444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2750
Market Overview
Biobanks play a pivotal role in medical research, offering a vast collection of biospecimens that enable scientists to investigate diseases, develop personalized treatments, and advance precision medicine. The Europe biobanks market is witnessing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for high-quality biological samples, advancements in biobanking technologies, and rising investments in healthcare research and development.
Meaning
A biobank refers to a facility that collects, stores, and manages biological samples, such as blood, tissues, cells, and DNA, along with associated clinical and demographic data. These valuable resources are stored in controlled environments to maintain their integrity and viability for future research and clinical applications.
Executive Summary
The Europe biobanks market is projected to experience substantial growth over the forecast period. This can be attributed to factors such as the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, growing investments in precision medicine, and the need for personalized therapies. The market is characterized by the presence of both public and private biobanks, each contributing to the diverse landscape of biospecimen repositories.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Dynamics
The Europe biobanks market is driven by a dynamic interplay of factors such as technological advancements, regulatory frameworks, collaborations, and evolving research priorities. The market is witnessing a shift toward more comprehensive biobanking solutions that incorporate advanced sample processing, long-term storage, and efficient data management systems. Additionally, the increasing adoption of automation and robotics in biobanks enhances operational efficiency and minimizes sample degradation risks.
Regional Analysis
Europe showcases a strong presence in the global biobanks market, primarily due to well-established healthcare infrastructure, advanced research capabilities, and supportive government policies. The region is home to several leading biobanks, known for their extensive collections of biospecimens and robust data repositories. Key European countries driving market growth include the United Kingdom, Germany, France, and Sweden.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Europe Biobanks Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.

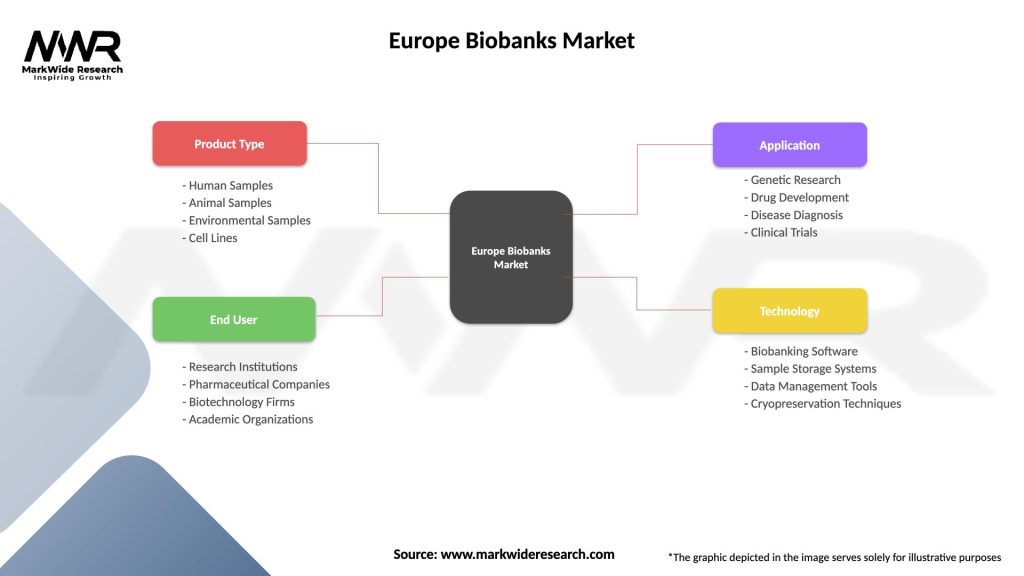
Segmentation
The Europe biobanks market can be segmented based on the type of biobank, sample type, application, and end-user. Types of biobanks include population-based biobanks, disease-oriented biobanks, and academic research biobanks. Sample types encompass blood, tissues, cells, DNA/RNA, and others. Applications of biobanking range from genomics and personalized medicine to drug discovery and epidemiological studies. End-users include research institutions, hospitals, pharmaceutical companies, and contract research organizations (CROs).
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the critical role of biobanks in understanding the virus, developing diagnostic tests, and facilitating vaccine research. Biobanks played a crucial part in collecting and storing samples for epidemiological studies and supporting clinical trials. The pandemic has accelerated the adoption of digital solutions in biobanking operations, such as remote consent and virtual sample collection, to ensure continuity during lockdowns and travel restrictions.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The Europe biobanks market is poised for steady growth in the coming years, driven by advancements in biobanking technologies, increased research funding, and growing collaborations among stakeholders. The integration of AI, blockchain, and digital solutions will reshape the landscape, enabling more efficient data management, enhanced sample quality, and improved patient care. The expansion of biobanks to include diverse populations and the establishment of virtual biobanking models will contribute to more comprehensive and impactful research outcomes.
Conclusion
Europe biobanks market has become invaluable resources for medical research, playing a critical role in advancing precision medicine and personalized healthcare. The Europe biobanks market is witnessing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for biospecimens, advancements in technology, and collaborative research efforts. As the industry evolves, maintaining ethical standards, promoting data harmonization, and embracing digitalization will be key to unlocking the full potential of biobanks and driving transformative advancements in healthcare and scientific discovery.
What is Biobanks?
Biobanks are facilities that collect, store, and manage biological samples, such as blood, tissue, and DNA, for research and clinical purposes. They play a crucial role in advancing personalized medicine and understanding diseases.
What are the key players in the Europe Biobanks Market?
Key players in the Europe Biobanks Market include biobanks like the UK Biobank, the Biobank of the University of Copenhagen, and the German Biobank Node, among others. These organizations contribute significantly to research in genomics and public health.
What are the growth factors driving the Europe Biobanks Market?
The Europe Biobanks Market is driven by increasing demand for personalized medicine, advancements in genomics, and the rising prevalence of chronic diseases. Additionally, collaborations between biobanks and research institutions enhance data availability for studies.
What challenges does the Europe Biobanks Market face?
The Europe Biobanks Market faces challenges such as ethical concerns regarding sample collection and consent, regulatory compliance issues, and the need for standardization in biobanking practices. These factors can hinder operational efficiency and public trust.
What opportunities exist in the Europe Biobanks Market?
Opportunities in the Europe Biobanks Market include the potential for expanding biobanking networks, increasing investment in biobanking technologies, and the growing interest in biobanks for drug discovery and development. These factors can enhance research capabilities.
What trends are shaping the Europe Biobanks Market?
Trends in the Europe Biobanks Market include the integration of digital technologies for sample management, the rise of biobanks focusing on rare diseases, and the increasing collaboration between biobanks and pharmaceutical companies. These trends are enhancing research efficiency.
Europe Biobanks Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Human Samples, Animal Samples, Environmental Samples, Cell Lines |
| End User | Research Institutions, Pharmaceutical Companies, Biotechnology Firms, Academic Organizations |
| Application | Genetic Research, Drug Development, Disease Diagnosis, Clinical Trials |
| Technology | Biobanking Software, Sample Storage Systems, Data Management Tools, Cryopreservation Techniques |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Europe Biobanks Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at