444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2750
The Europe Municipal Solid Waste Management Market represents a critical component of the continent’s environmental sustainability framework, encompassing comprehensive waste collection, treatment, recycling, and disposal services across urban and rural communities. European nations have established themselves as global leaders in waste management innovation, implementing advanced circular economy principles and achieving remarkable recycling rates of approximately 47% for municipal solid waste. The market demonstrates robust growth momentum driven by stringent environmental regulations, increasing urbanization, and growing public awareness regarding sustainable waste management practices.
Market dynamics reflect the region’s commitment to achieving ambitious waste reduction targets set forth by the European Union’s Circular Economy Action Plan. Countries such as Germany, Netherlands, and Sweden lead the continent in waste management efficiency, with some regions achieving waste-to-energy conversion rates exceeding 50% of total municipal solid waste generated. The integration of smart technologies, including IoT-enabled waste collection systems and AI-powered sorting facilities, continues to transform traditional waste management approaches across European municipalities.
Regulatory frameworks across Europe emphasize waste hierarchy principles, prioritizing prevention, reuse, recycling, and recovery over disposal. This comprehensive approach has resulted in significant reductions in landfill dependency, with several European countries achieving landfill diversion rates above 95% for municipal solid waste streams. The market encompasses diverse stakeholders including municipal authorities, private waste management companies, technology providers, and recycling specialists working collaboratively to achieve sustainable waste management objectives.
The Europe Municipal Solid Waste Management Market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of services, technologies, and infrastructure dedicated to the collection, transportation, treatment, recycling, and disposal of household and commercial waste generated within European urban and suburban areas. This market encompasses integrated waste management solutions that prioritize environmental sustainability, resource recovery, and circular economy principles while ensuring public health protection and regulatory compliance across diverse European jurisdictions.
Municipal solid waste management in Europe involves sophisticated waste streams including organic waste, recyclable materials, hazardous household waste, and residual waste requiring specialized handling protocols. The market integrates traditional waste collection services with advanced processing technologies such as mechanical biological treatment, anaerobic digestion, waste-to-energy facilities, and automated sorting systems. European waste management emphasizes extended producer responsibility, encouraging manufacturers to design products with end-of-life considerations and supporting comprehensive recycling infrastructure development.
Market participants include municipal waste management authorities, private waste collection companies, recycling processors, waste-to-energy operators, and technology solution providers. The sector operates within complex regulatory frameworks established by the European Union and individual member states, promoting harmonized waste management standards while accommodating regional variations in waste composition, infrastructure capabilities, and environmental priorities.
Europe’s municipal solid waste management market demonstrates exceptional maturity and innovation leadership, characterized by comprehensive regulatory frameworks, advanced technological integration, and strong commitment to circular economy principles. The market benefits from well-established infrastructure networks, high public participation in waste separation programs, and continuous investment in next-generation waste processing technologies. Key market drivers include stringent EU waste directives, increasing urbanization pressures, and growing consumer awareness regarding environmental sustainability.
Market segmentation reveals diverse opportunities across waste collection services, recycling operations, waste-to-energy generation, and organic waste processing. The sector experiences particularly strong growth in smart waste management solutions, with digital technology adoption rates increasing by approximately 15% annually across European municipalities. Regional variations exist in market development, with Western European countries leading in infrastructure sophistication while Eastern European markets present significant growth opportunities.
Competitive dynamics feature established European waste management companies alongside emerging technology providers and specialized recycling operators. The market emphasizes long-term service contracts, public-private partnerships, and integrated waste management solutions. Future growth prospects remain positive, supported by continued regulatory tightening, infrastructure modernization requirements, and increasing focus on resource recovery and circular economy implementation across European communities.

Strategic market insights reveal several critical trends shaping Europe’s municipal solid waste management landscape:
Regulatory mandates serve as the primary catalyst for Europe’s municipal solid waste management market expansion. The European Union’s Waste Framework Directive establishes ambitious recycling targets, requiring member states to achieve specific waste diversion and material recovery objectives. These regulatory requirements drive substantial investment in waste management infrastructure, technology upgrades, and service enhancement initiatives across European municipalities.
Urbanization trends continue to intensify waste generation pressures in European cities, necessitating sophisticated waste management solutions capable of handling increasing volumes and complexity. Population density increases in metropolitan areas require efficient collection systems, optimized transportation networks, and advanced processing facilities. The growing urban population generates diverse waste streams requiring specialized handling protocols and integrated management approaches.
Environmental consciousness among European consumers drives demand for sustainable waste management practices and transparent recycling processes. Public awareness campaigns promote waste separation, reduction behaviors, and support for environmentally responsible waste management initiatives. This consumer engagement creates favorable conditions for investment in advanced recycling technologies and circular economy implementation.
Technological advancement enables more efficient and cost-effective waste management operations through automation, digitalization, and process optimization. Innovation adoption includes smart collection systems, automated sorting technologies, and data analytics platforms that enhance operational efficiency and service quality while reducing environmental impact.
High capital requirements for waste management infrastructure development present significant barriers for municipalities and private operators seeking to implement advanced waste processing facilities. Investment costs for waste-to-energy plants, automated sorting systems, and comprehensive collection networks require substantial financial commitments that may strain municipal budgets and limit market expansion opportunities.
Regulatory complexity across different European jurisdictions creates operational challenges for waste management companies operating in multiple markets. Compliance requirements vary significantly between member states, necessitating specialized knowledge and adaptive operational approaches that increase administrative costs and complexity.
Public resistance to certain waste management facilities, particularly waste-to-energy plants and large-scale processing centers, can delay project implementation and increase development costs. NIMBY concerns require extensive community engagement and may necessitate alternative site selection or technology modifications.
Economic fluctuations impact recycled material markets, affecting the financial viability of recycling operations and material recovery facilities. Commodity price volatility for recycled materials creates uncertainty in revenue projections and may discourage investment in recycling infrastructure expansion.
Digital transformation initiatives present substantial opportunities for technology providers and waste management operators to develop innovative solutions that enhance operational efficiency and service quality. Smart city integration enables comprehensive waste management optimization through data analytics, predictive maintenance, and automated collection systems that reduce costs and environmental impact.
Circular economy expansion creates new business models focused on material recovery, remanufacturing, and resource optimization. Value chain integration opportunities exist for companies capable of connecting waste generation sources with material recovery and reprocessing operations, creating closed-loop systems that maximize resource utilization.
Eastern European market development offers significant growth potential as these regions modernize waste management infrastructure and align with EU regulatory requirements. Infrastructure investment needs in emerging European markets create opportunities for technology transfer, service provision, and public-private partnership development.
Organic waste processing represents a rapidly expanding market segment driven by separate collection mandates and biogas generation opportunities. Anaerobic digestion facilities and composting operations provide dual benefits of waste treatment and renewable energy generation, supporting both waste management and climate objectives.
Supply chain integration characterizes Europe’s municipal solid waste management market, with increasing emphasis on comprehensive service provision from collection through final processing. Vertical integration strategies enable waste management companies to optimize operations, control quality, and capture value across multiple stages of the waste management process. This integration trend supports improved efficiency and enhanced service reliability.
Technology convergence drives innovation in waste management operations through the integration of IoT devices, artificial intelligence, and advanced analytics. Operational optimization benefits from real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and route optimization technologies that reduce costs and improve service quality. According to MarkWide Research analysis, digital technology adoption in European waste management operations has accelerated significantly, with smart system implementation growing at approximately 12% annually.
Competitive consolidation continues as larger waste management companies acquire specialized operators and technology providers to expand service capabilities and geographic coverage. Market concentration enables economies of scale while maintaining regional service expertise and customer relationships. This consolidation trend supports infrastructure investment and technology advancement across the sector.
Sustainability integration influences all aspects of waste management operations, from collection vehicle electrification to renewable energy generation at processing facilities. Carbon footprint reduction initiatives drive operational improvements and technology adoption that support both environmental objectives and cost optimization goals.
Comprehensive market analysis employs multiple research methodologies to ensure accurate and reliable insights into Europe’s municipal solid waste management market. Primary research includes extensive interviews with industry executives, municipal waste management officials, technology providers, and regulatory authorities across major European markets. These stakeholder consultations provide firsthand insights into market trends, challenges, and growth opportunities.
Secondary research incorporates analysis of government publications, industry reports, regulatory documents, and company financial statements to establish market baselines and validate primary research findings. Data triangulation ensures accuracy and reliability through cross-referencing multiple information sources and analytical approaches.
Quantitative analysis utilizes statistical modeling and trend analysis to project market growth patterns and identify key performance indicators. Market segmentation analysis examines waste management services, technology categories, and regional variations to provide detailed market insights and growth projections.
Qualitative assessment evaluates market dynamics, competitive positioning, and strategic implications through expert analysis and industry benchmarking. This comprehensive approach ensures thorough understanding of market complexities and future development prospects across European waste management markets.
Western Europe maintains market leadership in municipal solid waste management sophistication, with countries such as Germany, Netherlands, and Switzerland achieving exceptional recycling rates and comprehensive waste management infrastructure. These markets demonstrate recycling efficiency rates exceeding 65% for municipal solid waste streams, supported by well-established collection systems, advanced processing facilities, and strong public participation in waste separation programs.
Nordic countries including Sweden, Norway, and Denmark lead in waste-to-energy implementation, with some regions achieving energy recovery rates above 50% of total municipal solid waste. These markets emphasize integrated waste management approaches that combine high recycling rates with efficient energy recovery from residual waste streams.
Central Europe presents dynamic growth opportunities as countries such as Poland, Czech Republic, and Hungary modernize waste management infrastructure to meet EU regulatory requirements. These markets experience rapid development in recycling capabilities and waste treatment facilities, supported by EU funding and private investment initiatives.
Southern Europe including Italy, Spain, and France demonstrates varied development levels, with urban areas achieving advanced waste management capabilities while rural regions require infrastructure enhancement. These markets benefit from increasing investment in organic waste processing and circular economy initiatives.
Eastern Europe represents the fastest-growing regional segment, with countries implementing comprehensive waste management system upgrades and regulatory alignment with EU standards. Infrastructure investment growth in these markets creates substantial opportunities for technology providers and service operators.
Market leadership in Europe’s municipal solid waste management sector features established multinational companies alongside specialized regional operators and emerging technology providers. The competitive environment emphasizes comprehensive service provision, technological innovation, and long-term customer relationships.
Competitive strategies emphasize technological differentiation, geographic expansion, and vertical integration to capture value across waste management value chains. Innovation focus includes digital transformation, automation implementation, and sustainable processing technology development.
By Service Type:
By Technology:
By End User:
Collection Services represent the foundational segment of Europe’s municipal solid waste management market, encompassing traditional collection operations alongside innovative smart collection systems. Service evolution includes frequency optimization, route efficiency improvements, and specialized collection for different waste streams. The segment benefits from increasing automation and digital integration that enhances operational efficiency and customer service quality.
Recycling Operations demonstrate exceptional growth driven by EU regulatory requirements and circular economy initiatives. Material recovery focuses on high-value recyclables including plastics, metals, and paper products, with increasing emphasis on quality improvement and contamination reduction. Advanced sorting technologies enable higher recovery rates and better material quality for secondary markets.
Waste-to-Energy serves as a critical component of integrated waste management strategies, providing renewable energy generation while reducing landfill dependency. Technology advancement includes improved emission control, higher energy efficiency, and enhanced material recovery from ash residues. This segment supports both waste management and renewable energy objectives across European markets.
Organic Waste Processing experiences rapid expansion driven by separate collection mandates and biogas generation opportunities. Processing technologies include anaerobic digestion for biogas production and composting for soil amendment applications. This segment provides dual benefits of waste treatment and renewable resource generation.
Smart Technologies increasingly integrate across all waste management categories, providing operational optimization, cost reduction, and service enhancement benefits. Digital solutions include predictive analytics, automated monitoring, and customer engagement platforms that transform traditional waste management approaches.
Municipal Authorities benefit from comprehensive waste management solutions that ensure regulatory compliance, cost optimization, and environmental sustainability. Service integration enables municipalities to achieve waste diversion targets while managing budget constraints and public service expectations. Long-term partnerships with waste management providers offer operational expertise and infrastructure investment support.
Waste Management Companies gain opportunities for revenue diversification through integrated service provision and value-added solutions. Market expansion potential exists through geographic growth, technology adoption, and specialized service development. Regulatory support for waste management infrastructure creates stable demand and investment opportunities.
Technology Providers access growing markets for innovative waste management solutions including smart collection systems, automated processing equipment, and digital platforms. Innovation demand from municipalities and operators creates opportunities for technology commercialization and market penetration across European markets.
Environmental Organizations benefit from improved waste management practices that support circular economy objectives and environmental protection goals. Collaboration opportunities exist for promoting best practices, supporting policy development, and advancing sustainable waste management initiatives.
Citizens and Communities receive enhanced waste management services, improved environmental quality, and opportunities for active participation in sustainability initiatives. Service improvements include convenient collection systems, transparent recycling processes, and educational programs that support waste reduction behaviors.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Digitalization acceleration transforms waste management operations through IoT integration, data analytics, and automated systems. Smart waste management solutions enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and operational optimization that reduce costs and improve service quality. This trend supports the development of comprehensive digital platforms that integrate collection, processing, and customer service functions.
Circular economy implementation drives fundamental changes in waste management approaches, emphasizing material recovery, reuse, and recycling over disposal. Value chain integration connects waste generators with material processors and end users, creating closed-loop systems that maximize resource utilization and minimize environmental impact.
Energy recovery expansion reflects growing recognition of waste-to-energy as a renewable energy source and waste management solution. Technology advancement includes improved efficiency, enhanced emission control, and integration with district heating systems. This trend supports both waste management objectives and renewable energy targets across European markets.
Organic waste separation becomes mandatory across European municipalities, driving investment in specialized collection systems and processing facilities. Biogas generation from organic waste provides renewable energy while reducing methane emissions from landfills. This trend creates opportunities for anaerobic digestion facility development and biogas utilization projects.
Extended producer responsibility expansion places greater accountability on manufacturers for product lifecycle management and waste generation. Packaging optimization and design for recyclability become critical considerations, influencing waste stream composition and recycling system requirements.
Regulatory advancement continues with the implementation of updated EU waste directives and national legislation that strengthen recycling targets and landfill restrictions. Policy development includes extended producer responsibility expansion, plastic waste reduction initiatives, and circular economy action plan implementation across member states.
Technology innovation accelerates with the deployment of advanced sorting systems, AI-powered waste identification, and automated processing equipment. Digital platform development enables comprehensive waste management optimization through data integration and predictive analytics capabilities.
Infrastructure investment increases across European markets, particularly in Eastern European countries modernizing waste management systems. Public-private partnerships facilitate large-scale facility development and technology deployment while sharing investment risks and operational expertise.
Market consolidation continues as major waste management companies acquire specialized operators and technology providers to expand service capabilities and geographic coverage. Strategic partnerships between waste management companies and technology providers accelerate innovation adoption and market development.
Sustainability initiatives expand across the waste management value chain, including electric collection vehicle deployment, renewable energy integration, and carbon footprint reduction programs. These developments support both environmental objectives and operational efficiency improvements.
Investment prioritization should focus on digital transformation initiatives that enhance operational efficiency and customer service quality. Technology adoption in smart collection systems, automated processing, and data analytics platforms offers significant competitive advantages and cost optimization opportunities. Companies should evaluate comprehensive digital strategies that integrate multiple waste management functions.
Geographic expansion strategies should prioritize Eastern European markets where infrastructure modernization creates substantial growth opportunities. Market entry approaches should consider public-private partnerships and technology transfer arrangements that leverage local expertise while providing advanced waste management capabilities.
Service diversification recommendations include organic waste processing, specialized recycling services, and circular economy solutions that capture additional value from waste streams. Vertical integration opportunities exist for companies capable of connecting waste collection with material recovery and reprocessing operations.
Regulatory compliance preparation should anticipate continued tightening of waste management requirements and recycling targets. Proactive adaptation to regulatory changes provides competitive advantages and reduces compliance risks. Companies should monitor policy developments and invest in capabilities that exceed current requirements.
Partnership development with technology providers, municipal authorities, and other stakeholders enhances service capabilities and market access. Collaborative approaches enable resource sharing, risk mitigation, and accelerated innovation adoption across waste management operations.
Market growth prospects remain exceptionally positive for Europe’s municipal solid waste management sector, driven by continued regulatory tightening, infrastructure modernization requirements, and increasing focus on circular economy implementation. MWR projections indicate sustained expansion across all market segments, with particularly strong growth in digital technologies and organic waste processing capabilities.
Technology integration will accelerate significantly over the forecast period, with smart system adoption rates projected to increase by approximately 18% annually across European waste management operations. Automation advancement includes AI-powered sorting systems, autonomous collection vehicles, and predictive analytics platforms that transform operational efficiency and service quality.
Regulatory evolution will continue driving market development through enhanced recycling targets, landfill restrictions, and extended producer responsibility expansion. Policy harmonization across European markets will facilitate technology standardization and cross-border operational efficiency while maintaining regional flexibility for local requirements.
Investment opportunities will expand particularly in Eastern European markets where infrastructure development needs create substantial growth potential. Public-private partnerships will facilitate large-scale facility development while sharing investment risks and operational expertise between municipal authorities and private operators.
Sustainability focus will intensify across all waste management operations, with increasing emphasis on carbon footprint reduction, renewable energy generation, and circular economy implementation. Innovation priorities will include advanced material recovery technologies, biogas optimization, and comprehensive resource utilization systems that maximize environmental and economic benefits.
Europe’s municipal solid waste management market represents a dynamic and rapidly evolving sector characterized by strong regulatory support, technological innovation, and comprehensive sustainability commitments. The market demonstrates exceptional maturity in Western European countries while presenting substantial growth opportunities in Eastern European markets undergoing infrastructure modernization. Key success factors include regulatory compliance excellence, technology adoption leadership, and integrated service provision that maximizes value across waste management value chains.
Future market development will be driven by continued digitalization, circular economy expansion, and energy recovery optimization. The sector benefits from stable regulatory frameworks, increasing public engagement, and growing recognition of waste management as a critical component of sustainable urban development. Investment opportunities remain attractive across multiple market segments, particularly in smart technologies, organic waste processing, and comprehensive service integration.
Strategic positioning for market success requires comprehensive understanding of regulatory requirements, technology capabilities, and regional market characteristics. Companies capable of providing integrated solutions that combine operational excellence with environmental sustainability will capture the greatest market opportunities. The European municipal solid waste management market continues to set global standards for sustainable waste management practices while creating substantial value for stakeholders across the waste management ecosystem.
What is Municipal Solid Waste Management?
Municipal Solid Waste Management refers to the processes involved in the collection, treatment, and disposal of solid waste generated in urban areas. This includes various activities such as recycling, composting, and landfilling aimed at minimizing environmental impact.
What are the key players in the Europe Municipal Solid Waste Management Market?
Key players in the Europe Municipal Solid Waste Management Market include Veolia Environnement, SUEZ, and Biffa, among others. These companies provide a range of services from waste collection to recycling and energy recovery.
What are the main drivers of the Europe Municipal Solid Waste Management Market?
The main drivers of the Europe Municipal Solid Waste Management Market include increasing urbanization, stringent environmental regulations, and growing public awareness about waste management. These factors contribute to the demand for efficient waste management solutions.
What challenges does the Europe Municipal Solid Waste Management Market face?
Challenges in the Europe Municipal Solid Waste Management Market include inadequate infrastructure, high operational costs, and public resistance to waste management initiatives. These issues can hinder the effective implementation of waste management strategies.
What opportunities exist in the Europe Municipal Solid Waste Management Market?
Opportunities in the Europe Municipal Solid Waste Management Market include advancements in recycling technologies, the growth of the circular economy, and increased investment in waste-to-energy projects. These trends can enhance sustainability and resource recovery.
What trends are shaping the Europe Municipal Solid Waste Management Market?
Trends shaping the Europe Municipal Solid Waste Management Market include the rise of smart waste management systems, increased focus on sustainability, and the adoption of innovative waste processing technologies. These trends aim to improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
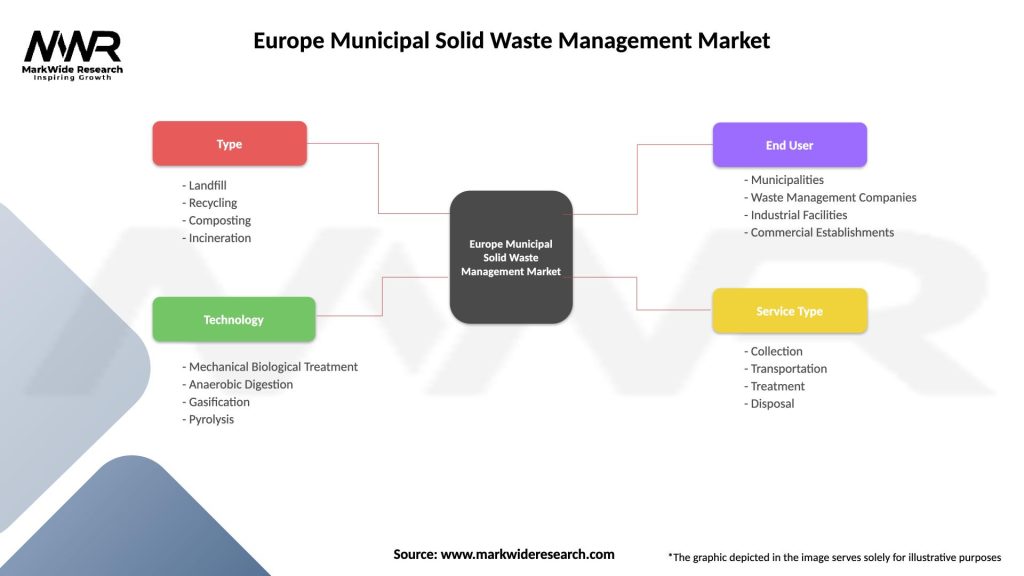
Europe Municipal Solid Waste Management Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Landfill, Recycling, Composting, Incineration |
| Technology | Mechanical Biological Treatment, Anaerobic Digestion, Gasification, Pyrolysis |
| End User | Municipalities, Waste Management Companies, Industrial Facilities, Commercial Establishments |
| Service Type | Collection, Transportation, Treatment, Disposal |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Europe Municipal Solid Waste Management Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at