444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview: The Fc Fusion Protein for Diabetes Market is a vital segment within the biopharmaceutical industry, catering to the treatment of diabetes mellitus, a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by hyperglycemia. Fc fusion proteins represent a novel therapeutic approach, leveraging the Fc region of immunoglobulins to enhance the pharmacokinetics, stability, and therapeutic efficacy of therapeutic proteins targeting diabetes-related pathways. The market is driven by the increasing prevalence of diabetes, demand for innovative treatment modalities, and advancements in biotechnology and protein engineering.
Meaning: Fc fusion proteins are recombinant molecules composed of a therapeutic protein or peptide fused to the Fc region of immunoglobulins, such as IgG. This fusion design confers several advantages, including prolonged half-life, enhanced bioavailability, and improved pharmacokinetic properties compared to conventional protein therapeutics. In the context of diabetes treatment, Fc fusion proteins target key molecular pathways involved in glucose homeostasis, insulin signaling, and pancreatic β-cell function, offering potential benefits in glycemic control and disease management.
Executive Summary: The Fc Fusion Protein for Diabetes Market is witnessing significant growth driven by the unmet medical needs in diabetes management, growing patient population, and increasing investment in biopharmaceutical research and development. Key highlights include the development of novel Fc fusion proteins targeting insulin resistance, β-cell regeneration, and inflammatory pathways implicated in diabetes pathogenesis. Despite challenges such as regulatory hurdles, clinical validation, and market access barriers, the market holds immense potential for innovation, market expansion, and therapeutic advancements in diabetes care.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights:
Market Drivers:
Market Restraints:
Market Opportunities:
Market Dynamics: The Fc Fusion Protein for Diabetes Market operates within a dynamic landscape shaped by scientific advancements, technological innovations, regulatory frameworks, and market dynamics influencing drug development, commercialization, and clinical practice in diabetes management. Market players must navigate these dynamics, leverage opportunities, and mitigate challenges to drive innovation, market growth, and therapeutic advancements in diabetes care.
Regional Analysis: Regional variations in diabetes prevalence, healthcare infrastructure, regulatory policies, and market access influence the adoption, market penetration, and commercial success of Fc fusion proteins for diabetes treatment. Developed regions with established biopharmaceutical industries, robust research ecosystems, and favorable reimbursement environments lead in Fc fusion protein development, clinical trials, and market introduction, while emerging markets offer growth opportunities driven by rising disease burden, healthcare investments, and regulatory reforms.
Competitive Landscape:
Leading Companies in the Fc Fusion Protein for Diabetes Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
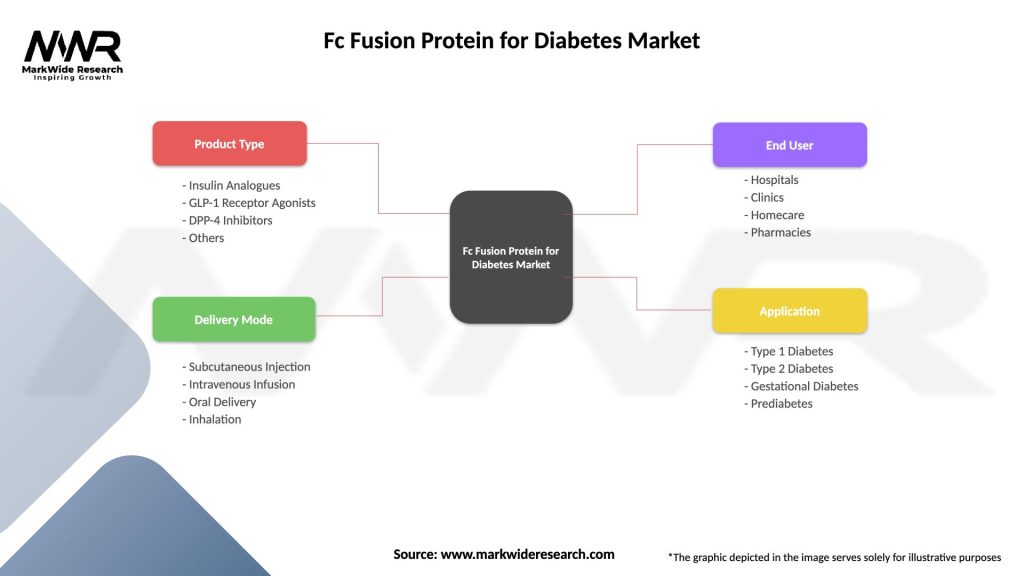
Segmentation: The Fc Fusion Protein for Diabetes Market can be segmented based on therapeutic target, mechanism of action, disease indication, and geographical region. Common segmentation categories include insulin resistance modulators, β-cell regenerative agents, inflammatory cytokine antagonists, type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM), type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and Rest of the World.
Category-wise Insights:
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis:
Market Key Trends:
Covid-19 Impact: The Covid-19 pandemic has underscored the importance of innovative therapies for diabetes management, given the heightened risk of severe outcomes and complications associated with diabetes in individuals infected with SARS-CoV-2. Fc fusion proteins for diabetes treatment continue to be developed and evaluated in clinical trials, offering potential benefits in mitigating inflammation, cytokine storm, and metabolic dysregulation associated with Covid-19 infection in patients with diabetes.
Key Industry Developments:
Analyst Suggestions:
Future Outlook: The future outlook for the Fc Fusion Protein for Diabetes Market is promising, driven by advancements in biotechnology, immunology, and diabetes research, as well as the growing demand for innovative therapeutic modalities capable of addressing the complex pathophysiology of diabetes and its associated complications. Market players must continue to invest in research and development, clinical translation, and market access strategies to capitalize on opportunities, mitigate risks, and drive sustainable growth in the dynamic landscape of diabetes therapeutics.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the Fc Fusion Protein for Diabetes Market represents a paradigm shift in diabetes therapeutics, offering innovative biologic agents with enhanced pharmacokinetics, target specificity, and therapeutic efficacy compared to conventional protein therapeutics. Despite challenges such as clinical development hurdles, regulatory constraints, and market access barriers, strategic initiatives focused on target validation, clinical trial design, and regulatory strategy will drive innovation, market expansion, and therapeutic advancements in diabetes care, ultimately improving outcomes and quality of life for patients with diabetes worldwide.
What is Fc Fusion Protein for Diabetes?
Fc Fusion Protein for Diabetes refers to a type of therapeutic protein that combines an Fc region of an antibody with a diabetes-related peptide. This fusion enhances the stability and half-life of the therapeutic agent, making it more effective in managing diabetes.
What are the key companies in the Fc Fusion Protein for Diabetes Market?
Key companies in the Fc Fusion Protein for Diabetes Market include Amgen, Eli Lilly, and Novo Nordisk, among others. These companies are involved in the development and commercialization of innovative Fc fusion proteins for diabetes treatment.
What are the growth factors driving the Fc Fusion Protein for Diabetes Market?
The growth of the Fc Fusion Protein for Diabetes Market is driven by the increasing prevalence of diabetes, advancements in biotechnology, and the demand for long-acting insulin therapies. Additionally, the rising focus on personalized medicine is contributing to market expansion.
What challenges does the Fc Fusion Protein for Diabetes Market face?
The Fc Fusion Protein for Diabetes Market faces challenges such as high development costs, regulatory hurdles, and competition from alternative diabetes treatments. These factors can hinder the timely introduction of new therapies into the market.
What opportunities exist in the Fc Fusion Protein for Diabetes Market?
Opportunities in the Fc Fusion Protein for Diabetes Market include the potential for novel drug formulations, partnerships between biotech firms and research institutions, and the expansion into emerging markets. These factors can enhance treatment options for diabetes patients.
What trends are shaping the Fc Fusion Protein for Diabetes Market?
Trends shaping the Fc Fusion Protein for Diabetes Market include the increasing use of biologics in diabetes management, advancements in drug delivery systems, and a growing emphasis on patient-centric therapies. These trends are expected to influence future product development.
Fc Fusion Protein for Diabetes Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Insulin Analogues, GLP-1 Receptor Agonists, DPP-4 Inhibitors, Others |
| Delivery Mode | Subcutaneous Injection, Intravenous Infusion, Oral Delivery, Inhalation |
| End User | Hospitals, Clinics, Homecare, Pharmacies |
| Application | Type 1 Diabetes, Type 2 Diabetes, Gestational Diabetes, Prediabetes |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Fc Fusion Protein for Diabetes Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at