444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2750
Market Overview
The Europe peat market refers to the production, distribution, and consumption of peat, a type of organic matter derived from partially decomposed vegetation. Peat is primarily used as a fuel source and in horticulture applications. The European peat market is characterized by a growing demand for alternative energy sources, sustainable farming practices, and increasing awareness of the environmental impact of peat extraction.
Meaning
Peat is a type of organic material formed in wetland ecosystems through the partial decomposition of plants and other organic matter. It is rich in carbon and is commonly found in marshes, bogs, and moors. Peat has been used as a fuel source for centuries and is also utilized in gardening and horticulture as a soil amendment.
Executive Summary
The Europe peat market is witnessing significant growth due to multiple factors, including the increasing demand for renewable energy sources, the growing popularity of peat-based gardening products, and the need for sustainable land management practices. However, the market also faces challenges related to environmental concerns, the depletion of peatlands, and the emergence of alternatives to peat-based products.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
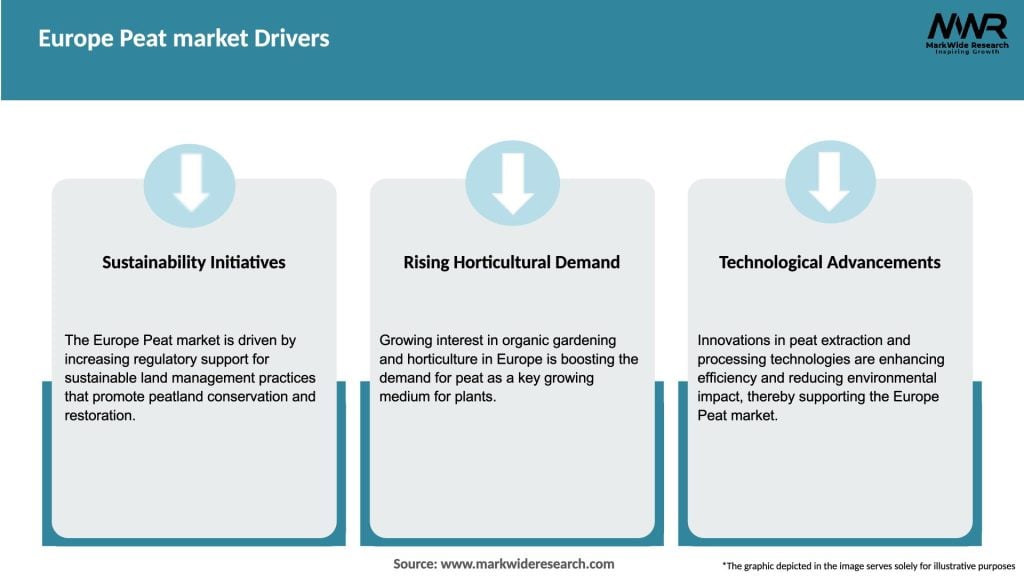
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities

Market Dynamics
The Europe peat market is influenced by various factors, including environmental regulations, shifting consumer preferences, technological advancements, and government initiatives promoting sustainable practices. The market dynamics are shaped by the delicate balance between the demand for peat-based products, the need for environmental conservation, and the development of alternatives.
Regional Analysis
The European peat market encompasses countries such as Ireland, Finland, Sweden, the United Kingdom, and Estonia, which are known for their significant peatland reserves and peat production activities. Each country has its regulations, environmental policies, and market dynamics that influence the peat industry.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in Europe Peat Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
The market can be segmented based on product types, including fuel peat and horticultural peat, as well as applications such as power generation, gardening, and agriculture. Understanding these segments allows for a deeper analysis of market trends, consumer preferences, and specific industry requirements.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Market Key Trends
COVID-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic had limited direct impact on the peat market. However, it highlighted the importance of sustainable practices, environmental conservation, and the need for resilient supply chains in the face of disruptions. The pandemic-induced economic slowdown affected the demand for peat-based products in some sectors, such as horticulture and construction.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future of the Europe peat market is subject to evolving environmental regulations, changing consumer preferences, and advancements in sustainable land management practices. The market’s growth will depend on the industry’s ability to address environmental concerns, develop peat alternatives, and adopt sustainable practices to ensure long-term viability.
Conclusion
The Europe peat market is witnessing significant growth driven by the demand for renewable energy sources, sustainable land management practices, and the popularity of peat-based gardening products. However, the market faces challenges related to environmental concerns, peatland depletion, and the emergence of alternatives. By embracing sustainable practices, diversifying product offerings, and fostering collaboration and innovation, the peat market can navigate these challenges and contribute to a greener and more sustainable future.
What is Peat?
Peat is an accumulation of partially decayed organic matter, primarily found in wetlands. It is used in various applications, including horticulture, energy production, and as a soil amendment.
What are the key players in the Europe Peat market?
Key players in the Europe Peat market include Bord na Móna, Klasmann-Deilmann, and Horticultural Peat Suppliers, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Europe Peat market?
The Europe Peat market is driven by increasing demand for organic gardening, the rise in bioenergy applications, and the growing awareness of sustainable agriculture practices.
What challenges does the Europe Peat market face?
The Europe Peat market faces challenges such as environmental concerns regarding peat extraction, regulatory pressures, and competition from alternative growing media.
What opportunities exist in the Europe Peat market?
Opportunities in the Europe Peat market include the development of eco-friendly peat alternatives, expansion into emerging markets, and innovations in peat-based products for horticulture.
What trends are shaping the Europe Peat market?
Trends in the Europe Peat market include a shift towards sustainable sourcing practices, increased research on peat’s role in carbon sequestration, and the growing popularity of peat-free products.
Europe Peat market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Horticultural Peat, Fuel Peat, Agricultural Peat, Peat Moss |
| End Use Industry | Agriculture, Horticulture, Energy, Landscaping |
| Packaging Type | Bags, Bulk, Pallets, Containers |
| Distribution Channel | Direct Sales, Retail, Online, Wholesalers |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in Europe Peat Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at