444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2750
Market Overview
The Europe nuclear reactor decommissioning market refers to the process of safely dismantling and decontaminating nuclear power plants that have reached the end of their operational life. Decommissioning involves the removal of radioactive materials, the management of waste, and the restoration of the site to its pre-operational state. The market for nuclear reactor decommissioning in Europe has gained significant traction in recent years due to the aging nuclear infrastructure, regulatory requirements, and the growing focus on renewable energy sources.
Meaning
Nuclear reactor decommissioning is the process of retiring and permanently shutting down a nuclear power plant. It involves a series of steps, including deactivation, decontamination, dismantling, and waste management. The goal is to ensure the safe removal of radioactive materials, mitigate environmental risks, and restore the site for other uses. Decommissioning is a complex and highly regulated process that requires specialized knowledge and expertise in nuclear safety and radiation protection.
Executive Summary
The Europe nuclear reactor decommissioning market has witnessed significant growth in recent years due to several factors, including the increasing number of nuclear power plants reaching the end of their operational life, stricter regulatory requirements, and the need to address public concerns about nuclear safety and environmental risks. The market is characterized by a range of stakeholders, including nuclear plant operators, engineering firms, waste management companies, and regulatory bodies. The market is expected to experience steady growth in the coming years as more nuclear power plants undergo decommissioning.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The Europe nuclear reactor decommissioning market is influenced by various dynamics, including regulatory frameworks, technological advancements, public acceptance, and market competition. Government policies and regulations play a crucial role in shaping the market landscape, ensuring safety standards, and managing radioactive waste. Technological advancements in robotics, remote handling, and radiation monitoring contribute to improved efficiency and safety during the decommissioning process. Public acceptance and engagement are essential for gaining social license and addressing concerns related to nuclear safety and environmental impact.
Regional Analysis
Europe is home to a significant number of nuclear power plants, many of which are approaching the end of their operational life. Germany, France, and the United Kingdom are key players in the European nuclear reactor decommissioning market, accounting for a significant share of decommissioning activities. Germany has taken a proactive approach to nuclear phase-out, with plans to shut down all nuclear power plants by 2022. France and the United Kingdom have also made commitments to reduce reliance on nuclear energy and transition towards renewable sources. Eastern European countries, such as Slovakia and Lithuania, are also expected to witness increased decommissioning activities.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Europe Nuclear Reactor Decommissioning Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.

Segmentation
The Europe nuclear reactor decommissioning market can be segmented based on various factors, including the type of nuclear power plant, decommissioning strategy, and waste management methods. Different reactor types, such as pressurized water reactors (PWR), boiling water reactors (BWR), and advanced gas-cooled reactors (AGR), require specific decommissioning approaches. Decommissioning strategies can vary from immediate dismantling to deferred dismantling. Waste management methods involve the handling, treatment, and disposal of radioactive materials generated during the decommissioning process.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic had an impact on the Europe nuclear reactor decommissioning market, causing delays and disruptions in decommissioning projects. Restrictions on travel, supply chain disruptions, and health and safety measures affected the progress of decommissioning activities. However, as the situation improved and safety protocols were implemented, the market witnessed a recovery. The pandemic highlighted the need for robust contingency plans, risk management strategies, and resilience in the nuclear industry.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future of the Europe nuclear reactor decommissioning market is expected to be driven by the increasing number of nuclear power plants reaching the end of their operational life, the need for safe and sustainable decommissioning practices, and the focus on renewable energy sources. The market will witness continued technological advancements, including the use of robotics, artificial intelligence, and digital solutions to enhance safety, efficiency, and project management. International collaborations and knowledge-sharing will play a crucial role in addressing challenges and achieving successful decommissioning outcomes.
Conclusion
The Europe nuclear reactor decommissioning market presents significant opportunities and challenges for industry participants and stakeholders. With the aging nuclear infrastructure and the increasing focus on renewable energy sources, decommissioning activities are expected to rise in the coming years. It is crucial for companies to prioritize safety, compliance, and waste management throughout the decommissioning process. Collaboration, innovation, and effective stakeholder communication will be key to ensuring the successful and sustainable decommissioning of nuclear power plants and the safe management of radioactive waste.
What is Nuclear Reactor Decommissioning?
Nuclear reactor decommissioning refers to the process of safely closing and dismantling a nuclear power plant after it has reached the end of its operational life. This involves the removal of nuclear fuel, management of radioactive waste, and decontamination of the site to ensure safety and environmental protection.
What are the key players in the Europe Nuclear Reactor Decommissioning Market?
Key players in the Europe Nuclear Reactor Decommissioning Market include companies such as Areva, Westinghouse Electric Company, and EDF Energy, which specialize in nuclear services and decommissioning projects, among others.
What are the main drivers of the Europe Nuclear Reactor Decommissioning Market?
The main drivers of the Europe Nuclear Reactor Decommissioning Market include the increasing number of aging nuclear facilities, stringent regulatory requirements for safety and environmental standards, and the growing emphasis on sustainable energy practices.
What challenges does the Europe Nuclear Reactor Decommissioning Market face?
Challenges in the Europe Nuclear Reactor Decommissioning Market include high costs associated with decommissioning processes, public opposition to nuclear waste management, and the technical complexities involved in safely dismantling nuclear facilities.
What opportunities exist in the Europe Nuclear Reactor Decommissioning Market?
Opportunities in the Europe Nuclear Reactor Decommissioning Market include advancements in decommissioning technologies, potential for international collaboration on best practices, and the increasing demand for skilled labor in nuclear decommissioning projects.
What trends are shaping the Europe Nuclear Reactor Decommissioning Market?
Trends shaping the Europe Nuclear Reactor Decommissioning Market include the adoption of innovative decommissioning techniques, increased investment in research and development for waste management solutions, and a growing focus on environmental sustainability in decommissioning practices.
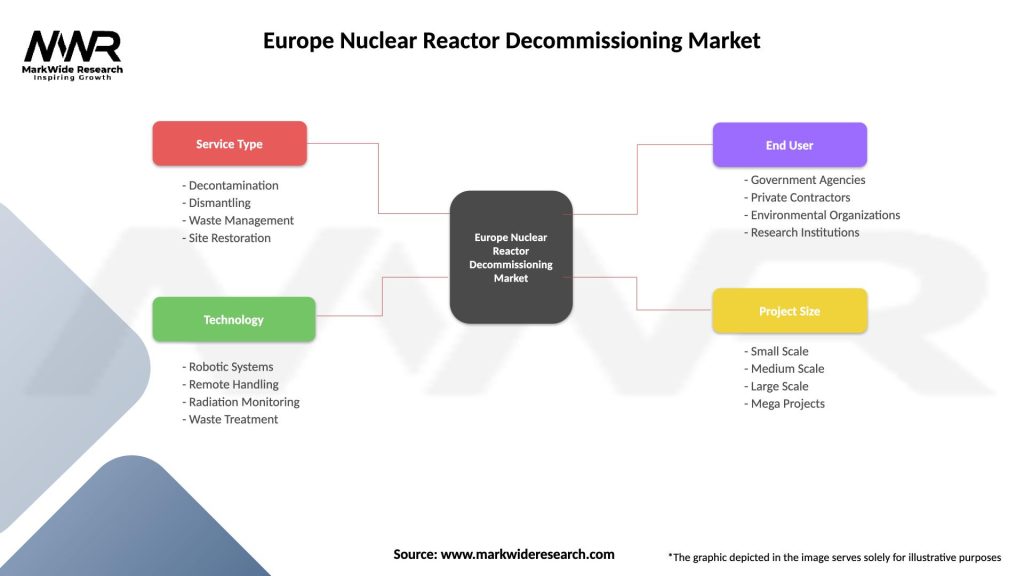
Europe Nuclear Reactor Decommissioning Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Service Type | Decontamination, Dismantling, Waste Management, Site Restoration |
| Technology | Robotic Systems, Remote Handling, Radiation Monitoring, Waste Treatment |
| End User | Government Agencies, Private Contractors, Environmental Organizations, Research Institutions |
| Project Size | Small Scale, Medium Scale, Large Scale, Mega Projects |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Europe Nuclear Reactor Decommissioning Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at