444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview:
The energy security market involves measures and strategies aimed at ensuring the reliable supply, distribution, and protection of energy resources. It encompasses various aspects, including energy infrastructure protection, cybersecurity, emergency preparedness, diversification of energy sources, and energy efficiency. This market overview provides insights into the meaning of energy security, key market trends, drivers, restraints, opportunities, and a regional analysis of the market.
Meaning:
Energy security refers to the ability of a country, region, or organization to have a stable and uninterrupted supply of energy resources to meet its needs. It involves protecting energy infrastructure from physical and cyber threats, diversifying energy sources to reduce dependence on a single source, ensuring the efficient use of energy, and having contingency plans in place to address potential disruptions.
Executive Summary:
The energy security market is of paramount importance as it directly impacts economic stability, national security, and the well-being of individuals and industries. The increasing reliance on energy resources, geopolitical tensions, climate change concerns, and the growing threat of cyberattacks highlight the need for robust energy security measures.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights:
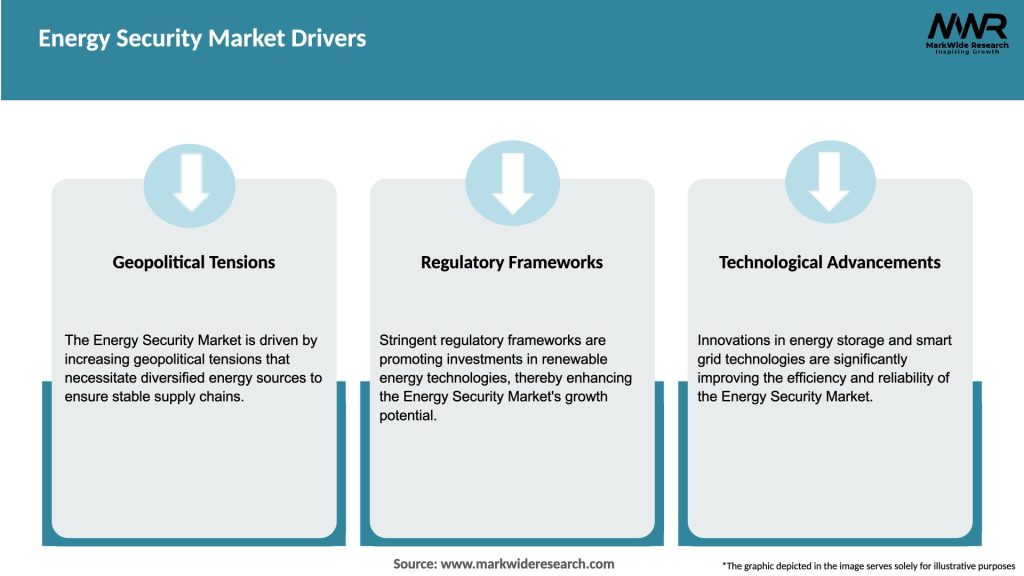
Market Drivers:
Market Restraints:
Market Opportunities:

Market Dynamics:
The energy security market is influenced by a combination of geopolitical, technological, environmental, and economic factors. It requires collaboration between governments, energy companies, and other stakeholders to address energy supply vulnerabilities, protect critical infrastructure, and ensure a reliable and sustainable energy supply.
Regional Analysis:
The energy security market is geographically segmented into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East and Africa. Asia Pacific is expected to dominate the market due to rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasing energy demand in countries such as China and India.
Competitive Landscape:
Leading Companies in the Energy Security Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation:
The energy security market can be segmented based on various factors such as solution type, end-use sector, and region.
By Solution Type
By End-Use Sector
Category-wise Insights:
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis:
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends:
Covid-19 Impact:
The Covid-19 pandemic had significant impacts on the energy security market. It highlighted the vulnerabilities in global supply chains, disruptions in energy demand, and the need for resilient energy systems. The pandemic emphasized the importance of diversifying energy sources, ensuring business continuity, and accelerating the transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy systems.
Key Industry Developments:
Analyst Suggestions:
Future Outlook:
The energy security market is expected to witness sustained growth in the coming years. The increasing focus on energy resilience, diversification of energy sources, and cybersecurity will drive market expansion. The adoption of renewable energy, decentralized energy systems, and advanced technologies will reshape energy security practices. Collaborative efforts between governments, energy companies, and stakeholders will be crucial in ensuring a secure and sustainable energy future.
Conclusion:
Energy security is a critical aspect of ensuring the reliable and uninterrupted supply of energy resources. The market encompasses measures and strategies aimed at protecting energy infrastructure, enhancing cybersecurity, promoting energy efficiency, and diversifying energy sources.
Energy security benefits industry participants and stakeholders by contributing to economic stability, national security, environmental sustainability, and resilient infrastructure. The market is driven by geopolitical uncertainties, cybersecurity threats, and the need for sustainable energy systems.
Future outlook for the market is positive, with continued investments in energy security measures, the integration of renewable energy, and the adoption of advanced technologies.
What is Energy Security?
Energy security refers to the reliable availability of energy resources at an affordable price. It encompasses the ability to access energy sources, maintain supply stability, and ensure resilience against disruptions in energy supply chains.
What are the key players in the Energy Security Market?
Key players in the Energy Security Market include companies like ExxonMobil, BP, and TotalEnergies, which are involved in oil and gas exploration, production, and distribution. Additionally, firms specializing in renewable energy solutions, such as NextEra Energy and Siemens, play a significant role in enhancing energy security, among others.
What are the main drivers of the Energy Security Market?
The main drivers of the Energy Security Market include the increasing demand for reliable energy sources, geopolitical tensions affecting energy supply, and the transition towards renewable energy technologies. Additionally, government policies aimed at enhancing energy independence contribute to market growth.
What challenges does the Energy Security Market face?
The Energy Security Market faces challenges such as fluctuating energy prices, regulatory uncertainties, and the need for significant investments in infrastructure. Environmental concerns and the impact of climate change also pose challenges to traditional energy sources.
What opportunities exist in the Energy Security Market?
Opportunities in the Energy Security Market include the development of smart grid technologies, advancements in energy storage solutions, and the integration of renewable energy sources. These innovations can enhance energy resilience and reduce dependency on fossil fuels.
What trends are shaping the Energy Security Market?
Trends shaping the Energy Security Market include the increasing adoption of decentralized energy systems, the rise of electric vehicles, and the focus on sustainability and carbon neutrality. Additionally, digital transformation in energy management is becoming more prevalent.
Energy Security Market
| Segmentation | Details |
|---|---|
| Solution | Physical Security, Network Security, Application Security, Others |
| Deployment | On-premises, Cloud-based |
| End User | Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Government, Others |
| Region | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Energy Security Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at