444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2750
The Europe E-Waste Management Market represents a critical component of the continent’s circular economy strategy, addressing the growing challenge of electronic waste disposal and recycling. Electronic waste, encompassing discarded computers, smartphones, televisions, and other electronic devices, has emerged as one of the fastest-growing waste streams globally. European nations are leading the charge in implementing comprehensive e-waste management solutions through advanced recycling technologies, stringent regulatory frameworks, and innovative collection systems.
Market dynamics indicate robust growth driven by increasing consumer electronics consumption, shorter product lifecycles, and heightened environmental awareness. The region’s commitment to achieving carbon neutrality by 2050 has accelerated investments in sustainable waste management infrastructure. Germany, France, and the United Kingdom dominate the market landscape, collectively accounting for approximately 55% of regional processing capacity. The integration of artificial intelligence and automation in sorting facilities has improved material recovery rates by 35% over the past five years.
Regulatory compliance remains a primary market driver, with the European Union’s Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive mandating specific collection and recycling targets. The directive requires member states to achieve 65% collection efficiency for electronic waste, creating substantial opportunities for specialized management companies. Extended Producer Responsibility programs have shifted accountability upstream, encouraging manufacturers to design more sustainable products while funding collection and recycling infrastructure.
The Europe E-Waste Management Market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of services, technologies, and infrastructure dedicated to the collection, processing, recycling, and responsible disposal of electronic waste across European nations. This market encompasses various stakeholders including specialized recycling companies, technology providers, logistics operators, and regulatory bodies working collectively to address the environmental and economic challenges posed by discarded electronic equipment.
E-waste management involves multiple stages from initial collection through final material recovery or safe disposal. The process includes collection and transportation of discarded electronics, dismantling and sorting of components, material extraction and purification, and responsible disposal of hazardous substances. Advanced facilities employ sophisticated technologies including automated disassembly systems, precious metal recovery processes, and environmentally controlled treatment of toxic materials such as mercury, lead, and cadmium.
Circular economy principles form the foundation of modern e-waste management, emphasizing resource recovery and material reuse. The market facilitates the extraction of valuable materials including gold, silver, copper, and rare earth elements, which can be reintegrated into manufacturing processes. This approach reduces dependency on virgin material extraction while minimizing environmental impact through proper handling of hazardous components.
Europe’s e-waste management sector has evolved into a sophisticated industry characterized by technological innovation, regulatory compliance, and environmental stewardship. The market demonstrates strong growth momentum driven by increasing electronic device penetration, regulatory mandates, and corporate sustainability initiatives. Collection rates have improved significantly, with several European countries achieving collection efficiency rates exceeding 70%, surpassing EU minimum requirements.
Key market segments include large household appliances, information technology equipment, consumer electronics, and lighting equipment. The IT equipment segment represents the fastest-growing category, driven by rapid technological advancement and shorter replacement cycles. Smartphone recycling has emerged as a particularly dynamic subsector, with specialized facilities processing millions of devices annually to recover precious metals and rare earth elements.
Technological advancement continues to reshape the industry landscape, with artificial intelligence, robotics, and advanced sorting technologies improving processing efficiency and material recovery rates. Automated disassembly systems have increased processing capacity while reducing labor costs and improving worker safety. The integration of blockchain technology for supply chain transparency and traceability is gaining traction among leading operators.
Market consolidation trends are evident as larger players acquire specialized companies to expand geographic coverage and technological capabilities. Strategic partnerships between recyclers, manufacturers, and technology providers are becoming increasingly common, creating integrated value chains that optimize material flow and recovery rates.

Critical market insights reveal the transformative nature of Europe’s e-waste management landscape and its strategic importance to the circular economy transition:
Multiple interconnected factors drive the expansion and evolution of Europe’s e-waste management market, creating a robust foundation for sustained growth and innovation.
Regulatory mandates serve as the primary catalyst for market development. The EU’s WEEE Directive establishes mandatory collection and recycling targets, compelling member states to develop comprehensive management infrastructure. Extended Producer Responsibility regulations transfer financial responsibility to manufacturers, creating dedicated funding streams for collection and processing operations. Recent updates to the directive have expanded coverage to include additional product categories and increased recycling targets.
Environmental consciousness among consumers and businesses drives demand for responsible disposal solutions. Corporate sustainability initiatives increasingly include e-waste management as a key performance indicator, with companies seeking certified recycling partners to meet environmental, social, and governance (ESG) objectives. The growing awareness of environmental impact associated with improper e-waste disposal motivates participation in formal collection programs.
Technological obsolescence accelerates e-waste generation as consumers replace devices more frequently. The proliferation of Internet of Things devices, smartphones, and connected appliances creates continuous waste streams requiring specialized processing capabilities. 5G technology deployment is expected to trigger significant replacement cycles for telecommunications equipment and consumer devices.
Resource scarcity concerns highlight the economic value of material recovery from electronic waste. Critical raw material dependencies motivate European policymakers to promote domestic recycling capabilities, reducing reliance on imports from geopolitically sensitive regions. The concentration of valuable materials in electronic devices makes recycling economically attractive compared to primary extraction.
Several challenges constrain the optimal development and efficiency of Europe’s e-waste management market, requiring strategic solutions and continued innovation.
High capital requirements for establishing advanced recycling facilities create barriers to entry for new market participants. Specialized equipment for safe dismantling, material separation, and hazardous substance treatment requires significant upfront investment. The need for certified facilities meeting strict environmental standards adds complexity and cost to facility development projects.
Illegal waste exports undermine formal recycling systems by diverting valuable material streams to unregulated processors. Enforcement challenges at borders and ports allow significant quantities of e-waste to leave Europe for processing in countries with less stringent environmental standards. This practice reduces material availability for European recyclers while potentially causing environmental damage in destination countries.
Collection inefficiencies limit the volume of material available for processing. Consumer behavior patterns, including hoarding of old devices and improper disposal through general waste streams, reduce collection rates below optimal levels. Rural area coverage remains challenging due to lower population density and higher collection costs per unit.
Technological complexity of modern electronic devices complicates recycling processes. Miniaturization trends make component separation more difficult, while the use of adhesives and integrated components reduces recyclability. Hazardous substance content requires specialized handling procedures and certified disposal methods, increasing processing costs and complexity.
Significant opportunities exist within Europe’s e-waste management market, driven by technological advancement, regulatory evolution, and changing consumer behaviors.
Artificial intelligence integration presents opportunities to revolutionize sorting and processing operations. Machine learning algorithms can optimize material separation processes, improve quality control, and predict maintenance requirements for processing equipment. Computer vision systems enable automated identification and sorting of complex electronic components, increasing processing speed and accuracy.
Urban mining expansion offers substantial potential for material recovery from accumulated e-waste stocks. Historical waste deposits in landfills and storage facilities contain valuable materials that can be recovered using advanced extraction technologies. The development of mobile processing units could enable cost-effective recovery from distributed waste sources.
Circular economy integration creates opportunities for closed-loop material flows between recyclers and manufacturers. Design for recyclability initiatives enable more efficient processing and higher material recovery rates. Remanufacturing programs for components and subassemblies can extend product lifecycles while creating additional revenue streams for recyclers.
Cross-border collaboration opportunities exist for optimizing processing capacity utilization across European markets. Specialized facility networks can process specific material types more efficiently than individual national systems. Technology transfer programs can accelerate the adoption of best practices across different European markets.
Complex market dynamics shape the evolution of Europe’s e-waste management sector, creating both challenges and opportunities for industry participants.
Supply and demand imbalances characterize different market segments and geographic regions. Processing capacity varies significantly across European countries, with some markets experiencing overcapacity while others face processing bottlenecks. Material quality variations affect pricing and processing efficiency, with higher-grade electronic waste commanding premium prices from recyclers.
Competitive dynamics are intensifying as the market matures and consolidation accelerates. Large integrated players leverage economies of scale and technological capabilities to compete effectively, while specialized niche operators focus on specific material types or processing technologies. Vertical integration strategies enable companies to control material flows and capture value across multiple stages of the recycling process.
Technology adoption cycles influence market dynamics as new processing technologies emerge and mature. Early adopters of advanced technologies gain competitive advantages through improved efficiency and material recovery rates. Technology standardization processes affect equipment compatibility and interoperability across different processing facilities.
Regulatory evolution continues to reshape market dynamics through updated requirements and expanded coverage. Policy harmonization across European markets reduces compliance complexity while creating larger addressable markets for service providers. Enforcement intensity variations affect competitive dynamics between formal and informal recycling channels.
Comprehensive research methodology underpins the analysis of Europe’s e-waste management market, incorporating multiple data sources and analytical approaches to ensure accuracy and reliability.
Primary research activities include extensive interviews with industry executives, regulatory officials, and technology providers across major European markets. Structured surveys capture quantitative data on processing capacities, material flows, and operational metrics from leading market participants. Site visits to advanced recycling facilities provide insights into technological capabilities and operational best practices.
Secondary research sources encompass regulatory databases, industry publications, academic research, and corporate financial reports. Government statistics on e-waste generation and collection rates provide baseline data for market sizing and trend analysis. Technology patent databases reveal innovation trends and competitive positioning among equipment manufacturers.
Market modeling techniques combine historical data analysis with forward-looking projections based on identified drivers and constraints. Scenario analysis evaluates potential market outcomes under different regulatory and economic conditions. Cross-validation procedures ensure consistency between different data sources and analytical approaches.
Expert validation processes involve review of findings by industry specialists and academic researchers to ensure accuracy and completeness. Peer review mechanisms provide additional quality assurance for key conclusions and market projections.
Regional market dynamics across Europe reveal significant variations in e-waste management capabilities, regulatory implementation, and market maturity levels.
Western Europe dominates the regional market, accounting for approximately 68% of total processing capacity. Germany leads with the most advanced infrastructure and highest collection rates, supported by well-established producer responsibility organizations and consumer awareness programs. France demonstrates strong growth in specialized recycling technologies, particularly for rare earth element recovery from electronic components.
Nordic countries showcase innovative approaches to e-waste management, with Sweden and Denmark achieving collection rates exceeding 75% of generated waste. These markets emphasize technology development and sustainable processing methods, serving as testing grounds for next-generation recycling technologies. Norway’s comprehensive tracking systems provide models for supply chain transparency and material flow optimization.
Central and Eastern Europe represent emerging markets with significant growth potential. Poland has invested heavily in modern processing infrastructure, while Czech Republic focuses on cross-border processing services for neighboring countries. These markets benefit from lower operational costs while gradually implementing advanced technologies and regulatory frameworks.
Southern Europe faces unique challenges related to informal recycling channels and enforcement gaps. Italy has made substantial progress in formalizing collection systems, while Spain focuses on rural area coverage expansion. According to MarkWide Research analysis, these markets show strong potential for growth as regulatory enforcement intensifies and infrastructure investments accelerate.
The competitive landscape of Europe’s e-waste management market features a diverse mix of specialized recyclers, integrated waste management companies, and technology providers.
Market consolidation trends are evident as larger players acquire specialized companies to expand geographic coverage and technological capabilities. Strategic partnerships between recyclers, manufacturers, and technology providers create integrated value chains optimizing material flows and recovery rates. Innovation investments focus on automation, artificial intelligence, and advanced material separation technologies.
Market segmentation reveals distinct characteristics and growth patterns across different product categories, processing technologies, and end-use applications.
By Product Category:
By Processing Technology:
Detailed category analysis reveals specific market dynamics, processing requirements, and value recovery opportunities across different e-waste segments.
IT Equipment Category represents the highest-value segment due to precious metals content and rapid replacement cycles. Server and data center equipment contains significant quantities of gold, silver, and palladium, making specialized processing highly profitable. Smartphone recycling has emerged as a particularly dynamic subsector, with processing facilities achieving material recovery rates exceeding 90% for key components.
Large Appliance Category focuses primarily on steel and aluminum recovery, with specialized attention to refrigerant management and foam treatment. Refrigerator processing requires certified facilities for safe refrigerant recovery and polyurethane foam treatment. Washing machine recycling emphasizes motor recovery and plastic separation for material reuse.
Consumer Electronics Category presents complex processing challenges due to diverse materials and miniaturized components. Television recycling requires specialized handling of display technologies, with different approaches for LCD, LED, and older CRT models. Audio equipment processing focuses on speaker magnet recovery and precious metals extraction from circuit boards.
Lighting Equipment Category emphasizes safe mercury recovery from fluorescent lamps and rare earth element extraction from LED components. Compact fluorescent lamp processing requires specialized mercury capture systems and glass recycling capabilities. LED fixture recycling focuses on driver electronics and aluminum heat sink recovery.
Multiple stakeholder groups derive significant benefits from Europe’s well-developed e-waste management ecosystem, creating value across the entire supply chain.
Environmental Benefits:
Economic Benefits:
Regulatory Benefits:
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Several transformative trends are reshaping Europe’s e-waste management market, driving innovation and creating new business opportunities.
Automation and Robotics Integration represents a major trend transforming processing operations. Robotic disassembly systems improve worker safety while increasing processing speed and precision. Automated sorting technologies using computer vision and artificial intelligence achieve higher material purity levels and reduce contamination rates. MWR data indicates that facilities implementing advanced automation report productivity improvements of 45% compared to manual operations.
Blockchain Technology Adoption enhances supply chain transparency and material traceability. Digital certificates provide verification of proper processing and material recovery, supporting corporate sustainability reporting requirements. Smart contracts automate payment processes and ensure compliance with recycling standards throughout the supply chain.
Circular Economy Integration drives closer collaboration between recyclers and manufacturers. Design for recyclability initiatives optimize product design for efficient end-of-life processing. Take-back programs create direct relationships between producers and recyclers, ensuring proper handling of branded products.
Rare Earth Element Recovery gains importance as supply chain security concerns intensify. Specialized processing facilities focus on extracting critical materials from electronic components, reducing European dependence on imports. Advanced separation technologies improve recovery rates and material purity for reuse in manufacturing applications.
Recent industry developments highlight the dynamic nature of Europe’s e-waste management sector and the continuous evolution of technologies and business models.
Technology Advancement Initiatives include major investments in next-generation processing equipment and artificial intelligence applications. European Union funding programs support research and development of innovative recycling technologies, with particular emphasis on critical material recovery and hazardous substance treatment. Public-private partnerships accelerate technology commercialization and deployment across multiple markets.
Regulatory Updates continue to expand coverage and increase requirements for e-waste management. Extended Producer Responsibility programs are being enhanced to include additional product categories and stricter performance targets. Cross-border enforcement initiatives aim to reduce illegal waste exports and improve material retention within European processing systems.
Industry Consolidation Activities include strategic acquisitions and partnerships among major market participants. Vertical integration strategies enable companies to control material flows from collection through final processing. Technology licensing agreements facilitate rapid deployment of advanced processing methods across different geographic markets.
Sustainability Certification Programs establish standards for responsible e-waste processing and material recovery. Third-party verification systems provide assurance of environmental compliance and processing quality. Corporate sustainability partnerships create long-term relationships between recyclers and major electronics manufacturers.
Strategic recommendations for industry participants focus on leveraging emerging opportunities while addressing key market challenges.
Technology Investment Priorities should emphasize automation and artificial intelligence applications that improve processing efficiency and material recovery rates. Robotic disassembly systems offer attractive returns through labor cost reduction and improved worker safety. Advanced sorting technologies enable processing of increasingly complex electronic devices while maintaining high material purity standards.
Geographic Expansion Strategies should target emerging European markets with developing infrastructure and growing e-waste generation. Central and Eastern European markets offer attractive growth opportunities with lower operational costs and increasing regulatory enforcement. Cross-border processing services can optimize capacity utilization while serving multiple national markets.
Partnership Development with manufacturers and technology providers creates competitive advantages through integrated value chains. Circular economy collaborations ensure access to material streams while supporting manufacturer sustainability objectives. Technology partnerships accelerate innovation adoption and reduce development costs for advanced processing methods.
Regulatory Compliance Excellence requires proactive monitoring of evolving requirements and investment in certified processing capabilities. Compliance management systems ensure adherence to complex regulatory frameworks while minimizing operational disruptions. Stakeholder engagement with regulatory authorities supports policy development and implementation processes.
The future trajectory of Europe’s e-waste management market appears highly promising, driven by continued technological advancement, regulatory evolution, and growing environmental consciousness.
Market expansion is expected to continue at a robust pace, with collection rates projected to reach 80% of generated e-waste by 2030 across major European markets. Processing capacity investments will focus on advanced technologies capable of handling increasingly complex electronic devices while maximizing material recovery rates. Geographic coverage expansion will address rural areas and emerging markets with developing infrastructure.
Technology evolution will emphasize artificial intelligence, robotics, and biotechnology applications for improved processing efficiency and environmental performance. Automated processing systems will become standard across major facilities, reducing labor requirements while improving safety and productivity. Advanced material separation technologies will enable recovery of critical materials currently lost in conventional processing methods.
Regulatory development will likely include expanded product coverage, increased recycling targets, and enhanced enforcement mechanisms. Circular economy policies will drive closer integration between recyclers and manufacturers, creating closed-loop material flows. International cooperation initiatives will address cross-border waste movements and technology transfer opportunities.
Market structure evolution will continue toward consolidation and vertical integration, with larger players acquiring specialized capabilities and geographic coverage. MarkWide Research projects that technology-focused companies will command premium valuations due to their competitive advantages in processing efficiency and material recovery rates. Innovation ecosystems will emerge around major processing centers, fostering collaboration between recyclers, technology providers, and research institutions.
Europe’s e-waste management market represents a critical component of the continent’s transition toward a circular economy, combining environmental stewardship with economic opportunity. The market has evolved from basic waste disposal to sophisticated material recovery operations that extract valuable resources while protecting environmental and human health. Regulatory leadership through comprehensive frameworks like the WEEE Directive has established Europe as a global benchmark for responsible e-waste management practices.
Technological innovation continues to drive market evolution, with artificial intelligence, robotics, and advanced processing methods improving efficiency and material recovery rates. The integration of these technologies enables processing of increasingly complex electronic devices while maintaining high environmental standards. Market participants who invest in advanced technologies and develop integrated value chains are positioned to capture the greatest value from growing e-waste streams.
Future success in this market will depend on continued innovation, regulatory compliance excellence, and strategic partnerships across the value chain. The growing importance of critical material recovery and circular economy principles creates substantial opportunities for companies that can adapt to evolving market requirements. Europe’s e-waste management market will continue serving as a model for sustainable waste management practices while generating significant economic and environmental benefits for all stakeholders involved.
What is E-Waste Management?
E-Waste Management refers to the processes involved in the collection, recycling, and disposal of electronic waste, which includes discarded electronic devices and components. This practice is essential for reducing environmental impact and recovering valuable materials from obsolete electronics.
What are the key players in the Europe E-Waste Management Market?
Key players in the Europe E-Waste Management Market include Veolia, SUEZ, and Electronic Recyclers International. These companies are involved in various aspects of e-waste management, including recycling, recovery of precious metals, and compliance with environmental regulations, among others.
What are the main drivers of the Europe E-Waste Management Market?
The main drivers of the Europe E-Waste Management Market include increasing electronic waste generation, stringent regulations on e-waste disposal, and growing awareness of environmental sustainability. Additionally, the demand for recovered materials from e-waste is rising, further fueling market growth.
What challenges does the Europe E-Waste Management Market face?
The Europe E-Waste Management Market faces challenges such as the high costs associated with recycling technologies and the complexity of e-waste materials. Moreover, illegal dumping and lack of consumer awareness about proper disposal methods hinder effective e-waste management.
What opportunities exist in the Europe E-Waste Management Market?
Opportunities in the Europe E-Waste Management Market include advancements in recycling technologies and the potential for developing new business models focused on circular economy principles. Additionally, increasing government initiatives to promote e-waste recycling present significant growth prospects.
What trends are shaping the Europe E-Waste Management Market?
Trends shaping the Europe E-Waste Management Market include the rise of eco-friendly recycling practices and the integration of digital technologies for tracking e-waste. Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on sustainable product design to minimize e-waste generation at the source.
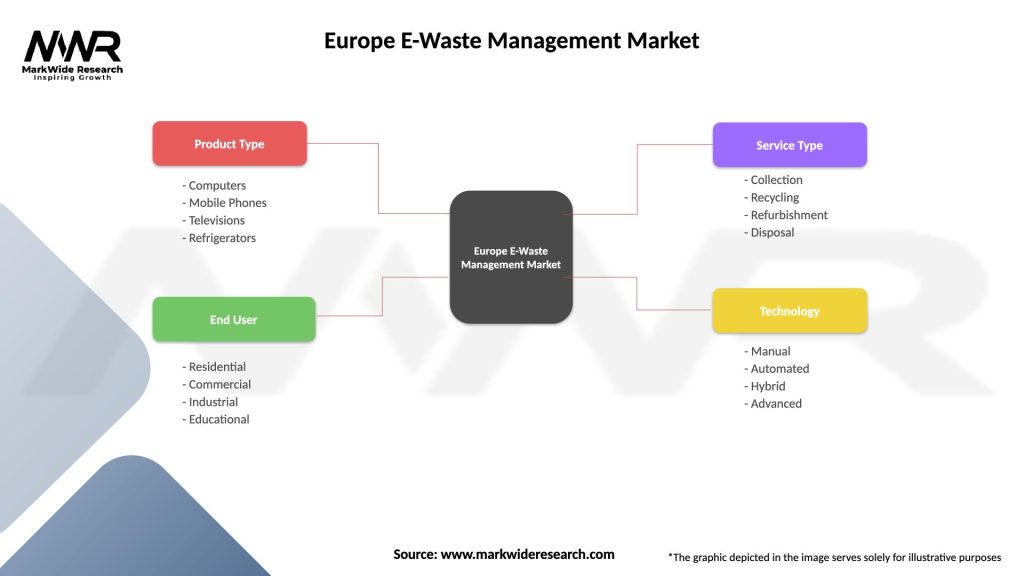
Europe E-Waste Management Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Computers, Mobile Phones, Televisions, Refrigerators |
| End User | Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Educational |
| Service Type | Collection, Recycling, Refurbishment, Disposal |
| Technology | Manual, Automated, Hybrid, Advanced |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Europe E-Waste Management Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at