444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The global AI in Agriculture market is experiencing significant growth as the agricultural industry seeks innovative solutions to enhance productivity, optimize resource utilization, and improve decision-making processes. AI in Agriculture refers to the application of artificial intelligence technologies, such as machine learning, computer vision, and data analytics, in various agricultural processes and systems. This comprehensive market analysis provides insights into the current state of the AI in Agriculture market, key trends, drivers, restraints, opportunities, and future outlook.
Meaning
AI in Agriculture involves the use of advanced technologies and algorithms to analyze agricultural data, automate tasks, and make intelligent predictions and recommendations. It encompasses a wide range of applications, including precision farming, crop and livestock monitoring, predictive analytics, agricultural robotics, and supply chain optimization. The goal of AI in Agriculture is to improve efficiency, sustainability, and profitability in the agricultural sector.
Executive Summary
The global AI in Agriculture market is witnessing rapid growth as the agriculture industry adopts advanced technologies to overcome the challenges of feeding a growing population and increasing resource constraints. This market analysis provides an overview of the key findings and trends in the AI in Agriculture industry, highlighting market drivers, restraints, opportunities, and the competitive landscape. It aims to provide industry participants and stakeholders with valuable insights to make informed decisions and leverage the potential of AI in Agriculture.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The AI in Agriculture market is driven by the increasing need for food security, optimization of resource utilization, growing demand for data-driven insights, advancements in sensor technologies, and integration of AI with agricultural machinery. Challenges include lack of awareness and expertise, high implementation costs, data privacy and security concerns, technical challenges, and interoperability issues. The market offers opportunities in precision agriculture, crop and livestock monitoring, supply chain optimization, agricultural robotics, and decision support systems.
Regional Analysis
The AI in Agriculture market can be segmented into several regions, including North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East and Africa. North America dominates the market, driven by the presence of major tech companies, advanced farming practices, and supportive government initiatives. Europe and Asia Pacific also contribute significantly to the market, with the adoption of precision agriculture and increasing investments in AI technologies for agriculture.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Global AI in Agriculture Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.

Segmentation
The AI in Agriculture market can be segmented based on the type of AI applications, such as precision farming, livestock monitoring, supply chain optimization, agricultural robotics, and data analytics. Additionally, organizations can be categorized based on the type of farming systems, including arable farming, livestock farming, horticulture, and aquaculture.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the significance of a resilient and sustainable agricultural sector. AI technologies in agriculture have played a crucial role in ensuring food production, mitigating supply chain disruptions, and optimizing resource utilization during the pandemic. The crisis has accelerated the adoption of AI in Agriculture, particularly in areas such as remote monitoring, contactless operations, and supply chain optimization.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future of the AI in Agriculture market is promising, with increasing adoption of AI technologies to address the challenges faced by the agriculture industry. The market will continue to witness advancements in precision agriculture, agricultural robotics, data analytics, and decision support systems. However, addressing the challenges of awareness, high implementation costs, data privacy, and technical complexities will be crucial for widespread adoption. Continued research, innovation, collaboration, and stakeholder engagement will shape the future of AI in Agriculture, transforming the industry towards more efficient, sustainable, and resilient agricultural practices.
Conclusion
The global AI in Agriculture market is witnessing significant growth, driven by the need for increased productivity, resource optimization, data-driven decision-making, and advancements in technology. The market offers opportunities in precision farming, crop and livestock monitoring, supply chain optimization, agricultural robotics, and decision support systems. However, challenges such as limited awareness, high implementation costs, data privacy concerns, and technical complexities need to be addressed. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of AI in Agriculture, highlighting the importance of resilient and sustainable agricultural practices. The future outlook for the AI in Agriculture market is promising, with continued focus on innovation, collaboration, and stakeholder engagement shaping the industry towards more efficient, sustainable, and data-driven agriculture practices.
What is AI in Agriculture?
AI in Agriculture refers to the application of artificial intelligence technologies to enhance farming practices, improve crop yields, and optimize resource management. This includes the use of machine learning, data analytics, and robotics in various agricultural processes.
What are the key players in the Global AI in Agriculture market?
Key players in the Global AI in Agriculture market include companies like IBM, Microsoft, and Trimble, which provide innovative solutions for precision farming, crop monitoring, and agricultural data management, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Global AI in Agriculture market?
The main drivers of growth in the Global AI in Agriculture market include the increasing demand for food due to population growth, the need for sustainable farming practices, and advancements in AI technologies that enhance productivity and efficiency.
What challenges does the Global AI in Agriculture market face?
Challenges in the Global AI in Agriculture market include high implementation costs, the need for skilled labor to operate AI systems, and concerns regarding data privacy and security in agricultural practices.
What opportunities exist in the Global AI in Agriculture market?
Opportunities in the Global AI in Agriculture market include the development of smart farming solutions, the integration of AI with IoT devices for real-time monitoring, and the potential for AI to assist in climate-resilient agriculture practices.
What trends are shaping the Global AI in Agriculture market?
Trends shaping the Global AI in Agriculture market include the increasing adoption of drones for crop surveillance, the use of predictive analytics for yield forecasting, and the rise of autonomous farming equipment that utilizes AI technologies.
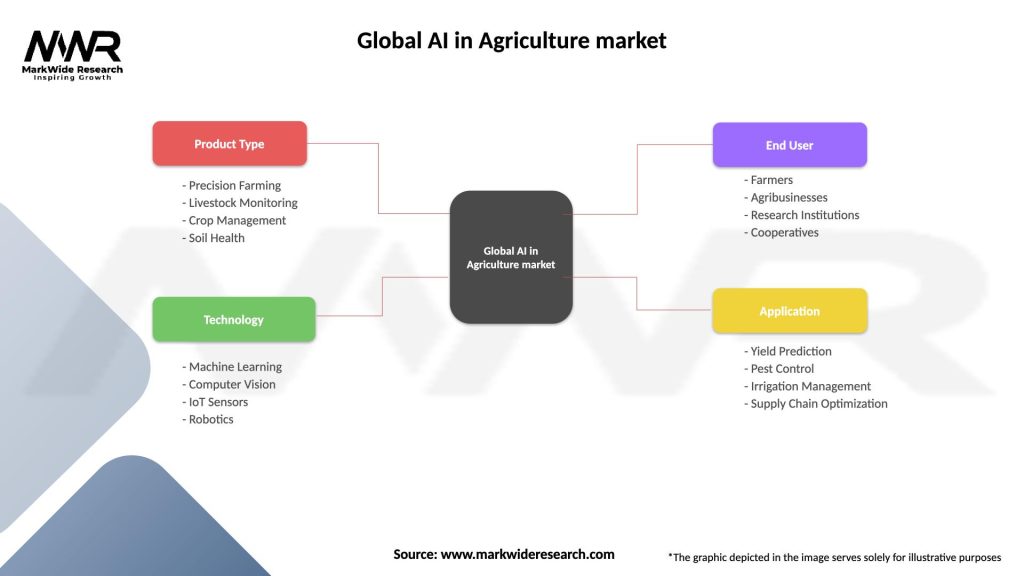
Global AI in Agriculture market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Precision Farming, Livestock Monitoring, Crop Management, Soil Health |
| Technology | Machine Learning, Computer Vision, IoT Sensors, Robotics |
| End User | Farmers, Agribusinesses, Research Institutions, Cooperatives |
| Application | Yield Prediction, Pest Control, Irrigation Management, Supply Chain Optimization |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Global AI in Agriculture Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at