444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The global neobanking market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, revolutionizing the traditional banking landscape. Neobanks, also known as digital banks or challenger banks, are innovative financial institutions that operate entirely online, providing customers with a seamless and user-friendly banking experience. These digital-first banks leverage technology, data analytics, and mobile applications to offer a wide range of financial services, including account opening, payments, loans, and savings. The market is driven by the increasing adoption of digital banking, changing consumer preferences, and the need for convenient and accessible financial solutions.
Meaning
Neobanks are a new breed of financial institutions that operate exclusively online, without any physical branches. Unlike traditional banks, neobanks prioritize digital channels and offer a streamlined and user-friendly banking experience. By leveraging advanced technology, neobanks provide innovative solutions that cater to the evolving needs of customers, such as quick and easy account setup, real-time transaction tracking, personalized financial insights, and convenient access to financial services through mobile applications. Neobanks aim to disrupt the traditional banking model by offering greater convenience, transparency, and personalized experiences.
Executive Summary
The global neobanking market has witnessed remarkable growth as digital disruption continues to transform the banking industry. Neobanks, with their digital-first approach, are redefining the way individuals and businesses manage their finances. This market is driven by the growing adoption of digital banking, changing consumer expectations, and the advantages offered by neobanks, including convenience, cost-effectiveness, and enhanced user experiences. The market is highly competitive, with both traditional banks and fintech companies vying to establish their presence in the digital banking space. As the market continues to evolve, collaboration between traditional banks and neobanks is becoming more common, fostering innovation and expanding the reach of digital banking services.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The global neobanking market is dynamic and highly competitive, driven by ongoing technological advancements, changing consumer behavior, and evolving regulatory frameworks. Neobanks are constantly innovating to differentiate themselves and gain market share. Traditional banks are responding to the rise of neobanks by enhancing their digital offerings or establishing their own digital subsidiaries. Regulatory bodies are closely monitoring the neobanking space, adapting regulations to address emerging challenges while fostering innovation and ensuring consumer protection. The market dynamics are further influenced by partnerships and collaborations between neobanks, fintech firms, and traditional banks, fostering an ecosystem of innovation and customer-centric financial services.
Regional Analysis
The adoption and growth of neobanks vary across regions, influenced by factors such as technological infrastructure, regulatory environment, and consumer preferences. Developed regions, such as North America and Europe, have seen significant neobank adoption, driven by a tech-savvy population and favorable regulatory frameworks. Emerging markets, particularly in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, offer substantial growth opportunities due to their large unbanked populations and increasing smartphone penetration.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Global Neobanking Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
The neobanking market can be segmented based on factors such as target customer segment, service offerings, and geographical focus. Target customer segments may include retail customers, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), or specific demographic groups. Service offerings may encompass payment services, savings and investment accounts, lending products, and personalized financial management tools. Geographical focus may vary, with some neobanks targeting specific regions or operating globally.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of digital banking services, including neobanking. Lockdowns, social distancing measures, and changing consumer behaviors have led to increased reliance on online banking solutions. Neobanks, with their digital infrastructure and remote access capabilities, have been well-positioned to meet the evolving needs of customers during the pandemic. The crisis has highlighted the importance of digital financial services and the resilience of neobanks in providing uninterrupted access to banking services. However, the pandemic has also posed challenges, such as economic uncertainty, changing customer priorities, and potential disruptions in fundraising activities for neobanks.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future of the global neobanking market is promising, with continued growth expected in the coming years. The market will witness increased competition and consolidation as traditional banks enhance their digital capabilities and new players enter the market. Neobanks that prioritize innovation, customer experience, and strategic partnerships will have a competitive advantage. The ongoing evolution of regulatory frameworkswill shape the market landscape, with regulators adapting to the rise of neobanks while ensuring consumer protection. Global expansion, product diversification, and collaborations with traditional banks and fintech companies will be key strategies for neobanks to capitalize on market opportunities. As customer preferences continue to shift towards digital banking, neobanks have the potential to become significant players in the global financial industry.
Conclusion
The global neobanking market is transforming the traditional banking landscape by offering convenient, accessible, and user-friendly financial services. Neobanks leverage technology, data analytics, and mobile applications to provide a seamless and personalized banking experience to customers. The market is driven by the increasing adoption of digital banking, changing consumer expectations, and the cost-effectiveness of neobanks. However, regulatory challenges, limited product offerings, and customer trust and security concerns pose potential obstacles. Nonetheless, neobanks have significant opportunities for market expansion, partnerships with traditional banks, and international growth. The market dynamics are characterized by intense competition, collaboration, and ongoing technological advancements. Neobanks that prioritize user experience, product innovation, regulatory compliance, and strategic partnerships will thrive in the future. With the continuous evolution of the banking industry and customer preferences, neobanks are well-positioned to shape the future of banking and provide innovative financial solutions globally.
What is Neobanking?
Neobanking refers to digital-only banks that operate without physical branches, offering services such as online banking, payment processing, and financial management through mobile apps and websites.
What are the key players in the Global Neobanking Market?
Key players in the Global Neobanking Market include Chime, N26, Revolut, and Monzo, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Global Neobanking Market?
The main drivers of growth in the Global Neobanking Market include the increasing adoption of smartphones, the demand for convenient banking solutions, and the rise of digital payment methods.
What challenges does the Global Neobanking Market face?
Challenges in the Global Neobanking Market include regulatory compliance, cybersecurity threats, and competition from traditional banks and fintech companies.
What opportunities exist in the Global Neobanking Market?
Opportunities in the Global Neobanking Market include expanding services to underserved populations, integrating advanced technologies like AI for personalized banking experiences, and partnerships with e-commerce platforms.
What trends are shaping the Global Neobanking Market?
Trends shaping the Global Neobanking Market include the rise of open banking, increased focus on customer experience, and the integration of blockchain technology for secure transactions.
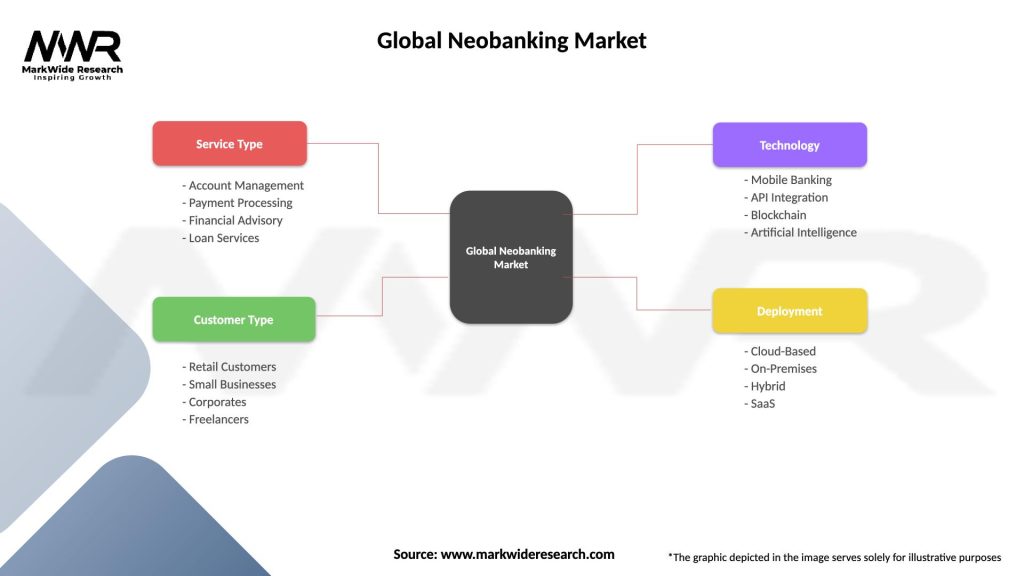
Global Neobanking Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Service Type | Account Management, Payment Processing, Financial Advisory, Loan Services |
| Customer Type | Retail Customers, Small Businesses, Corporates, Freelancers |
| Technology | Mobile Banking, API Integration, Blockchain, Artificial Intelligence |
| Deployment | Cloud-Based, On-Premises, Hybrid, SaaS |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Global Neobanking Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at