Market Dynamics
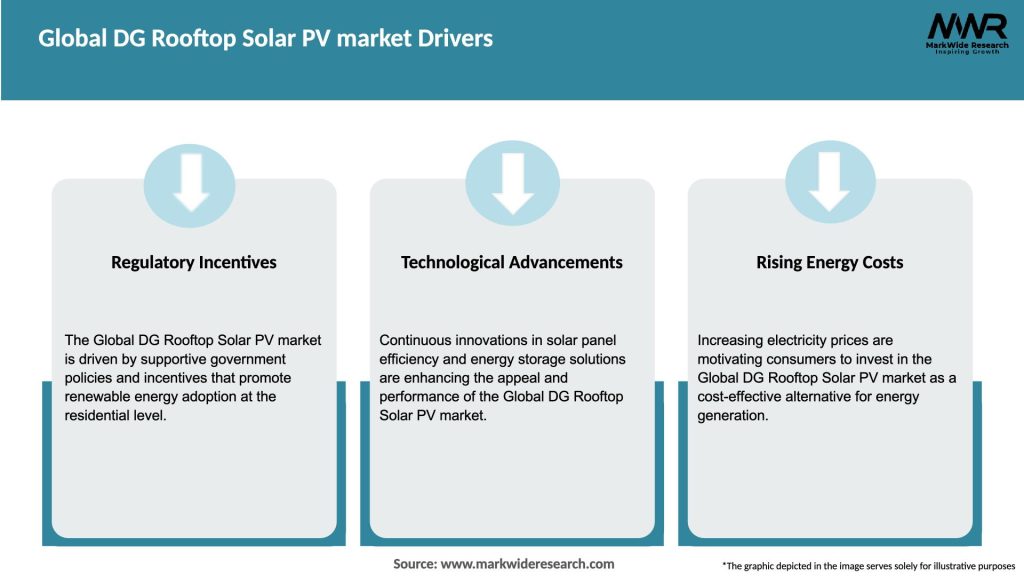
Complex interactions between technology, policy, economics, and consumer behavior shape market evolution. Learning curve effects continue driving cost reductions as cumulative installations increase and manufacturing scales. Policy evolution balances renewable energy goals against utility concerns, grid management, and subsidy affordability. Utility transformation from resistance toward adaptation and new business models embracing distributed generation. Supply chain globalization with manufacturing concentrated in Asia while installation markets span globally. Technology convergence integrating solar with storage, smart home systems, EVs, and building management platforms. Consumer awareness gradually improving though significant education needs persist around benefits and processes.
Competitive intensity among installers in mature markets drives innovation and cost reduction while potentially affecting quality. Capital flow patterns with institutional investors and energy companies allocating increasing resources to distributed solar assets. Regulatory frameworks adapting to high penetration scenarios addressing grid integration, compensation, and infrastructure requirements. International cooperation through technology transfer, standards development, and policy learning accelerating global deployment. Real estate market integration with solar systems increasingly considered in property valuations and transactions. Weather and climate impacts affecting generation patterns and system performance requiring geographic-specific approaches, with capacity factors typically ranging 15-25% depending on location, orientation, and system quality determining actual energy production relative to peak capacity influencing economic returns and system sizing decisions.
Research Methodology
Comprehensive research underpinning this analysis employed multiple methodologies ensuring accuracy and global market insight. Primary research included structured interviews with solar manufacturers, installation companies, financing providers, utility representatives, policymakers, and industry analysts providing firsthand perspectives on opportunities, challenges, and trends. Installation data analysis examined deployment statistics, capacity additions, and market penetration rates across regions and sectors. Secondary research synthesized information from renewable energy reports, policy documents, technical studies, and industry publications. Economic modeling assessed system costs, electricity prices, incentive values, and payback calculations across diverse markets and scenarios. Technology evaluation examined panel efficiency, inverter capabilities, mounting systems, and emerging innovations affecting performance and costs.
Policy framework analysis reviewed incentive programs, net metering regulations, renewable mandates, and interconnection standards across major markets. Competitive landscape research analyzed manufacturers, installers, and service providers assessing capabilities, positioning, and strategies. Customer research investigated adoption drivers, barriers, satisfaction levels, and decision processes across residential and commercial segments. Regional analysis examined market characteristics considering solar resources, electricity markets, policy environments, and economic conditions. Value chain mapping traced flows from manufacturing through distribution, installation, and ongoing operation understanding value creation and capture. Expert validation involved consulting with renewable energy specialists, grid integration experts, and market analysts verifying findings and incorporating specialized insights.
Regional Analysis
Asia-Pacific leads global capacity with approximately 45% market share, driven by massive installations in China, strong adoption in Australia and Japan, and emerging markets in India and Southeast Asia. China dominates absolute capacity with government support, domestic manufacturing, and urban and rural deployment programs. Australia demonstrates world-leading per-capita adoption with favorable solar resources, high electricity prices, and supportive policies. Japan maintains strong residential sector following feed-in tariff programs despite recent policy adjustments. India shows explosive growth potential with government targets, improving economics, and solar-favorable geography. Europe pioneered market development maintaining approximately 28% global share with mature markets and strong policy frameworks. Germany leads European deployment with early feed-in tariffs establishing robust industry despite northern latitude challenges. Italy, Spain, and UK demonstrate significant capacity with varying policy trajectories affecting recent growth. Netherlands and Belgium show strong adoption relative to size and solar resources. Eastern Europe represents emerging opportunity with improving economics and policy development.
North America exhibits robust market with approximately 23% global share led by United States residential and commercial strength. California dominates US market with aggressive renewable targets, high electricity rates, and solar-favorable climate. Northeast and Southwest states show strong growth with policy support and favorable economics. Canada demonstrates selective adoption concentrated in provinces with supportive policies despite northern climate. Mexico shows growing commercial and industrial sector interest. Latin America represents emerging market with Brazil, Chile, and Mexico leading early adoption supported by solar resources and electricity market characteristics. Middle East demonstrates growing interest particularly in UAE and Saudi Arabia combining excellent solar resources with diversification from fossil fuel dependency. Africa maintains limited development given economic constraints though South Africa shows modest market presence and off-grid opportunities exist throughout continent.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment features diverse participants across value chain:
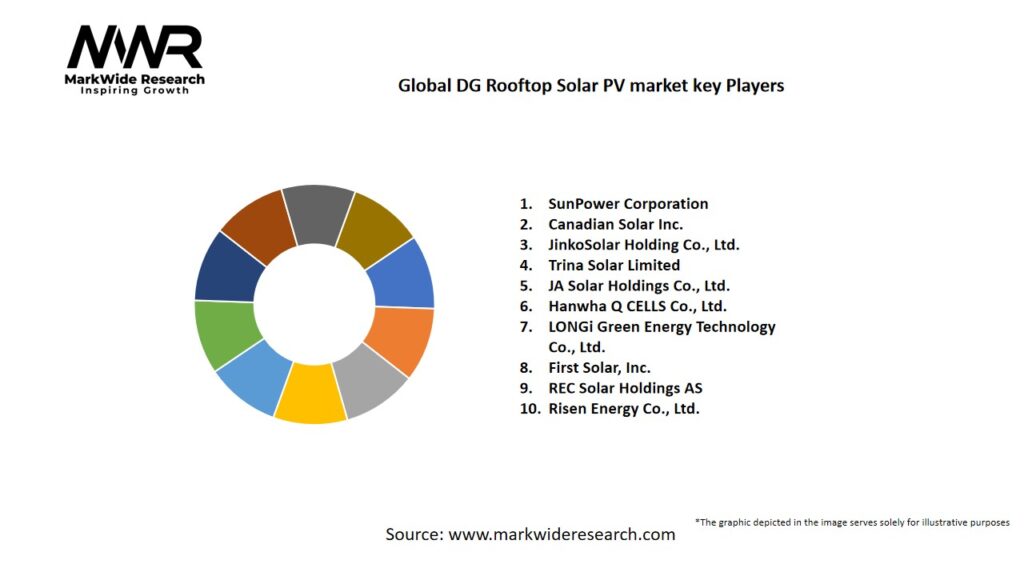
- JinkoSolar Holding – Leading global panel manufacturer with comprehensive product portfolio and competitive pricing
- Trina Solar – Major Chinese manufacturer offering high-efficiency modules and complete system solutions
- Canadian Solar – Vertically integrated producer with manufacturing and project development capabilities globally
- Longi Green Energy – Technology leader in monocrystalline modules with efficiency focus
- First Solar – US-based thin-film manufacturer with differentiated technology and sustainability focus
- SunPower Corporation – Premium efficiency residential and commercial systems with integrated installation services
- Sunrun Inc. – Leading US residential installer with extensive financing and service offerings
- Tesla Energy – Integrated solar and storage solutions with direct-to-consumer model and brand strength
- Vivint Solar – Residential focused installer with financing and monitoring services
- Enphase Energy – Microinverter technology leader enabling panel-level optimization and monitoring
- SolarEdge Technologies – Power optimizer and inverter systems with monitoring platforms
- Huawei Technologies – Chinese technology giant providing inverters and smart energy solutions
Segmentation
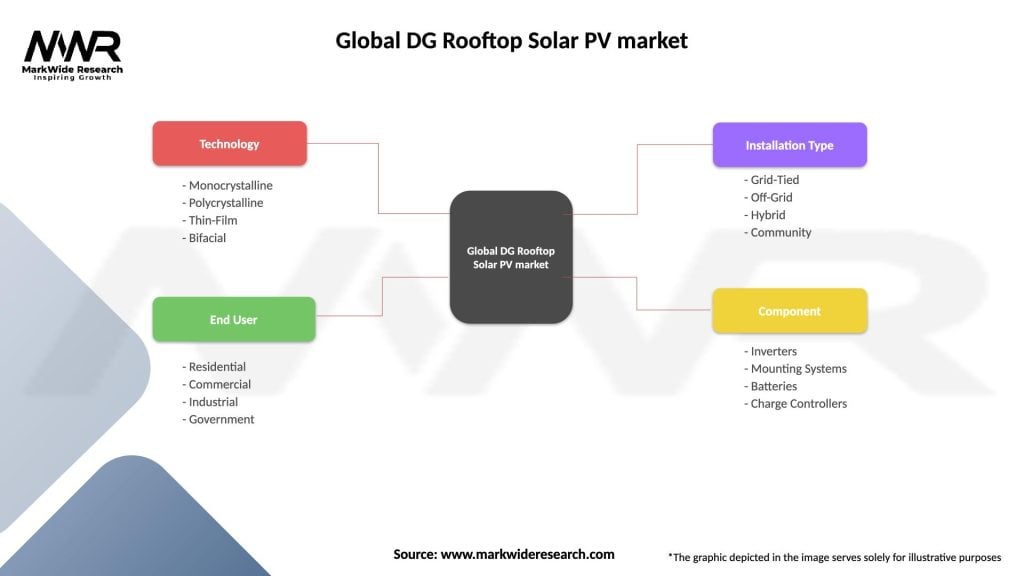
By Installation Type: The market segments into residential rooftop systems on single-family and multi-family homes, commercial installations on office buildings and retail facilities, industrial systems on manufacturing plants and warehouses, and institutional applications on schools, hospitals, and government buildings. Residential sector leads installation volumes while commercial and industrial represent larger average system sizes and capacity.
By System Size: Classification includes small residential systems typically under 10kW, medium commercial systems 10-100kW, large commercial installations 100-1000kW, and industrial-scale rooftop systems exceeding 1MW capacity. System sizing balances available roof space, energy consumption, grid interconnection capabilities, and project economics.
By Ownership Model: Segments encompass customer-owned systems purchased outright or financed with loans, third-party owned systems through power purchase agreements or leases where service providers retain ownership, and community solar programs with shared ownership or virtual net metering. Ownership model significantly affects customer value proposition, upfront costs, and ongoing responsibilities.
By Grid Connection: Categories include grid-tied systems without storage feeding excess to utility, grid-tied with battery storage enabling backup capabilities, and off-grid systems relying entirely on solar and storage. Grid-tied configurations dominate developed markets while off-grid solutions serve remote locations and areas with unreliable grid access.
By Technology: Segments include monocrystalline panels offering highest efficiency, polycrystalline modules providing cost-effectiveness, thin-film technologies with flexibility advantages, and emerging options including bifacial and half-cut cell designs. Monocrystalline technology increasingly dominates premium applications while polycrystalline serves cost-sensitive markets.
Category-wise Insights
Residential Rooftop Solar represents largest installation segment globally with homeowners pursuing energy independence and environmental benefits. Typical system sizes range 5-10kW accommodating household consumption and roof space constraints. Financing options including loans, leases, and power purchase agreements critical for market penetration given upfront costs. Payback periods vary dramatically based on location, incentives, and electricity rates from under 5 years in favorable markets to 10+ years in challenging environments. Property value impacts with studies showing installations increasing home values in many markets though impact varies by region. Aesthetic considerations increasingly important with all-black panels and integrated mounting systems improving visual appeal. Customer education requirements around process, costs, benefits, and maintenance critical for adoption decision confidence.
Commercial Rooftop Installations serve businesses pursuing sustainability goals, energy cost reduction, and corporate social responsibility demonstrations. System sizes typically larger than residential spanning 50-500kW depending on facility size and energy needs. Economic drivers emphasize return on investment with shorter payback periods often achievable given commercial electricity rates and depreciation benefits. Sustainability reporting value from renewable energy generation supporting environmental goals and stakeholder communications. Brand enhancement through visible environmental commitment and leadership. Roof assessment complexity greater given building codes, structural considerations, and ongoing business operations during installation. Power purchase agreement prevalence enabling adoption without capital expenditure and off-balance-sheet treatment.
Industrial Rooftop Solar utilizes large roof areas on manufacturing facilities and warehouses for substantial generation capacity. System scales frequently exceeding 1MW providing meaningful percentage of facility energy consumption. Load matching advantages when industrial operations occur during solar generation hours improving economic returns. Energy cost management critical for competitive manufacturing operations with solar providing long-term price certainty. Sustainability supply chain pressure from customers and investors driving corporate renewable energy adoption. Technical considerations around three-phase power, high voltage equipment, and integration with facility electrical systems. Structural capacity evaluation essential given panel and mounting system weight loading aging industrial buildings.
Battery Storage Integration represents rapidly growing category enhancing solar system value and capabilities. Energy independence enabling consumption of solar generation after sunset and during grid outages. Backup power providing resilience during outages increasingly important following extreme weather events. Time-of-use optimization storing solar energy for use during peak rate periods in markets with time-based electricity pricing. Self-consumption increase reducing grid exports where compensation rates decline or net metering unavailable. Grid services provision through aggregated distributed batteries participating in demand response and frequency regulation. Cost challenges with battery systems substantially increasing total project costs though prices declining and benefits expanding justifying adoption, with battery-solar combinations reaching 15-20% of new residential installations in leading markets demonstrating growing acceptance despite cost premiums as value propositions strengthen through resilience benefits, utility incentives, and economic optimization.
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
System Owners gain electricity bill savings, energy price certainty, environmental impact reduction, and potential property value enhancement while contributing to renewable energy transition. Energy independence particularly when combined with storage reduces grid dependence and provides backup capabilities during outages.
Solar Manufacturers access growing global market with strong policy support and improving economics creating sustained demand for panels, inverters, and system components. Technology leadership and efficiency improvements enable competitive differentiation and premium positioning.
Installation Companies benefit from market expansion while relatively fragmented industry provides opportunities for growth and consolidation. Service revenues from ongoing monitoring, maintenance, and performance guarantees supplement installation income creating recurring relationships.
Financing Providers generate returns from solar assets through interest, lease payments, and power purchase agreements while supporting renewable energy transition. Portfolio diversification and tax benefits make solar attractive investment for appropriate capital sources.
Utilities potentially benefit despite disruption challenges through managed distributed generation providing peak shaving, transmission relief, and renewable portfolio standard compliance while developing new business models around solar services and integration.
Society gains emission reductions, grid resilience enhancement, job creation, energy security improvement, and progress toward climate goals through decentralized renewable generation deployment across built environment.
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
- Dramatic Cost Declines: Continued price reductions making solar increasingly competitive with grid electricity across diverse markets without subsidies
- Proven Technology: Decades of deployment demonstrating reliability, performance, and longevity providing customer confidence and investor certainty
- Environmental Benefits: Zero emission electricity generation providing clear climate and air quality advantages supporting policy and consumer support
- Scalability and Modularity: Flexible system sizing from small residential to large industrial enabling serving diverse applications and customer segments
Weaknesses:
- Intermittency Challenges: Generation dependent on sunlight creates variability requiring grid integration solutions or storage systems
- Upfront Cost Barriers: Despite declining prices, initial investment requirements remain obstacle particularly in developing markets with limited financing
- Space Requirements: Roof area constraints and suitability limitations restrict addressable market and system capacity potential
- Policy Dependency: Market development heavily influenced by government incentives and regulations creating uncertainty and vulnerability to policy changes
Opportunities:
- Emerging Market Expansion: Developing nations with growing electricity demand and improving economics represent enormous growth potential
- Storage Integration: Battery systems transforming value proposition enabling energy independence, backup power, and enhanced grid services
- Building Integration: Next-generation designs incorporating solar generation directly into building materials and aesthetic elements from initial construction
- Electrification Synergies: Transportation and heating electrification creating new load and solar adoption drivers through electric vehicle charging and heat pump integration
Threats:
- Policy Reversal: Incentive reductions, net metering elimination, or regulatory changes potentially affecting economics and adoption momentum
- Grid Integration Limits: High penetration creating technical challenges and potential utility pushback affecting interconnection and compensation
- Technology Disruption: Alternative renewable or energy efficiency technologies potentially competing for customer investment and attention
- Economic Volatility: Recessions affecting discretionary investment and financing availability particularly for residential sector
Market Key Trends
Building Integrated Photovoltaics advances beyond traditional panel mounting toward seamless architectural integration. Solar roof tiles replacing conventional roofing materials combine weather protection with electricity generation. Facade integration utilizing vertical building surfaces expanding generation area beyond horizontal rooftops. Transparent solar windows in development potentially transforming entire building envelopes into generation surfaces. Aesthetic improvements through all-black panels and frameless designs addressing appearance concerns. Design phase integration considering solar from initial building plans optimizing orientation and structural capacity.
Artificial Intelligence and Optimization enhances system design, performance monitoring, and maintenance. Automated design software utilizing satellite imagery and machine learning optimizing panel placement and configuration. Predictive analytics identifying maintenance needs before failures occur reducing downtime. Performance optimization through continuous monitoring and adaptive inverter settings maximizing generation. Shading analysis using advanced algorithms quantifying impacts and optimizing layouts. Yield forecasting improving accuracy for financing and operational planning decisions.
Virtual Power Plant Aggregation coordinates distributed solar and storage resources providing grid services. Demand response participation with aggregated systems reducing consumption during peak periods. Frequency regulation services through rapid battery response stabilizing grid operations. Renewable energy smoothing compensating for cloud-induced generation variability. Market participation accessing wholesale electricity and ancillary service revenues. Grid support providing voltage control and congestion relief benefits.
Community Solar Expansion serves customers unable to install rooftop systems due to renting, shading, or unsuitable roofs. Virtual net metering allocating generation credits to multiple subscribers. Shared installations on municipal buildings, parking structures, or dedicated sites. Subscription models enabling participation without ownership responsibilities. Low-income programs ensuring access for disadvantaged communities. Corporate participation by businesses lacking adequate roof space.
Financing Innovation continues removing adoption barriers through novel structures. Green mortgages incorporating solar costs into home loans with favorable terms. Property Assessed Clean Energy programs enabling repayment through property taxes. Community choice aggregation facilitating bulk purchasing and financing. Securitization of solar assets creating liquid investment products. Blockchain applications potentially enabling peer-to-peer energy trading and microgrids, with financing closing rates improving to 70-80% of proposals in mature markets as processes streamline and customer awareness increases.
Key Industry Developments
Recent years have witnessed numerous significant developments influencing market trajectories. Module efficiency breakthroughs with commercial panels exceeding 22% and laboratory cells approaching 27% improving power density. Bifacial technology commercialization capturing reflected light from roof surfaces increasing generation by 10-20% in favorable conditions. Half-cut cell adoption reducing resistive losses and improving low-light performance becoming industry standard. Perovskite research progress potentially enabling next-generation efficiency gains and cost reductions though commercialization challenges persist. Policy developments including US Investment Tax Credit extensions, European Green Deal initiatives, and emerging market feed-in tariffs supporting deployment. Net metering modifications in several jurisdictions reducing compensation rates affecting economics and business models. Battery cost declines exceeding 85% over past decade making storage integration economically viable.
Corporate commitments by major companies including RE100 participants driving commercial installations. Utility solar programs with traditional electricity providers offering turnkey residential and commercial services. Supply chain disruptions during global events creating cost volatility and delivery delays. Manufacturing capacity expansion particularly in Southeast Asia and United States diversifying production beyond China concentration. Recycling infrastructure development addressing end-of-life panel management as early installations reach retirement. Grid modernization investments improving distributed generation accommodation and smart grid capabilities. Electric vehicle integration with solar systems enabling clean transportation charging creating combined value propositions.
Analyst Suggestions
Strategic positioning for DG rooftop solar market participants should emphasize comprehensive solutions integrating generation, storage, monitoring, and services rather than component sales alone. Customer experience focus simplifying processes from initial consultation through installation and ongoing operation reduces friction and improves satisfaction. Technology partnerships between manufacturers, installers, and software providers create integrated offerings delivering superior value. Geographic expansion strategies targeting emerging markets with improving economics and supportive policies captures growth opportunities.
Product development priorities should balance advancing efficiency and performance against cost optimization and installation simplicity. Storage integration development offering seamless solar-battery systems addresses growing demand for backup and independence. Aesthetic improvements making installations visually appealing reduces resistance from appearance-conscious customers and restrictive communities. Smart features including monitoring, optimization, and grid services integration differentiate offerings and enable premium positioning. Durability enhancement extending system lifespans and reducing maintenance requirements improves total cost of ownership.
Financing innovation addressing upfront cost barriers remains critical for market expansion particularly in residential sector. Accessible loan products with competitive rates and streamlined approvals democratize adoption. Power purchase agreements requiring no customer capital while providing savings attract risk-averse and cash-constrained segments. Performance guarantees reducing customer concerns about generation shortfalls or equipment failures. Community financing models enabling collective purchasing potentially reducing costs through scale.
Installation quality emphasis through training, certification, and quality assurance protects industry reputation and customer satisfaction. Standardized practices improving consistency while enabling efficiency gains and reducing errors. Safety protocols protecting workers and building occupants essential given electrical and height hazards. Warranty fulfillment honoring commitments when issues arise maintains trust and supports long-term industry health. Customer education setting realistic expectations around performance, maintenance, and economics prevents dissatisfaction.
Policy engagement advocating for supportive frameworks while demonstrating industry responsibility and value. Grid integration collaboration working with utilities and regulators addressing technical challenges constructively. Community benefits communication articulating local job creation, tax revenues, and energy resilience advantages. Utility dialogue exploring win-win business models recognizing distributed generation as opportunity rather than pure threat. Standards development participation ensuring regulations reflect technology capabilities and industry best practices.
Data and analytics investment enabling performance optimization, predictive maintenance, and customer insights. Monitoring platforms providing real-time visibility into system performance and issues. Benchmarking databases comparing installations identifying optimization opportunities. Customer behavior analysis informing product development and marketing strategies. Grid impact modeling supporting utility planning and integration solutions.
Future Outlook
Long-term prospects for the global DG rooftop solar PV market remain exceptionally positive driven by continued cost declines, efficiency improvements, policy support, and climate imperatives creating sustained growth across diverse markets and applications. MarkWide Research projects robust continued expansion with the sector achieving double-digit growth as technology advancement persists, emerging markets develop, and mature markets pursue higher penetration levels supporting decarbonization goals.
Technology evolution continues improving performance and reducing costs through efficiency gains, manufacturing optimization, and materials innovation. Tandem cell architectures potentially breaking current efficiency barriers approaching 30% commercial modules. Perovskite integration if commercialization challenges resolved could dramatically improve performance-cost ratios. Advanced inverters with grid support capabilities becoming standard enabling high-penetration scenarios. Integrated storage systems with declining battery costs making combined solutions increasingly attractive and accessible.
Market expansion sees continued growth in established markets combined with acceleration in emerging economies. India pursues ambitious rooftop targets with improving policies and economics. Southeast Asian nations including Vietnam, Thailand, and Indonesia develop supportive frameworks. Latin America capitalizes on solar resources and electricity market reforms. Sub-Saharan Africa potentially leapfrogging grid development through distributed generation. Middle East diversification from fossil fuels includes substantial solar deployment.
Policy frameworks likely continue supporting distributed generation though incentive structures may evolve toward more sustainable long-term models. Carbon pricing mechanisms improving solar economics relative to fossil alternatives. Renewable mandates requiring specified clean energy percentages creating demand certainty. Building codes potentially requiring or incentivizing solar installation in new construction. Grid integration standards establishing technical requirements for high-penetration scenarios. Net metering evolution toward compensation structures reflecting actual grid value and time-of-generation.
Business model innovation creates new approaches beyond traditional ownership or third-party financing. Solar-as-a-service offerings providing comprehensive energy solutions. Virtual power plants aggregating distributed resources participating in energy markets. Peer-to-peer trading enabled by blockchain potentially creating local energy economies. Community ownership models distributing benefits broadly while enabling scale. Utility integration with traditional providers offering solar services rather than viewing as competition.
Grid transformation accommodates and enables high distributed generation penetration through infrastructure and operational changes. Smart grid deployment providing visibility and control over distributed resources. Energy storage integration addressing intermittency and enabling time-shifting. Demand flexibility through responsive loads complementing variable generation. Distribution system upgrades handling bidirectional power flows and voltage management. Advanced forecasting improving prediction accuracy enabling better system operation.
Electrification synergies create combined value propositions driving solar adoption. Electric vehicle integration utilizing rooftop solar for clean transportation charging. Heat pump coupling providing renewable heating and cooling powered by on-site generation. Hydrogen production potentially utilizing excess solar generation for energy storage or industrial feedstock. Desalination applications in water-stressed regions powering purification with solar electricity.
Social equity considerations increasingly addressed ensuring distributed generation benefits reach diverse communities. Low-income programs providing access through subsidies, community solar, or targeted financing. Workforce development creating installation and maintenance careers across communities. Energy justice frameworks ensuring equitable distribution of clean energy benefits. Community ownership models keeping value local rather than extracting to distant investors.
Circular economy approaches address lifecycle impacts through recycling, refurbishment, and sustainable manufacturing. Panel recycling infrastructure developing to handle growing volumes reaching end-of-life. Material recovery extracting valuable elements including silicon, silver, and rare materials. Repurposing applications finding second-life uses for degraded panels. Sustainable manufacturing reducing production energy and environmental impacts achieving projected cumulative capacity potentially reaching 4-5 terawatts globally by decade end compared to current levels representing massive expansion as rooftop solar becomes mainstream electricity source across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors contributing substantially to global decarbonization and renewable energy transition goals.
Conclusion
The global DG rooftop solar PV market represents a transformative force in electricity generation and consumption, characterized by dramatic technology cost reductions, expanding policy support, and growing recognition of distributed renewable generation’s environmental and economic benefits across diverse markets and applications globally. Market expansion driven by continued solar panel cost declines, efficiency improvements, supportive policy frameworks, and increasing consumer and commercial interest in energy independence creates exceptional growth trajectory across residential, commercial, and industrial segments. Despite facing challenges including upfront cost barriers, policy uncertainties, grid integration complexities, and information gaps, the sector demonstrates remarkable momentum through technological innovation, financing creativity, and expanding ecosystem of manufacturers, installers, and service providers.
Diverse stakeholders including panel manufacturers, installation companies, financing providers, utilities, and policymakers collectively shape market development while competing and collaborating across complex value chains serving millions of customers globally. Regional dynamics reveal Asia-Pacific capacity leadership driven by Chinese deployment and Australian adoption, European market maturity with Germany pioneering pathways, North American residential strength particularly in United States, and emerging market acceleration in India, Southeast Asia, and Latin America. Technology advancement through efficiency improvements, bifacial designs, storage integration, and smart capabilities continuously enhances value propositions while driving down costs supporting mainstream adoption beyond early adopter segments. Economic viability improving dramatically as solar approaches or achieves grid parity in growing number of markets even without subsidies fundamentally transforming electricity sector competitive dynamics and consumer options. Policy frameworks including incentives, mandates, net metering, and renewable energy targets critically influence adoption rates and market development pace though underlying economics increasingly support deployment independent of government support. Financing innovation through loans, power purchase agreements, leases, and novel structures removes upfront cost barriers democratizing access and enabling adoption across income levels and customer segments.
Grid integration challenges around intermittency, voltage control, and infrastructure requirements increasingly addressed through smart grid development, storage deployment, and advanced management systems enabling high penetration scenarios. Storage convergence with solar systems creates comprehensive energy solutions enabling independence, backup power, and optimized consumption patterns enhancing value propositions and addressing intermittency concerns. Environmental benefits through zero-emission generation, transmission loss reduction, and fossil fuel displacement support climate goals while providing clear differentiation and supporting policy advocacy. Social impacts including job creation, energy access expansion, community resilience enhancement, and bill savings distribution represent important co-benefits beyond pure emissions reduction objectives.
The global DG rooftop solar PV market exemplifies successful renewable energy technology scaling from niche applications to mainstream electricity source through sustained innovation, policy support, and market development transforming how society generates and consumes electricity. As technology continues advancing, costs decline further, policies evolve supportively, and climate imperatives intensify, distributed rooftop solar appears positioned for continued robust growth becoming ubiquitous feature of built environment across residential, commercial, and industrial buildings worldwide. Industry participants demonstrating installation excellence, customer service quality, technological innovation, and financial accessibility while navigating complex policy environments and utility relationships appear best positioned to capitalize on substantial opportunities contributing to global energy transition, climate change mitigation, and sustainable development goals. The market’s outlook remains fundamentally positive supported by compelling economics, proven technology, supportive policies, and growing recognition that distributed renewable generation represents essential component of sustainable energy future enabling billions of building rooftops to contribute clean electricity while providing economic benefits to owners, grid resilience to communities, and environmental protection to future generations through fundamental transformation of electricity generation from centralized fossil fuel dependency toward decentralized renewable production integrated throughout built environment globally.