444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
The global industrial assembly equipment market is witnessing significant growth due to the increasing demand for efficient and automated assembly processes in various industries. Assembly equipment plays a crucial role in streamlining production lines and improving overall operational efficiency. This comprehensive market analysis provides insights into the key trends, drivers, restraints, opportunities, and future outlook of the industrial assembly equipment market.
Industrial assembly equipment refers to a wide range of machinery, tools, and systems used in manufacturing processes to assemble components or products. These equipment ensure precise and efficient assembly operations, reduce manual labor, minimize errors, and enhance productivity. They are extensively employed in industries such as automotive, electronics, aerospace, machinery, and consumer goods.
Executive Summary:
The executive summary of this market analysis provides a concise overview of the global industrial assembly equipment market. It highlights the key findings and major insights, including market size, growth rate, competitive landscape, and key trends impacting the market. This summary serves as a quick reference for industry professionals and stakeholders to understand the market landscape and make informed decisions.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Electrification of Mobility: The burgeoning EV market requires novel assembly equipment for battery modules, electric drivetrains, and high‑precision sensor installation, driving demand for specialized automation.
Miniaturization in Electronics: Smartphones, wearables, and IoT devices involve intricate assemblies of tiny components. High‑precision pick‑and‑place robots and vision‑based alignment systems are essential.
Collaborative Robotics: Cobots allow safe human‑robot collaboration without safety guards, ideal for low‑volume, high‑mix production environments where flexibility is paramount.
Digital Integration: Seamless connectivity between assembly equipment and MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) enables real‑time data capture, analytics, and adaptive process control.
Sustainability Pressures: Energy‑efficient motors, regenerative braking on robots, and equipment designed for easy maintenance and retrofit support manufacturers’ ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) goals.
These insights underscore the market’s evolution toward intelligent, connected, and adaptable assembly solutions that meet modern manufacturing demands.
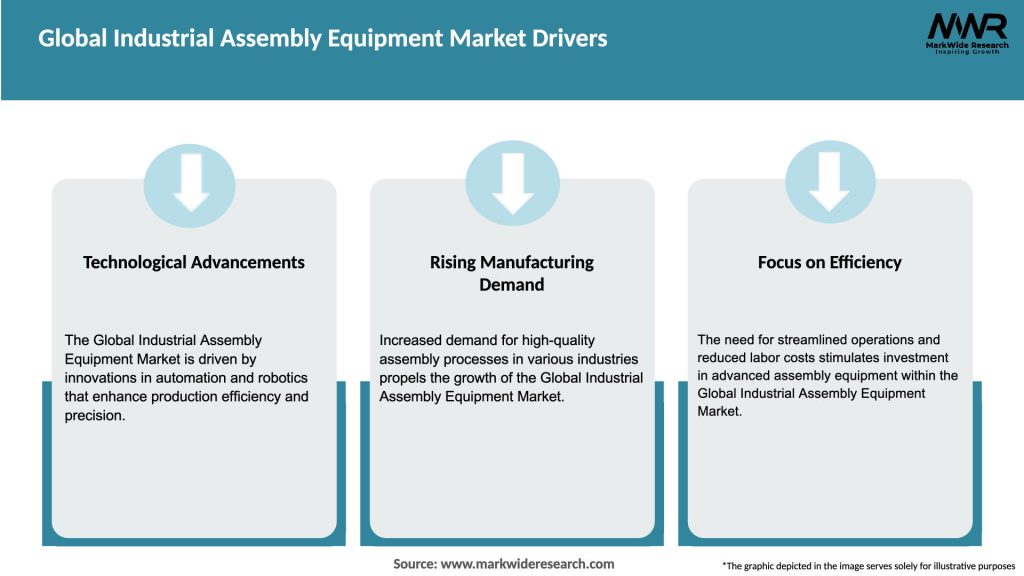
Market Drivers
Industry 4.0 Adoption: Subsidies and tax incentives for smart factory upgrades encourage investment in automated assembly lines integrated with IoT and AI .
Labor Shortages and Wage Inflation: Rising labor costs in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia drive automation to maintain competitiveness.
Quality and Traceability Requirements: Industries such as aerospace, medical devices, and defense demand 100% traceability of assembly operations, pushing adoption of vision‑based inspection and data logging equipment.
Mass Customization: Consumer preference for personalized products requires equipment that can switch between product variants with minimal downtime, boosting demand for modular, reconfigurable workcells.
E‑Mobility Growth: The shift to electric propulsion systems entails complex assemblies (battery packs, power electronics) that cannot be reliably produced by manual methods.
Integration of AI and Machine Learning: Predictive maintenance, adaptive process control, and defect detection through AI analytics enhance uptime and yield, making automation more attractive economically.
Market Restraints
High Initial Capital Investment: Advanced assembly equipment and integration costs can be prohibitive for small and medium‑sized enterprises (SMEs).
Integration Complexity: Retrofitting legacy production lines with new automation and ensuring interoperability across diverse equipment brands can delay projects.
Workforce Skill Gaps: Lack of trained personnel to program, maintain, and troubleshoot robotic cells remains a barrier, necessitating investments in training and upskilling.
Cybersecurity Risks: Increased connectivity raises concerns about intellectual property theft and operational disruption from cyberattacks, requiring robust OT (Operational Technology) security measures.
Product Lifecycle Mismatch: Rapid design changes in consumer electronics can outpace the deployment cycle of fixed automation equipment, limiting ROI in high‑mix industries.
Market Opportunities
SME Automation Solutions: Development of low‑cost, plug‑and‑play automation kits and subscription‑based robotics services can open SME segments.
AI‑Enhanced Quality Control: Integrating edge‑AI vision systems that detect micro‑defects in real time can reduce recalls and waste.
Human‑Machine Interface (HMI) Innovations: Intuitive interfaces, augmented reality (AR) guidance, and voice commands can lower the skill barrier for robot programming.
Robotics‑as‑a‑Service (RaaS): Subscription models for robotics hardware and software that include maintenance, upgrades, and training can reduce upfront costs and accelerate adoption.
Sustainable Manufacturing Initiatives: Equipment designed for energy efficiency, lower life‑cycle CO₂ emissions, and remanufacturing/retrofitting supports corporate sustainability goals.
Market Dynamics
Supply Side: Leading robotics and automation vendors invest heavily in R&D for sensor integration, AI algorithms, and modular cell designs. Strategic acquisitions are consolidating capabilities across mechatronics, vision, and software.
Demand Side: OEMs and contract manufacturers seek flexible, scale‑ready solutions for global supply chain resiliency. Demand surges in high‑growth sectors (EVs, renewable energy equipment, medical devices) drive equipment orders.
Economic/Policy Influences: Government grants in industrialized nations for digital manufacturing initiatives and zero‑emission vehicle production accelerate automation purchases. Conversely, geopolitical tensions and trade tariffs introduce supply chain unpredictability.
Regional Analysis
North America: Mature market with high automation penetration. Key drivers include reshoring of manufacturing, adoption of RaaS, and stringent quality/regulatory standards in aerospace and medical sectors.
Europe: Strong emphasis on Industry 4.0, collaborative robotics, and sustainability. Germany, Italy, and France lead in automotive and machinery automation. EU Green Deal spurs eco‑efficient equipment upgrades.
Asia‑Pacific: Fastest‑growing region driven by China’s “Made in China 2025,” India’s manufacturing initiatives, and Southeast Asia’s electronics hubs. Competitive labor costs balanced by automation to maintain quality.
Latin America: Emerging adoption with growth in automotive assembly in Mexico and Brazil. Infrastructure and workforce skills remain developing.
Middle East & Africa: Early stage, driven by oil & gas equipment assembly, defense hardware, and ambition to diversify economies via Smart City and industrial zone projects.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Global Industrial Assembly Equipment Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
By Equipment Type:
Robotic Systems: Articulated robots, SCARA, Delta, gantry robots.
Material Handling: Conveyors, AGVs, AMRs (Autonomous Mobile Robots).
Fastening & Joining: Automatic screwdrivers, riveters, welding cells.
Vision & Inspection: 2D/3D cameras, laser profilometers, X‑ray inspection.
Testing & Validation: Leak testers, functional testers, gauge systems.
By Automation Level:
Fully Automated Cells (24/7 operation, minimal human intervention)
Semi‑Automated Workstations (operator‑assisted robotics)
Manual Aids (power tools, torque‑controlled screwdrivers)
By End‑User Industry:
Automotive & Transportation
Electronics & Semiconductors
Aerospace & Defense
Consumer Goods & Appliances
Medical Devices & Pharmaceuticals
Heavy Machinery & Equipment
By Geography: North America, Europe, Asia‑Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa.
Category‑wise Insights
Robotic Systems: Highest growth due to expanding cobot segment and precision demands in electronics.
AGVs/AMRs: Surge driven by e‑commerce fulfillment centers and just‑in‑time automotive parts delivery.
Vision Systems: Crucial for zero‑defect manufacturing; linked tightly with AI‑driven analytics.
Fastening Equipment: Transition from pneumatic to electric screwdriving for precision torque control, traceability, and data logging.
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
Increased Throughput & Quality: Automation reduces cycle times and defects, boosting yield.
Operational Flexibility: Modular cells and cobots enable quick line reconfiguration.
Cost Savings: Long‑term reduction in labor costs, rework, and scrap.
Scalability: Equipment can be scaled incrementally to match demand growth.
Data‑Driven Decisions: Real‑time monitoring and analytics optimize maintenance and process parameters.
Safety & Ergonomics: Cobots and ergonomic tools reduce worker fatigue and injury risks.
SWOT Analysis
Strengths: High precision; scalability; ability to integrate with digital platforms.
Weaknesses: Capital intensity; complexity of integration; skill shortages.
Opportunities: RaaS models; AI‑driven adaptive systems; SME‑focused turnkey solutions.
Threats: Economic downturns impacting CapEx; cybersecurity vulnerabilities; rapid technology obsolescence.
Market Key Trends
Edge AI Analytics: Embedding AI at the equipment level for real‑time anomaly detection.
Universal Robots & Cobots: Growing use in low‑volume, high‑mix contexts, especially among SMEs.
Digital Twins: Virtual replicas of assembly lines for process simulation, optimization, and predictive maintenance.
Eco‑Design: Energy‑efficient motors, regenerative braking, and materials to reduce lifecycle carbon footprint.
5G Connectivity: Enabling real‑time remote control and monitoring of assembly equipment across distributed plants.
Covid‑19 Impact
Acceleration of Automation: Social distancing needs and workforce disruptions drove urgent investment in automation.
Supply Chain Realignment: Companies diversified suppliers and invested in local equipment production to mitigate global logistics risks.
Digital Transformation: Pandemic‑era lockdowns spurred adoption of remote monitoring, digital maintenance, and virtual commissioning.
Key Industry Developments
Siemens–Amazon Web Services Partnership: Cloud‑based MindSphere integration for predictive maintenance on assembly equipment.
ABB–Fanzor Cobots: Launch of small footprint cobots with built‑in force sensors for intricate assembly tasks.
KUKA–Case Studies: Modular automotive EV battery assembly lines delivered with <24‑hour installation times.
Universal Robots–UMECH Collaboration: Plug‑and‑play end‑effectors reducing integration time by 50%.
Analyst Suggestions
Pursue RaaS: Offer subscription models to lower adoption barriers.
Invest in Workforce Development: Partner with vocational schools for robotics and automation training.
Focus on Cyber‑Physical Security: Build robust OT cybersecurity protocols into equipment.
Expand SME‑Targeted Products: Develop affordable, modular systems with self‑configuring software.
Leverage Digital Twin Deployment: Use virtual commissioning to cut physical downtime and integration costs.
Future Outlook
The global industrial assembly equipment market is poised for sustained growth, driven by digitalization, the rise of EVs, and the continued push for operational efficiency. As AI, edge computing, and sustainability metrics become integral to manufacturing, equipment that seamlessly integrates with digital ecosystems and offers modular flexibility will outpace legacy systems. North America and Europe will continue to lead in high‑value sectors like aerospace and medical devices, while Asia‑Pacific gains share through large‑scale electronics and automotive production. Strategic players that innovate around cobots, RaaS offerings, and digital services will capture the biggest growth opportunities, securing their place in the future of smart manufacturing.
Conclusion
The Global Industrial Assembly Equipment Market is undergoing a transformative shift from traditional, fixed automation to agile, intelligent, and connected systems. Underpinned by Industry 4.0, AI, and sustainability imperatives, manufacturers worldwide are investing in solutions that deliver precision, flexibility, and data‑driven insights. While challenges around capital investment, integration complexity, and workforce skills persist, the long‑term benefits of enhanced productivity, quality consistency, and reduced operational costs create a compelling business case.
In conclusion, the global industrial assembly equipment market is poised for significant growth due to the increasing demand for automation, operational efficiency, and improved product quality. The market analysis provides valuable insights into the market dynamics, trends, drivers, restraints, and opportunities. By leveraging these insights, industry participants can make informed decisions, develop effective strategies, and capitalize on the lucrative opportunities presented by the industrial assembly equipment market.
What is Global Industrial Assembly Equipment?
Global Industrial Assembly Equipment refers to the tools and machinery used in the assembly processes of various industries, including automotive, electronics, and consumer goods. These equipment types enhance efficiency and precision in manufacturing operations.
What are the key players in the Global Industrial Assembly Equipment Market?
Key players in the Global Industrial Assembly Equipment Market include companies like Siemens, ABB, Rockwell Automation, and KUKA, among others. These companies are known for their innovative solutions and extensive product offerings in assembly technologies.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Global Industrial Assembly Equipment Market?
The main drivers of growth in the Global Industrial Assembly Equipment Market include the increasing demand for automation in manufacturing, the rise of smart factories, and the need for enhanced production efficiency. Additionally, advancements in robotics and AI are also contributing to market expansion.
What challenges does the Global Industrial Assembly Equipment Market face?
The Global Industrial Assembly Equipment Market faces challenges such as high initial investment costs and the need for skilled labor to operate advanced machinery. Additionally, rapid technological changes can lead to obsolescence of existing equipment.
What opportunities exist in the Global Industrial Assembly Equipment Market?
Opportunities in the Global Industrial Assembly Equipment Market include the growing trend of Industry Four Point Zero, which emphasizes automation and data exchange in manufacturing technologies. There is also potential for growth in emerging markets where industrialization is on the rise.
What trends are shaping the Global Industrial Assembly Equipment Market?
Trends shaping the Global Industrial Assembly Equipment Market include the integration of IoT technologies for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, as well as the increasing use of collaborative robots (cobots) in assembly lines. Sustainability practices are also becoming more prominent in equipment design and operation.
Global Industrial Assembly Equipment Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Equipment Type | Robots, Automated Systems, Material Handling Systems, Others |
| Industry | Automotive, Electronics, Aerospace & Defense, Manufacturing, Others |
| Region | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Global Industrial Assembly Equipment Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at