444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
The global antifungal drugs market is experiencing significant growth due to the rising incidence of fungal infections across the world. Fungal infections can affect various parts of the body, including the skin, nails, respiratory system, and bloodstream. These infections can range from mild to severe, and if left untreated, they can lead to serious complications. Antifungal drugs are pharmaceutical agents designed to inhibit the growth and spread of fungi, helping to eliminate the infection and restore the health of patients.
Antifungal drugs, also known as antimycotics, are medications used to treat fungal infections. These drugs work by targeting the fungal cells and either killing them or inhibiting their growth. They can be classified into several categories based on their mechanism of action, including azoles, polyenes, echinocandins, and allylamines. Each category of antifungal drugs has its own specific mode of action, making them effective against different types of fungal infections.
Executive Summary
The global antifungal drugs market is projected to witness substantial growth in the coming years. The increasing prevalence of fungal infections, coupled with advancements in drug development and rising awareness about fungal diseases, are driving the market growth. Additionally, the growing geriatric population and the rising incidence of immunosuppressive conditions, such as HIV/AIDS and cancer, contribute to the expanding market demand for antifungal drugs.
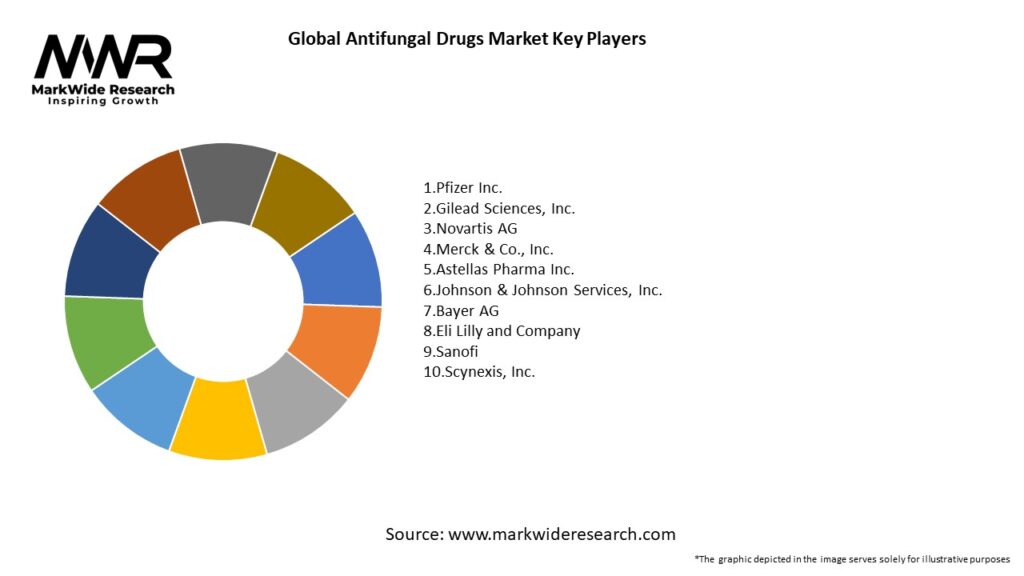
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
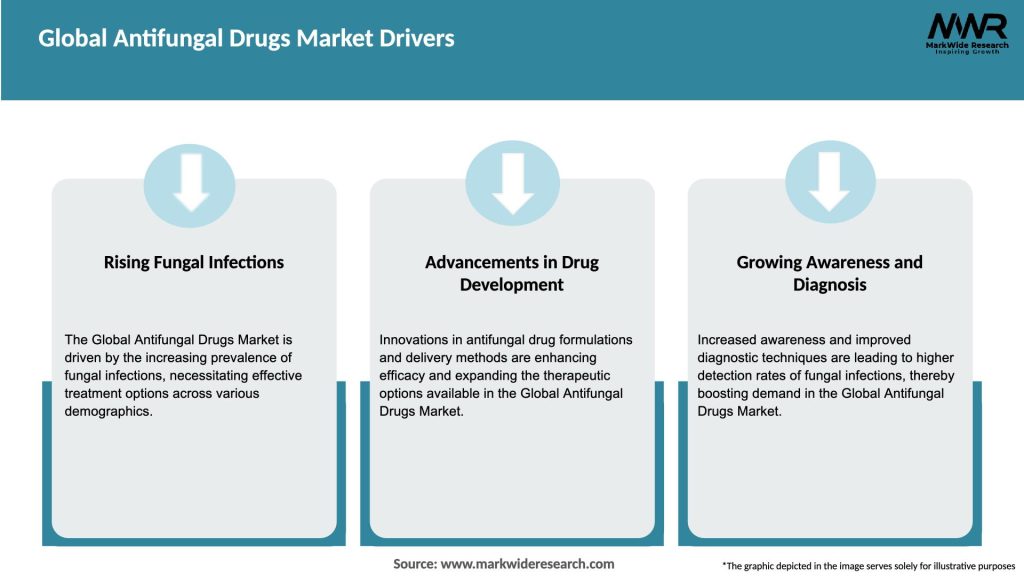
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The global antifungal drugs market is influenced by several dynamics, including market drivers, restraints, and opportunities. The increasing prevalence of fungal infections and advancements in drug development are driving the market growth. However, side effects and drug resistance pose challenges to market expansion. The development of combination therapies and a focus on developing countries present significant opportunities for market players to gain a competitive edge.
Regional Analysis
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Global Antifungal Drugs Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
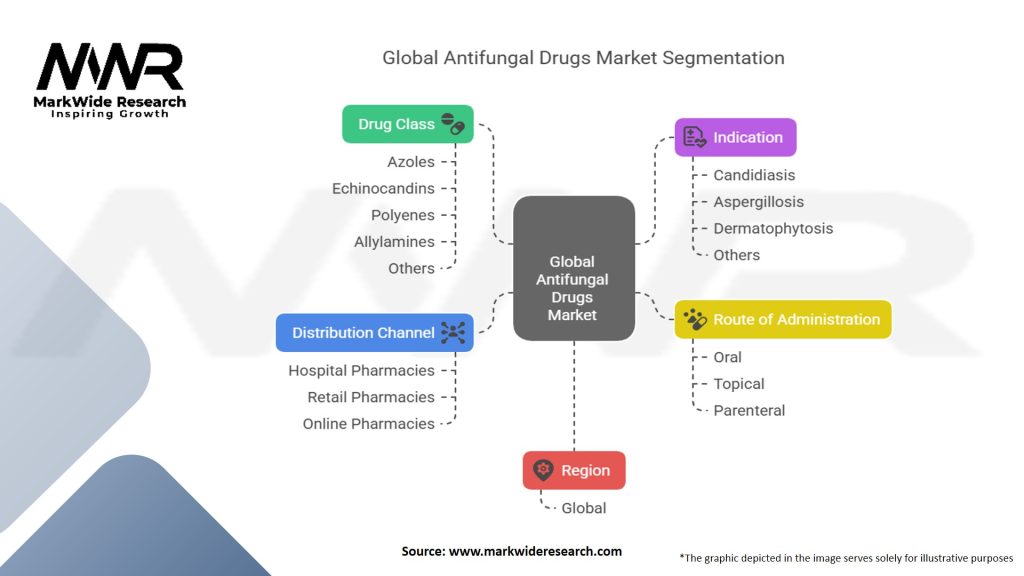
Segmentation
The global antifungal drugs market can be segmented based on drug class, indication, route of administration, and distribution channel.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a moderate impact on the global antifungal drugs market. While the primary focus has been on the management and treatment of COVID-19, the incidence of fungal infections, particularly in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, has increased. The use ofimmunosuppressive medications, prolonged hospital stays, and the use of invasive medical devices contribute to the risk of fungal infections in COVID-19 patients.
The demand for antifungal drugs has witnessed a surge due to the need for effective treatment options for fungal co-infections in COVID-19 patients. Antifungal drugs, such as azoles and echinocandins, have been used to manage invasive fungal infections, such as invasive aspergillosis and candidiasis, in critically ill COVID-19 patients.
However, the COVID-19 pandemic has also posed challenges to the antifungal drugs market. The diversion of healthcare resources and the overwhelming focus on COVID-19 management have resulted in delays in the diagnosis and treatment of fungal infections in non-COVID-19 patients. The disruptions in the global supply chain and the manufacturing of pharmaceutical products have also affected the availability and accessibility of antifungal drugs.
Overall, the impact of COVID-19 on the antifungal drugs market is a mix of opportunities and challenges. The increased awareness about fungal infections and the demand for antifungal drugs in COVID-19 patients present opportunities for market players. However, the disruptions in healthcare services and the supply chain pose challenges to market growth.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The global antifungal drugs market is expected to witness continued growth in the coming years. The rising prevalence of fungal infections, advancements in drug development, and increasing awareness about fungal diseases are the key drivers of market expansion. The development of novel antifungal drugs, focus on combination therapies, and penetration into emerging markets present significant opportunities for market players.
However, challenges such as drug resistance, side effects, and the high cost of antifungal drugs need to be addressed. Strategic collaborations, research and development investments, and patient education initiatives are crucial for the sustainable growth of the market. With continued efforts in innovation and market expansion, the antifungal drugs market is poised to contribute to the improved management of fungal infections and better patient outcomes.
Conclusion
The global antifungal drugs market is witnessing significant growth driven by the increasing prevalence of fungal infections, advancements in drug development, and rising awareness about fungal diseases. Market players are focusing on developing novel antifungal drugs, exploring combination therapies, and expanding their presence in emerging markets. Strategic collaborations, research and development investments, and patient education initiatives are key factors in sustaining market growth.
Despite challenges such as drug resistance and the high cost of antifungal drugs, the market presents opportunities for industry participants and stakeholders. Continued efforts in innovation, addressing affordability, and expanding access to antifungal drugs can contribute to better management of fungal infections and improved patient outcomes. The future outlook for the antifungal drugs market is promising, with the potential for continued growth and advancements in treatment options.
What are antifungal drugs in the context of the Global Antifungal Drugs Market?
Antifungal drugs are medications used to treat fungal infections by inhibiting the growth of fungi. They are essential in managing conditions such as candidiasis, aspergillosis, and dermatophyte infections.
Who are the key players in the Global Antifungal Drugs Market?
Key players in the Global Antifungal Drugs Market include Pfizer, Merck & Co., Gilead Sciences, and Novartis, among others. These companies are involved in the development and distribution of various antifungal medications.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Global Antifungal Drugs Market?
The growth of the Global Antifungal Drugs Market is driven by the increasing prevalence of fungal infections, rising awareness about antifungal treatments, and advancements in drug development technologies.
What challenges does the Global Antifungal Drugs Market face?
The Global Antifungal Drugs Market faces challenges such as the emergence of drug-resistant fungal strains, high costs of new antifungal therapies, and regulatory hurdles in drug approval processes.
What opportunities exist in the Global Antifungal Drugs Market?
Opportunities in the Global Antifungal Drugs Market include the development of novel antifungal agents, expansion into emerging markets, and increasing investment in research and development for innovative treatment options.
What trends are shaping the Global Antifungal Drugs Market?
Trends in the Global Antifungal Drugs Market include the growing focus on combination therapies, the rise of personalized medicine approaches, and the integration of digital health technologies in treatment management.
Global Antifungal Drugs Market Segmentation:
| Segment | Segmentation Details |
|---|---|
| Drug Class | Azoles, Echinocandins, Polyenes, Allylamines, Others |
| Indication | Candidiasis, Aspergillosis, Dermatophytosis, Others |
| Route of Administration | Oral, Topical, Parenteral |
| Distribution Channel | Hospital Pharmacies, Retail Pharmacies, Online Pharmacies |
| Region | Global |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Global Antifungal Drugs Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at