444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The global continuous manufacturing market has experienced significant growth in recent years. Continuous manufacturing refers to the uninterrupted and automated production process in which raw materials are transformed into finished products. This approach offers several advantages over traditional batch manufacturing, such as increased efficiency, reduced waste, and improved product quality. Continuous manufacturing is widely adopted in industries like pharmaceuticals, chemicals, food and beverages, and electronics.
Meaning
Continuous manufacturing involves the continuous flow of materials throughout the production process, eliminating the need for batch processing. It enables real-time monitoring and control, allowing manufacturers to make adjustments on the go. The process integrates various steps, such as mixing, reaction, separation, and packaging, into a single continuous line, resulting in streamlined operations and faster time-to-market.
Executive Summary
The global continuous manufacturing market has witnessed robust growth due to its ability to enhance operational efficiency and product quality. Continuous manufacturing offers advantages such as reduced production costs, improved scalability, and enhanced supply chain management. The market is expected to continue its upward trajectory, driven by advancements in technology, increasing demand for high-quality products, and the need for cost-effective manufacturing processes.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The global continuous manufacturing market is driven by a combination of factors, including technological advancements, increasing demand for high-quality products, and the need for cost-effective manufacturing processes. Market dynamics are influenced by regulatory requirements, industry-specific challenges, and the competitive landscape. Continuous investments in research and development, strategic partnerships, and mergers and acquisitions contribute to the market’s growth and expansion.
Regional Analysis
The continuous manufacturing market is geographically diverse, with North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and Latin America being key regions. North America dominates the market due to the presence of major pharmaceutical companies, strong regulatory frameworks, and significant investments in research and development. Europe follows closely, driven bya robust pharmaceutical industry and favorable government initiatives promoting continuous manufacturing. Asia-Pacific is expected to witness substantial growth due to the increasing adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies in countries like China and India. Latin America and the Middle East and Africa regions are also witnessing gradual adoption of continuous manufacturing, driven by the expansion of the pharmaceutical and chemical industries.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Global Continuous Manufacturing Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
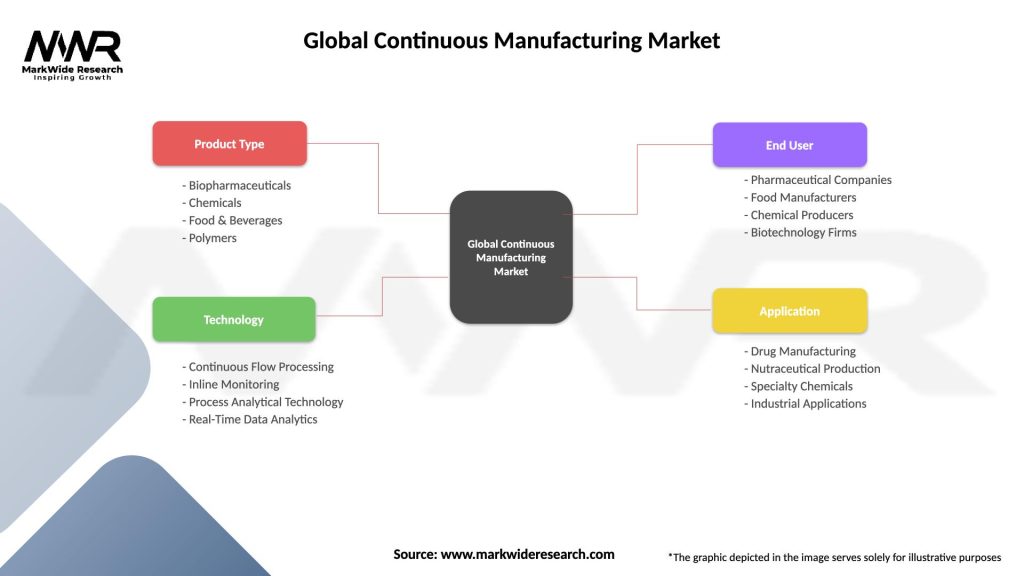
Segmentation
The continuous manufacturing market can be segmented based on industry, product type, and region:
By Industry:
By Product Type:
By Region:
Category-wise Insights
Pharmaceuticals:
Chemicals:
Food and Beverages:
Electronics:
Others:
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has had mixed effects on the continuous manufacturing market. While certain industries experienced disruptions in their supply chains and manufacturing processes, others witnessed increased demand and adoption of continuous manufacturing solutions.
The pharmaceutical industry, in particular, recognized the importance of continuous manufacturing in ensuring a stable supply of essential drugs during the pandemic. The ability to quickly adapt production lines, scale up or down, and maintain consistent product quality became crucial.
The pandemic also highlighted the need for resilient and agile manufacturing processes. Continuous manufacturing offers advantages such as reduced reliance on manual labor, improved process control, and the ability to adapt to changing market demands, making it a preferred choice for companies seeking to build robust supply chains.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future of the global continuous manufacturing market looks promising. Advancements in automation, data analytics, and AI are expected to drive further optimization and integration within the continuous manufacturing process. As industries recognize the benefits of continuous manufacturing, there will be increased adoption across various sectors, including pharmaceuticals, chemicals, food and beverages, electronics, and more.
The market will witness technological advancements that improve process efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance product quality. Modular and flexible systems will become more prevalent, allowing manufacturers to easily adapt to changing demands and customize their production lines. Additionally, the focus on sustainability and eco-friendly manufacturing practices will continue to shape the future of continuous manufacturing.
Conclusion
The global continuous manufacturing market is experiencing significant growth and transformation, driven by the need for operational efficiency, improved product quality, and cost savings. Continuous manufacturing offers numerous benefits, including streamlined operations, reduced waste, enhanced scalability, and better supply chain management.
Pharmaceuticals, chemicals, food and beverages, and electronics are among the key industries adopting continuous manufacturing. The pharmaceutical sector, in particular, has been a major driver due to regulatory requirements and the demand for consistent product quality. However, continuous manufacturing is also expanding into other industries, such as automotive, consumer goods, and energy, presenting new opportunities for growth.
What is Continuous Manufacturing?
Continuous manufacturing refers to a production process that operates without interruption, allowing for the constant flow of materials and products. This method is commonly used in industries such as pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and food processing to enhance efficiency and reduce production costs.
What are the key players in the Global Continuous Manufacturing Market?
Key players in the Global Continuous Manufacturing Market include companies like Siemens, Johnson & Johnson, and GSK, which are known for their innovative approaches to manufacturing processes. These companies focus on integrating advanced technologies to improve production efficiency and product quality, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Global Continuous Manufacturing Market?
The main drivers of growth in the Global Continuous Manufacturing Market include the increasing demand for high-quality products, the need for cost-effective manufacturing solutions, and advancements in automation technologies. Additionally, the push for sustainability in production processes is also contributing to market expansion.
What challenges does the Global Continuous Manufacturing Market face?
The Global Continuous Manufacturing Market faces challenges such as the high initial investment required for technology implementation and the complexity of integrating continuous processes into existing manufacturing systems. Additionally, regulatory compliance and the need for skilled workforce can also pose significant hurdles.
What opportunities exist in the Global Continuous Manufacturing Market?
Opportunities in the Global Continuous Manufacturing Market include the potential for innovation in process technologies and the growing trend of digital transformation in manufacturing. Companies are increasingly exploring smart manufacturing solutions that leverage IoT and AI to enhance operational efficiency.
What trends are shaping the Global Continuous Manufacturing Market?
Trends shaping the Global Continuous Manufacturing Market include the adoption of Industry Four Point Zero technologies, increased focus on sustainability, and the integration of real-time data analytics for process optimization. These trends are driving manufacturers to adopt more agile and responsive production methods.
Global Continuous Manufacturing Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Biopharmaceuticals, Chemicals, Food & Beverages, Polymers |
| Technology | Continuous Flow Processing, Inline Monitoring, Process Analytical Technology, Real-Time Data Analytics |
| End User | Pharmaceutical Companies, Food Manufacturers, Chemical Producers, Biotechnology Firms |
| Application | Drug Manufacturing, Nutraceutical Production, Specialty Chemicals, Industrial Applications |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at