444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
Foreign exchange market, also known as Forex or FX market, is a global decentralized marketplace where currencies are traded. It is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with a daily turnover of trillions of dollars. The Forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, and encompasses a wide range of participants, including central banks, commercial banks, investment firms, corporations, and individual traders.
Meaning
The foreign exchange market is a platform where different currencies are bought and sold. It enables individuals, businesses, and financial institutions to convert one currency into another. For example, if a company based in the United States wants to import goods from Japan, it needs to convert its U.S. dollars into Japanese yen to complete the transaction. This conversion is facilitated through the foreign exchange market.
Executive Summary
The foreign exchange market plays a crucial role in facilitating international trade and investment. It provides a mechanism for participants to hedge against currency risks and speculate on currency movements. The market operates through a network of financial institutions and electronic trading platforms, which connect buyers and sellers from around the world.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Several key factors drive the foreign exchange market:
Market Restraints
Despite its significant size and liquidity, the foreign exchange market faces certain challenges and restraints:
Market Opportunities
The foreign exchange market presents several opportunities for participants:
Market Dynamics
The foreign exchange market is dynamic and constantly evolving. It is influenced by a combination of economic, political, and technological factors. The following dynamics shape the market:
Regional Analysis
The foreign exchange market operates globally, without any physical location or central exchange. However, certain regions play a significant role in the market:
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Foreign Exchange Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.

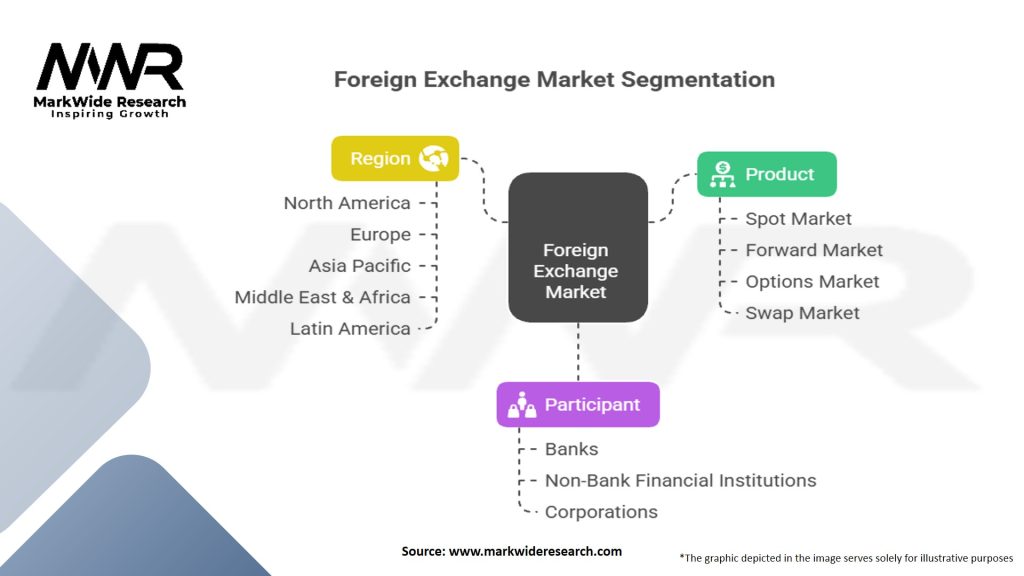
Segmentation
The foreign exchange market can be segmented based on various criteria:
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
The foreign exchange market offers several benefits for industry participants and stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) analysis of the foreign exchange market can provide insights into its overall position:
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Several key trends are shaping the foreign exchange market:
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic had a significant impact on the foreign exchange market:
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The foreign exchange market is expected to continue growing and evolving in the future:
Conclusion
The foreign exchange market is a dynamic and vast marketplace that enables the exchange of currencies for various purposes, including trade, investment, hedging, and speculation. It is influenced by a wide range of factors, including economic indicators, geopolitical events, and technological advancements. Participants in the market face opportunities and challenges, and it is crucial to stay informed, adopt risk management strategies, and leverage technology to navigate the market successfully. With ongoing developments and evolving trends, the future of the foreign exchange market holds both promise and exciting opportunities for industry participants and stakeholders.
What is the Foreign Exchange?
The Foreign Exchange refers to the global marketplace for trading national currencies against one another. It is essential for international trade, investment, and tourism, allowing businesses and individuals to convert one currency into another.
Who are the major players in the Foreign Exchange Market?
Major players in the Foreign Exchange Market include large financial institutions such as JPMorgan Chase, Citibank, and Deutsche Bank, which facilitate currency trading for clients and themselves, among others.
What are the key drivers of the Foreign Exchange Market?
Key drivers of the Foreign Exchange Market include interest rate differentials, economic indicators, and geopolitical stability. These factors influence currency values and trading volumes significantly.
What challenges does the Foreign Exchange Market face?
The Foreign Exchange Market faces challenges such as regulatory changes, market volatility, and the impact of economic crises. These factors can lead to unpredictable currency fluctuations and affect trading strategies.
What opportunities exist in the Foreign Exchange Market?
Opportunities in the Foreign Exchange Market include the rise of digital currencies, advancements in trading technology, and increasing participation from retail investors. These trends can enhance liquidity and create new trading strategies.
What are the current trends in the Foreign Exchange Market?
Current trends in the Foreign Exchange Market include the growing use of algorithmic trading, the impact of social media on trading decisions, and the increasing importance of emerging market currencies. These trends are reshaping how traders approach the market.
Foreign Exchange Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product | Spot Market, Forward Market, Options Market, Swap Market, Others |
| Participant | Banks, Non-Bank Financial Institutions, Corporations, Others |
| Region | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East & Africa, Latin America |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Foreign Exchange Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at