444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2750
The Europe wearable medical device market represents a transformative segment of the healthcare technology industry, experiencing unprecedented growth driven by technological advancement and increasing health consciousness among consumers. This dynamic market encompasses a comprehensive range of connected health monitoring devices, from fitness trackers and smartwatches to specialized medical monitoring equipment designed for chronic disease management and preventive healthcare.
Market expansion across European countries has been particularly robust, with the region demonstrating a 12.3% compound annual growth rate over recent years. The integration of advanced sensors, artificial intelligence, and cloud-based analytics has revolutionized how healthcare providers and patients approach continuous health monitoring, creating substantial opportunities for market participants.
Consumer adoption patterns vary significantly across European markets, with Nordic countries leading in penetration rates while Southern European nations show accelerating growth trajectories. The market benefits from strong regulatory frameworks, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and increasing government initiatives supporting digital health transformation across the European Union.
Technological convergence between consumer electronics and medical devices has created new product categories that blur traditional market boundaries. Wearable devices now incorporate sophisticated biometric sensors capable of monitoring heart rate variability, blood oxygen levels, sleep patterns, and even early indicators of potential health complications, positioning them as essential tools in preventive healthcare strategies.
The Europe wearable medical device market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of body-worn electronic devices designed to monitor, track, and analyze various health parameters and medical conditions across European countries. These devices combine advanced sensor technology, wireless connectivity, and data analytics capabilities to provide continuous health monitoring and medical insights to users, healthcare providers, and medical institutions.
Wearable medical devices encompass a broad spectrum of products ranging from consumer-oriented fitness trackers and smartwatches to clinical-grade monitoring equipment used in hospital settings and chronic disease management programs. The market includes devices for cardiovascular monitoring, diabetes management, sleep disorder analysis, rehabilitation tracking, and general wellness monitoring.
Market definition extends beyond traditional medical equipment to include hybrid devices that serve both consumer and medical purposes, reflecting the evolving nature of healthcare delivery and patient engagement. These devices typically feature real-time data collection, cloud-based storage, mobile application integration, and often incorporate artificial intelligence for predictive health analytics.
Market dynamics in the European wearable medical device sector demonstrate exceptional growth momentum, driven by convergence of several key factors including aging population demographics, increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, and growing consumer awareness of preventive healthcare benefits. The market has experienced significant expansion across all major European economies, with particularly strong performance in Germany, United Kingdom, France, and Scandinavian countries.
Technology advancement continues to be a primary growth catalyst, with manufacturers introducing increasingly sophisticated devices capable of monitoring multiple health parameters simultaneously. Recent innovations include continuous glucose monitoring integration, advanced cardiac rhythm analysis, and early warning systems for various medical conditions, expanding the addressable market significantly.
Regulatory landscape across Europe has evolved to accommodate the growing wearable medical device sector, with the European Medicines Agency and national regulatory bodies establishing clear frameworks for device approval and market entry. This regulatory clarity has encouraged investment and innovation while ensuring patient safety and data security standards.
Market penetration rates vary considerably across European regions, with Northern European countries achieving 68% adoption rates among target demographics, while Central and Eastern European markets present substantial growth opportunities with rapidly increasing consumer acceptance and healthcare digitization initiatives.
Consumer behavior patterns reveal significant shifts toward proactive health management, with European consumers increasingly viewing wearable medical devices as essential healthcare tools rather than optional fitness accessories. This behavioral change has been accelerated by recent global health events and growing awareness of chronic disease prevention strategies.
Integration trends show increasing convergence between wearable devices and traditional healthcare systems, with hospitals and clinics incorporating wearable data into patient care protocols and treatment decisions. This integration has improved patient outcomes while reducing healthcare costs across European healthcare systems.
Demographic transformation across Europe serves as a fundamental market driver, with aging populations requiring continuous health monitoring and chronic disease management solutions. The proportion of elderly citizens continues to increase, creating sustained demand for wearable medical devices that enable independent living while ensuring medical oversight.
Healthcare cost pressures have motivated European healthcare systems to embrace preventive care technologies that reduce long-term treatment expenses. Wearable medical devices enable early detection of health issues, potentially preventing costly emergency interventions and hospitalizations while improving patient quality of life.
Technological advancement in sensor miniaturization, battery life, and wireless connectivity has made wearable medical devices more practical and user-friendly. Modern devices offer extended battery life, water resistance, and seamless integration with smartphones and healthcare platforms, addressing previous adoption barriers.
Government initiatives across European Union countries actively promote digital health adoption through funding programs, regulatory support, and healthcare digitization strategies. These initiatives include reimbursement policies for certain wearable medical devices and integration requirements for national healthcare systems.
Consumer health awareness has reached unprecedented levels, with European consumers actively seeking tools to monitor and improve their health status. This awareness extends beyond fitness tracking to include serious medical monitoring, creating demand for clinically validated wearable devices.
Privacy concerns regarding health data collection and storage represent significant market restraints, particularly in European markets with strict data protection regulations. Consumers express hesitation about sharing sensitive health information, despite potential benefits, creating adoption barriers for certain device categories.
Regulatory complexity across different European countries creates challenges for manufacturers seeking to launch products across multiple markets simultaneously. Varying approval processes, clinical trial requirements, and certification standards increase time-to-market and development costs for new devices.
Accuracy limitations in consumer-grade wearable devices have created skepticism among healthcare professionals and patients regarding the reliability of device-generated health data. Inconsistent readings and false alarms can undermine confidence in wearable medical device technology.
Cost considerations remain significant barriers for widespread adoption, particularly for advanced medical-grade wearable devices. High upfront costs and ongoing subscription fees for data services can limit accessibility for certain consumer segments and healthcare institutions.
Integration challenges with existing healthcare information systems create implementation barriers for healthcare providers considering wearable device adoption. Compatibility issues, data format standardization, and workflow integration requirements can complicate deployment processes.
Artificial intelligence integration presents substantial opportunities for enhancing wearable medical device capabilities through predictive analytics, personalized health recommendations, and automated health risk assessment. AI-powered devices can provide more accurate health insights and early warning systems for various medical conditions.
Telemedicine expansion across European healthcare systems creates significant opportunities for wearable medical devices to serve as remote monitoring tools, enabling healthcare providers to maintain patient oversight without requiring frequent in-person visits. This trend has been accelerated by recent healthcare delivery changes.
Chronic disease management represents a substantial growth opportunity, with European populations experiencing increasing rates of diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and other chronic conditions requiring continuous monitoring. Specialized wearable devices can improve patient outcomes while reducing healthcare system burden.
Corporate wellness programs across European companies are increasingly incorporating wearable medical devices to promote employee health and reduce healthcare costs. This B2B market segment offers substantial volume opportunities for device manufacturers and service providers.
Emerging markets within Eastern Europe present significant expansion opportunities as healthcare infrastructure develops and consumer purchasing power increases. These markets show strong growth potential with increasing awareness of preventive healthcare benefits.
Competitive intensity within the European wearable medical device market has increased significantly as traditional medical device manufacturers compete with technology companies and specialized startups. This competition drives innovation while creating pricing pressures across different market segments.
Supply chain considerations have become increasingly important following recent global disruptions, with manufacturers focusing on supply chain resilience and regional production capabilities. European companies are investing in local manufacturing and supplier diversification strategies.
Partnership strategies between device manufacturers, healthcare providers, and technology companies are reshaping market dynamics. These collaborations enable comprehensive health monitoring solutions that combine hardware, software, and healthcare services into integrated offerings.
Regulatory evolution continues to influence market dynamics as European authorities adapt regulations to accommodate emerging technologies while ensuring patient safety. New guidelines for AI-powered medical devices and data privacy requirements are shaping product development strategies.
Consumer expectations continue to evolve, with users demanding more sophisticated features, longer battery life, and seamless integration with digital health ecosystems. These expectations drive continuous innovation and product improvement cycles across the market.
Primary research methodologies employed in analyzing the European wearable medical device market include comprehensive surveys of healthcare professionals, device manufacturers, and end-users across major European markets. These surveys provide insights into adoption patterns, usage preferences, and market barriers.
Secondary research encompasses analysis of industry reports, regulatory filings, patent databases, and clinical trial data to understand technological trends, competitive positioning, and market development patterns. This research provides quantitative data on market size, growth rates, and segment performance.
Market segmentation analysis involves detailed examination of different device categories, application areas, and geographic regions to identify growth opportunities and market dynamics. This segmentation enables precise targeting of market opportunities and competitive positioning strategies.
Expert interviews with industry leaders, healthcare professionals, and technology specialists provide qualitative insights into market trends, challenges, and future developments. These interviews offer perspectives on regulatory changes, technological advancement, and market evolution patterns.
Data validation processes ensure accuracy and reliability of market analysis through cross-referencing multiple data sources, statistical analysis, and expert review. This validation provides confidence in market projections and strategic recommendations.
Germany represents the largest European market for wearable medical devices, accounting for approximately 28% regional market share, driven by advanced healthcare infrastructure, high consumer purchasing power, and strong regulatory support for digital health initiatives. German consumers demonstrate high adoption rates for medical-grade wearable devices.
United Kingdom maintains a significant market position despite recent political changes, with the National Health Service increasingly incorporating wearable medical devices into patient care protocols. The UK market shows particular strength in cardiovascular monitoring and diabetes management applications.
France demonstrates strong growth in wearable medical device adoption, supported by government healthcare digitization initiatives and increasing consumer health awareness. French healthcare providers are actively integrating wearable device data into patient care systems.
Nordic countries including Sweden, Norway, and Denmark lead in per-capita adoption rates, achieving 72% penetration among target demographics. These markets benefit from advanced digital infrastructure, high health awareness, and supportive regulatory environments.
Italy and Spain show accelerating growth trajectories with increasing consumer acceptance and healthcare system integration. These markets present substantial opportunities for expansion, particularly in elderly care and chronic disease management applications.
Eastern European markets including Poland, Czech Republic, and Hungary demonstrate rapid growth potential with improving healthcare infrastructure and increasing consumer purchasing power. These markets show 35% annual growth rates in wearable medical device adoption.
Market leadership is distributed among several key categories of companies, including established medical device manufacturers, technology giants, and specialized wearable device companies. This diverse competitive landscape drives innovation and market expansion across different segments.
Innovation strategies among leading companies focus on sensor advancement, artificial intelligence integration, and healthcare system connectivity. Companies are investing heavily in research and development to maintain competitive advantages in rapidly evolving market segments.
Partnership approaches are increasingly common, with device manufacturers collaborating with healthcare providers, insurance companies, and technology platforms to create comprehensive health monitoring ecosystems. These partnerships enable broader market reach and enhanced value propositions.
By Device Type: The market segments into fitness trackers, smartwatches, medical monitoring devices, and specialized therapeutic devices. Smartwatches currently dominate with 45% market share, while medical monitoring devices show the fastest growth rates.
By Application: Key application segments include cardiovascular monitoring, diabetes management, sleep tracking, fitness monitoring, and chronic disease management. Cardiovascular applications lead market adoption, followed by diabetes management solutions.
By End User: Market segmentation includes individual consumers, healthcare providers, corporate wellness programs, and elderly care facilities. Consumer segment represents the largest volume, while healthcare provider segment shows highest value per device.
By Technology: Segmentation includes Bluetooth-enabled devices, cellular-connected devices, and hybrid connectivity solutions. Bluetooth remains dominant, while cellular connectivity shows rapid growth for medical applications.
By Price Range: Market segments span budget devices under €100, mid-range devices €100-300, and premium devices above €300. Premium segment shows strongest growth in medical applications, while budget segment drives volume adoption.
Cardiovascular Monitoring: This category leads market adoption with sophisticated ECG monitoring, heart rate variability analysis, and arrhythmia detection capabilities. European regulatory approval for medical-grade cardiac monitoring has expanded addressable market significantly, with devices now capable of detecting atrial fibrillation and other cardiac conditions.
Diabetes Management: Continuous glucose monitoring represents a rapidly growing category with 31% annual growth across European markets. Integration with insulin delivery systems and smartphone applications has improved patient outcomes while reducing healthcare costs. Advanced devices now offer predictive glucose trend analysis and automated insulin adjustment recommendations.
Sleep Monitoring: Sophisticated sleep tracking capabilities including sleep stage analysis, sleep apnea detection, and circadian rhythm monitoring have created new market opportunities. Healthcare providers increasingly use sleep data for diagnosis and treatment planning, expanding beyond consumer wellness applications.
Fitness and Wellness: Traditional fitness tracking continues to evolve with advanced biometric monitoring, workout optimization, and recovery analysis. Integration with nutrition tracking and mental health monitoring creates comprehensive wellness management platforms.
Elderly Care: Specialized devices for elderly populations include fall detection, medication reminders, emergency response, and health status monitoring. These devices enable independent living while providing family members and caregivers with peace of mind through continuous monitoring capabilities.
Healthcare Providers benefit from continuous patient monitoring capabilities that enable early intervention, reduced hospital readmissions, and improved patient outcomes. Wearable device data integration with electronic health records provides comprehensive patient health pictures for better treatment decisions.
Patients gain increased awareness of their health status, early warning systems for potential health issues, and tools for managing chronic conditions more effectively. Continuous monitoring enables proactive health management and improved quality of life through better health insights.
Insurance Companies can offer personalized premiums based on health data, encourage preventive care behaviors, and reduce claim costs through early health issue detection. Wearable device programs create win-win scenarios for insurers and policyholders.
Device Manufacturers access expanding market opportunities across consumer and medical segments, with potential for recurring revenue through data services and software subscriptions. The market offers opportunities for both hardware sales and ongoing service relationships.
Healthcare Systems can reduce costs through preventive care, remote patient monitoring, and reduced emergency interventions. Wearable devices enable more efficient resource allocation and improved population health management strategies.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Artificial Intelligence Integration represents the most significant trend shaping the European wearable medical device market, with manufacturers incorporating machine learning algorithms for predictive health analytics, personalized recommendations, and automated health risk assessment. AI-powered devices can identify patterns in health data that may indicate developing health issues before symptoms appear.
Continuous Monitoring Evolution has transformed wearable devices from periodic measurement tools to continuous health monitoring systems. Modern devices provide 24/7 tracking of vital signs, sleep patterns, activity levels, and other health parameters, creating comprehensive health profiles for users and healthcare providers.
Healthcare System Integration continues to accelerate as hospitals and clinics incorporate wearable device data into patient care protocols. This integration enables remote patient monitoring, reduces hospital readmissions, and improves treatment outcomes through continuous health data availability.
Personalized Medicine applications are expanding as wearable devices collect individual health data that enables customized treatment recommendations and medication adjustments. This trend supports precision medicine approaches that consider individual patient characteristics and health patterns.
Multi-Parameter Monitoring devices are becoming standard, with single devices capable of tracking multiple health parameters simultaneously. This consolidation reduces device complexity for users while providing comprehensive health monitoring capabilities in compact form factors.
Regulatory Approvals for medical-grade wearable devices have accelerated across European markets, with several devices receiving approval for clinical use in cardiovascular monitoring, diabetes management, and sleep disorder diagnosis. These approvals expand market opportunities and validate wearable device technology for medical applications.
Partnership Announcements between major technology companies and healthcare providers have created new market dynamics, with collaborations focusing on integrated health monitoring solutions that combine devices, software platforms, and healthcare services. MarkWide Research analysis indicates these partnerships are reshaping competitive landscapes.
Technology Breakthroughs in sensor miniaturization and battery technology have enabled new device form factors and extended monitoring capabilities. Recent developments include non-invasive glucose monitoring, advanced cardiac rhythm analysis, and early-stage disease detection capabilities.
Investment Activity in European wearable medical device companies has increased substantially, with venture capital and private equity firms recognizing growth potential in digital health technologies. This investment supports research and development, market expansion, and technology advancement initiatives.
Clinical Validation Studies have demonstrated effectiveness of wearable medical devices in improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs. These studies provide evidence supporting broader adoption by healthcare providers and insurance companies across European markets.
Market Entry Strategies for new participants should focus on specialized applications rather than competing directly with established players in general fitness tracking. Opportunities exist in niche medical applications, elderly care, and chronic disease management where specialized expertise provides competitive advantages.
Technology Investment priorities should emphasize artificial intelligence capabilities, sensor accuracy improvements, and healthcare system integration features. Companies that can demonstrate clinical-grade accuracy and seamless healthcare workflow integration will capture premium market segments.
Partnership Development with healthcare providers, insurance companies, and technology platforms can accelerate market penetration and create sustainable competitive advantages. Strategic partnerships enable access to distribution channels, clinical validation opportunities, and integrated solution development.
Regulatory Compliance should be prioritized early in product development processes, with companies engaging regulatory authorities throughout development cycles. Understanding and addressing regulatory requirements can significantly reduce time-to-market and development costs.
Data Strategy development is crucial for long-term success, with companies needing clear approaches to data collection, analysis, and privacy protection. Strong data capabilities enable recurring revenue opportunities through software and service offerings beyond hardware sales.
Market expansion is projected to continue at robust rates, with the European wearable medical device market expected to maintain double-digit growth over the next five years. This growth will be driven by technological advancement, increasing health awareness, and expanding healthcare system integration.
Technology evolution will focus on enhanced accuracy, expanded monitoring capabilities, and improved user experiences. Future devices will likely incorporate advanced biometric sensors, longer battery life, and more sophisticated artificial intelligence capabilities for predictive health analytics.
Healthcare integration will deepen as medical professionals become more comfortable with wearable device data and regulatory frameworks evolve to support broader clinical applications. This integration will transform wearable devices from consumer gadgets to essential medical monitoring tools.
Market consolidation may occur as successful companies acquire specialized technology and smaller competitors to expand their capabilities and market reach. This consolidation could create more comprehensive health monitoring platforms and integrated solution providers.
Geographic expansion into Eastern European markets presents significant growth opportunities as healthcare infrastructure develops and consumer purchasing power increases. According to MWR projections, these markets could achieve 40% annual growth rates over the next three years.
The Europe wearable medical device market stands at a transformative juncture, with technological advancement, demographic trends, and healthcare system evolution creating unprecedented growth opportunities. The market has evolved from simple fitness tracking to sophisticated medical monitoring capabilities that provide real value to patients, healthcare providers, and healthcare systems across European countries.
Market dynamics indicate sustained growth potential driven by aging populations, increasing chronic disease prevalence, and growing consumer awareness of preventive healthcare benefits. The integration of artificial intelligence, advanced sensors, and healthcare system connectivity positions wearable medical devices as essential tools in modern healthcare delivery.
Success factors for market participants include focus on clinical accuracy, regulatory compliance, healthcare system integration, and comprehensive data strategies. Companies that can demonstrate medical-grade reliability while maintaining user-friendly experiences will capture the most attractive market segments and growth opportunities.
The future trajectory of the European wearable medical device market appears highly positive, with continued innovation, expanding applications, and deepening healthcare integration supporting sustained growth. Market participants who invest in technology advancement, strategic partnerships, and regulatory compliance will be well-positioned to capitalize on the substantial opportunities ahead in this dynamic and rapidly evolving market.
What is Wearable Medical Device?
Wearable medical devices are electronic devices that can be worn on the body to monitor health metrics, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and physical activity. They are increasingly used in personal healthcare management and remote patient monitoring.
What are the key players in the Europe Wearable Medical Device Market?
Key players in the Europe Wearable Medical Device Market include Philips, Fitbit, and Garmin, which are known for their innovative health monitoring solutions. These companies focus on developing devices that enhance patient engagement and improve health outcomes, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Europe Wearable Medical Device Market?
The Europe Wearable Medical Device Market is driven by factors such as the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, the growing demand for remote patient monitoring, and advancements in sensor technology. Additionally, rising health awareness among consumers contributes to market growth.
What challenges does the Europe Wearable Medical Device Market face?
Challenges in the Europe Wearable Medical Device Market include data privacy concerns, regulatory hurdles, and the need for interoperability among devices. These factors can hinder the adoption and integration of wearable technologies in healthcare systems.
What future opportunities exist in the Europe Wearable Medical Device Market?
The Europe Wearable Medical Device Market presents opportunities in areas such as personalized medicine, integration with telehealth services, and the development of advanced analytics for health data. Innovations in artificial intelligence and machine learning also hold potential for enhancing device capabilities.
What trends are shaping the Europe Wearable Medical Device Market?
Trends in the Europe Wearable Medical Device Market include the rise of smartwatches with health monitoring features, the integration of wearables with mobile health applications, and an increasing focus on mental health tracking. These trends reflect a shift towards holistic health management.
Europe Wearable Medical Device Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
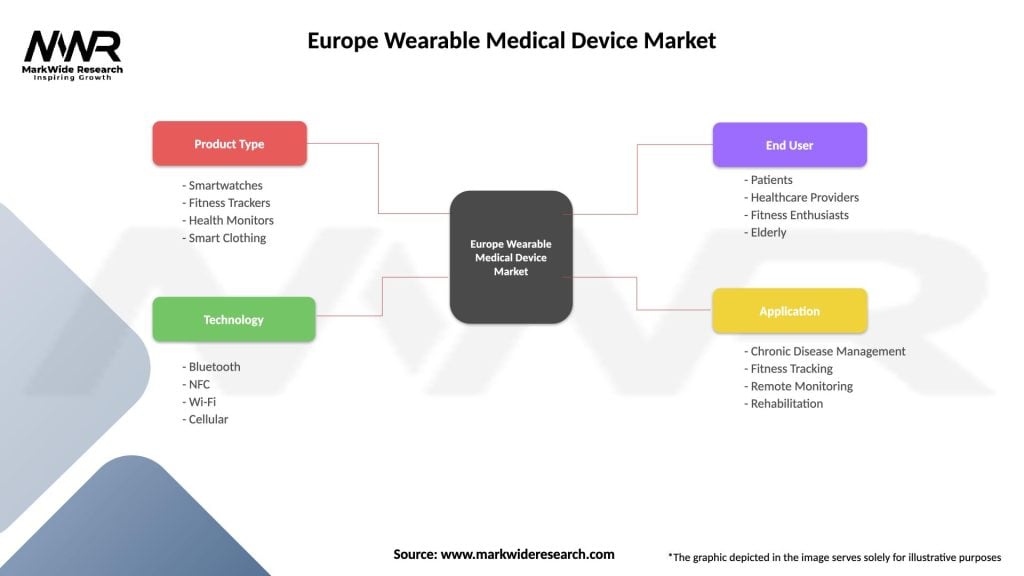
| Product Type | Smartwatches, Fitness Trackers, Health Monitors, Smart Clothing |
| Technology | Bluetooth, NFC, Wi-Fi, Cellular |
| End User | Patients, Healthcare Providers, Fitness Enthusiasts, Elderly |
| Application | Chronic Disease Management, Fitness Tracking, Remote Monitoring, Rehabilitation |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Europe Wearable Medical Device Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at