each segment.
Category-wise Insights
Category-wise insights provide a deeper understanding of the different aspects and progress within specific categories of fusion research.
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) analysis provides an assessment of the nuclear fusion market’s internal and external factors.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
A SWOT analysis helps identify the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats surrounding the nuclear fusion market, providing insights for industry participants and stakeholders.
Market Key Trends
Market key trends reflect the current advancements, innovations, and collaborative efforts within the nuclear fusion market.
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has had an impact on the nuclear fusion market, primarily in terms of research activities and project timelines. The pandemic caused disruptions in the operations of research facilities, delayed construction milestones, and affected the mobility of researchers and experts. However, the impact varied across regions, depending on the severity of the outbreak and the government’s response.
Despite the challenges posed by the pandemic, research and development in fusion energy continued. Virtual collaborations, remote work, and modified work protocols allowed researchers to maintain progress. Governments and funding agencies also recognized the importance of continued support for fusion research and provided financial assistance to mitigate the effects of the pandemic.
The pandemic’s long-term impact on the nuclear fusion market is expected to be minimal, as the underlying drivers and opportunities for fusion energy remain unchanged. Efforts are being made to ensure the resumption of construction and research activities as global vaccination campaigns progress and restrictions ease.
Key Industry Developments
Key industry developments highlight the progress, investments, and support for fusion research from both public and private sectors.
Analyst Suggestions
Analyst suggestions provide guidance for industry participants, stakeholders, and policymakers to foster the growth and advancement of the nuclear fusion market.
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the global nuclear fusion market is optimistic, despite the challenges and uncertainties. The progress made in fusion research, coupled with increasing investments and collaborations, indicates a strong commitment to achieving practical fusion energy.
In the near term, the focus will remain on the construction and commissioning of ITER, which will serve as a critical milestone in fusion research. The knowledge gained from ITER’s operation and the advancements in plasma physics and engineering will pave the way for the development of commercial fusion reactors.
Further advancements in plasma confinement, materials science, and innovative fusion concepts are expected. Research breakthroughs and technological innovations will contribute to overcoming technical challenges and driving the commercialization of fusion energy.
While the timeline for practical fusion energy remains uncertain, industry participants, stakeholders, and governments are increasingly optimistic about its potential. Fusion energy has the capacity to revolutionize the global energy landscape, providing a clean, sustainable, and virtually limitless source of power.
Conclusion
The global nuclear fusion market is witnessing significant growth and progress as stakeholders recognize its potential in addressing the world’s energy needs. Fusion energy offers a clean, sustainable, and virtually limitless source of power, with the ability to mitigate climate change and reduce dependence on fossil fuels. While technical challenges, high costs, and uncertain timelines remain as hurdles, advancements in plasma confinement, materials science, and engineering solutions are paving the way for the commercialization of fusion energy. Government support, private investments, and international collaborations are driving the development of fusion technology. The market presents opportunities for energy transition, job creation, and the development of spin-off technologies.
What is Nuclear Fusion?
Nuclear fusion is a process where two light atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, releasing a significant amount of energy. This process is the same that powers the sun and has the potential to provide a nearly limitless source of clean energy.
What are the key players in the Global Nuclear Fusion market?
Key players in the Global Nuclear Fusion market include ITER Organization, General Fusion, and TAE Technologies, among others. These companies are at the forefront of developing fusion technologies and advancing research in this field.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Global Nuclear Fusion market?
The main drivers of growth in the Global Nuclear Fusion market include the increasing demand for sustainable energy solutions, advancements in fusion technology, and government investments in research and development. These factors are pushing the industry towards viable fusion energy production.
What challenges does the Global Nuclear Fusion market face?
The Global Nuclear Fusion market faces several challenges, including the high costs of research and development, technical difficulties in achieving stable fusion reactions, and regulatory hurdles. These challenges can slow down the progress towards commercial fusion energy.
What opportunities exist in the Global Nuclear Fusion market?
Opportunities in the Global Nuclear Fusion market include potential partnerships between private companies and governments, advancements in materials science for reactor construction, and the growing interest in fusion as a solution to climate change. These factors could accelerate the development of fusion energy.
What trends are shaping the Global Nuclear Fusion market?
Trends shaping the Global Nuclear Fusion market include increased collaboration between international research institutions, the rise of private sector investment in fusion technologies, and innovations in plasma confinement methods. These trends are crucial for the future of fusion energy development.
Global Nuclear Fusion market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Technology | Magnetic Confinement, Inertial Confinement, Laser Fusion, Plasma Physics |
| End User | Research Institutions, Government Agencies, Energy Companies, Private Sector |
| Application | Power Generation, Space Exploration, Medical Applications, Industrial Heating |
| Component | Reactors, Superconductors, Fuel Systems, Control Systems |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Global Nuclear Fusion Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at