444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The Fuel Cell for Data Centre market is experiencing significant growth and is poised to revolutionize the energy landscape in the coming years. As data centers continue to expand in size and complexity, the need for efficient and sustainable power solutions has become paramount. Fuel cells offer a promising alternative to traditional power sources by providing clean and reliable electricity with minimal environmental impact. This market overview will delve into the meaning of fuel cells, provide key insights, analyze market drivers, restraints, and opportunities, explore market dynamics, regional analysis, competitive landscape, segmentation, category-wise insights, and discuss the key benefits for industry participants and stakeholders. Additionally, a SWOT analysis, examination of market key trends, the impact of Covid-19, key industry developments, analyst suggestions, and future outlook will be presented, culminating in a comprehensive conclusion.
Meaning
Fuel cells are devices that convert the chemical energy of a fuel, typically hydrogen, into electricity through an electrochemical process. Unlike traditional power generation methods, such as combustion engines, fuel cells produce electricity without the need for combustion, resulting in reduced emissions and improved efficiency. Fuel cells offer several advantages for data centers, including high efficiency, low carbon footprint, scalability, and the ability to provide uninterrupted power supply. With advancements in fuel cell technology, such as proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) and solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs), the potential for integrating fuel cells into data centers is expanding rapidly.
Executive Summary
The fuel cell market for data centers is witnessing remarkable growth due to the increasing demand for sustainable and reliable power sources. Data centers, which consume vast amounts of electricity, are under pressure to reduce their environmental impact while maintaining uninterrupted operations. Fuel cells offer a compelling solution, providing clean and efficient energy that can address these challenges. This executive summary provides a concise overview of the market, highlighting key insights, market drivers, restraints, and opportunities. It also explores the market dynamics, regional analysis, competitive landscape, segmentation, and category-wise insights. Furthermore, the key benefits for industry participants and stakeholders, along with a SWOT analysis, market key trends, the impact of Covid-19, key industry developments, analyst suggestions, future outlook, and conclusion, will be discussed in detail.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The Fuel Cell for Data Centre market is driven by a combination of factors, including the increasing demand for sustainable power solutions, government support and incentives, the growing data center industry, advancements in fuel cell technology, and the focus on energy resilience. However, certain restraints, such as high initial costs, limited hydrogen infrastructure, complex integration, perception challenges, and competition from alternative technologies, hinder market growth. Despite these challenges, the market offers significant opportunities, including the growing demand for green data centers, partnerships and collaborations, infrastructure development, emerging markets, and research and development efforts. These dynamics shape the landscape of the fuel cell market for data centers, driving innovation, market adoption, and future growth.
Regional Analysis
The fuel cell market for data centers exhibits regional variations, influenced by factors such as energy policies, government initiatives, infrastructure development, and data center growth. The market is experiencing significant growth in North America, driven by the presence of major data center operators and favorable regulatory frameworks promoting clean energy. Europe is also a prominent market, with countries like Germany and the Netherlands leading the adoption of fuel cells in data centers. Asia-Pacific, particularly China and Japan, shows immense potential due to the increasing number of data centers and government support for fuel cell technology. Other regions, including Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa, are gradually recognizing the benefits of fuel cells for data centers and are expected to witness growing adoption in the coming years.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Fuel Cell for Data Centre Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
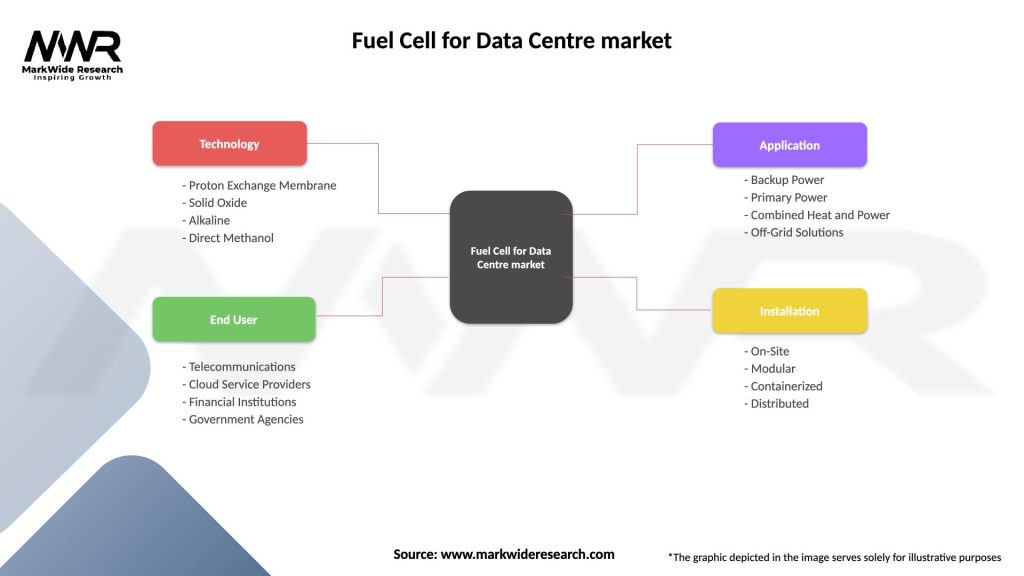
The fuel cell market for data centers can be segmented based on fuel cell type, power capacity, and end-user.
Segmenting the market enables a better understanding of customer requirements, facilitates targeted marketing strategies, and allows companies to tailor their offerings to specific segments.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic has had both positive and negative impacts on the fuel cell market for data centers. On one hand, the pandemic has highlighted the importance of reliable and resilient power supply for data centers, driving interest in fuel cell solutions. The increased focus on remote work, digitalization, and cloud services has led to a surge in data center demand, further bolstering the market. On the other hand, the pandemic has caused disruptions in the global supply chain, leading to delays in fuel cell manufacturing, component shortages, and logistical challenges. Additionally, economic uncertainties and budget constraints have affected investment decisions, potentially delaying the adoption of fuel cells in some data centers. However, the long-term prospects for the fuel cell market remain positive, as the need for sustainable and resilient power solutions becomes increasingly evident in a post-pandemic world.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future of the fuel cell market for data centers looks promising, driven by the increasing demand for sustainable and reliable power solutions. Fuel cells offer a compelling alternative to traditional power sources, providing clean energy, high efficiency, and energy resilience. The market is expected to witness significant growth as data centers continue to expand, driven by the digital transformation and the need for efficient data storage and processing. Technological advancements, cost reductions, and increased investments in hydrogen infrastructure will further propel market growth. As sustainability goals become a priority for organizations, fuel cells are poised to play a crucial role in powering the data centers of the future.
Conclusion
The fuel cell market for data centers represents a significant opportunity to revolutionize the energy landscape, offering clean, efficient, and resilient power solutions. Fuel cells provide numerous benefits, including high energy efficiency, scalability, reliability, and reduced environmental impact. While challenges such as high initial costs, limited hydrogen infrastructure, and complex integration persist, the market is witnessing positive developments driven by government support, partnerships, and technological advancements. The future outlook for the market is promising, with increasing demand for sustainable power solutions and a growing data center industry. The fuel cell market for data centers is poised for substantial growth, contributing to a greener and more resilient energy ecosystem.
What is Fuel Cell for Data Centre?
Fuel Cell for Data Centre refers to the use of fuel cell technology to provide reliable and efficient power solutions for data centers, enhancing energy security and reducing carbon emissions.
What are the key players in the Fuel Cell for Data Centre market?
Key players in the Fuel Cell for Data Centre market include Bloom Energy, FuelCell Energy, and Plug Power, among others.
What are the main drivers of the Fuel Cell for Data Centre market?
The main drivers of the Fuel Cell for Data Centre market include the increasing demand for sustainable energy solutions, the need for reliable backup power, and the growing focus on reducing operational costs in data centers.
What challenges does the Fuel Cell for Data Centre market face?
Challenges in the Fuel Cell for Data Centre market include high initial investment costs, limited infrastructure for hydrogen supply, and competition from other energy sources such as traditional generators.
What opportunities exist in the Fuel Cell for Data Centre market?
Opportunities in the Fuel Cell for Data Centre market include advancements in fuel cell technology, increasing government incentives for clean energy, and the rising trend of green data centers.
What trends are shaping the Fuel Cell for Data Centre market?
Trends shaping the Fuel Cell for Data Centre market include the integration of renewable energy sources, the development of hybrid systems combining fuel cells with batteries, and the growing emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainability.
Fuel Cell for Data Centre market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Technology | Proton Exchange Membrane, Solid Oxide, Alkaline, Direct Methanol |
| End User | Telecommunications, Cloud Service Providers, Financial Institutions, Government Agencies |
| Application | Backup Power, Primary Power, Combined Heat and Power, Off-Grid Solutions |
| Installation | On-Site, Modular, Containerized, Distributed |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Fuel Cell for Data Centre Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at