444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The Emission Trading Schemes market refers to the trading of emissions allowances or permits, which are used to control and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Emission trading schemes, also known as cap-and-trade systems, provide a market-based approach to tackling climate change by putting a price on carbon emissions. This market allows companies to buy and sell emissions allowances, encouraging emission reduction and providing economic incentives for adopting cleaner technologies and practices.
Meaning
Emission trading schemes involve the establishment of a regulatory framework that sets a limit, or cap, on the total amount of greenhouse gas emissions allowed within a specified jurisdiction. Emissions allowances are allocated to companies or entities, which can then trade these allowances in a market. Companies that can reduce their emissions below their allocated allowances can sell their excess allowances to companies that exceed their emission limits. This system creates a market-based mechanism to incentivize emission reductions and achieve climate change mitigation goals.
Executive Summary
The Emission Trading Schemes market has witnessed significant growth in recent years as countries and regions around the world seek effective solutions to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. These schemes have gained popularity due to their potential to achieve emission reduction targets in a cost-effective and efficient manner. The market is driven by increasing regulatory focus on climate change, the growing adoption of carbon pricing mechanisms, and the need for sustainable practices across industries. However, challenges such as market volatility and the need for international cooperation remain. The future outlook for the market is positive, with opportunities for innovation, market expansion, and the integration of emission trading schemes into broader climate change strategies.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The Emission Trading Schemes market is influenced by various dynamics, including regulatory frameworks, market forces, technological advancements, and stakeholder engagement. The market operates based on the principles of supply and demand, with the price of emission allowances determined by market forces. Regulatory changes and updates, such as the adjustment of emission caps or the inclusion of additional sectors, can impact the market dynamics. Technological advancements play a crucial role in facilitating emission reduction and trading activities. Stakeholder engagement, including collaboration between governments, industries, and environmental organizations, is essential for the effective implementation and functioning of emission trading schemes.
Regional Analysis
The Emission Trading Schemes market can be analyzed based on different regions, including North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East and Africa. Each region has its own emission trading schemes, regulatory frameworks, and market dynamics. For example, the European Union Emission Trading System (EU ETS) is one of the largest and most mature emission trading schemes globally, while regions like Asia Pacific are witnessing the emergence of new emission trading schemes and initiatives. The regional analysis provides insights into the specific challenges, opportunities, and trends in each market.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Emission Trading Schemes Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.

Segmentation
The Emission Trading Schemes market can be segmented based on various factors, including the type of scheme, geographical regions, and industry sectors. Types of schemes may include mandatory schemes, voluntary schemes, and regional schemes. Geographical segmentation allows for a deeper understanding of specific market dynamics and regulatory frameworks in different regions. Industry sector segmentation helps identify the emission-intensive sectors and their participation in emission trading. Each segment provides valuable insights into market size, trends, challenges, and opportunities.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has had both direct and indirect impacts on the Emission Trading Schemes market. Directly, the economic slowdown caused by the pandemic led to a temporary decrease in emissions, resulting in a surplus of emission allowances in some markets. This has led to a decline in carbon prices and reduced trading activities.
Indirectly, the pandemic has highlighted the importance of building resilience and addressing global challenges, including climate change. Governments and stakeholders are recognizing the need to align economic recovery efforts with sustainable development goals and emission reduction targets. This has the potential to drive increased investments in green technologies and stimulate the implementation of more ambitious emission trading schemes in the post-pandemic era.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the Emission Trading Schemes market is promising. Governments worldwide are committed to addressing climate change and reducing greenhouse gas emissions, leading to the implementation of more ambitious emission reduction targets and the expansion of emission trading schemes. Technological advancements, market integration, and stakeholder collaboration will drive the evolution of the market, fostering innovation, efficiency, and transparency. The market will continue to adapt to changing regulatory frameworks, market dynamics, and global challenges, playing a significant role in achieving global climate change mitigation goals.
Conclusion
The Emission Trading Schemes market provides a market-based approach to address climate change by incentivizing companies to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions. These schemes have gained traction globally, with governments and regulatory bodies implementing emission trading schemes to achieve emission reduction targets. The market offers various benefits, including cost-effective emission reduction, revenue generation opportunities, and incentives for innovation. However, challenges such as market volatility, policy uncertainty, and the need for international cooperation remain. The future outlook for the market is positive, with opportunities for expansion, technological innovation, and integration with broader climate change strategies. Collaboration among stakeholders and continuous adaptation to changing market dynamics will be crucial for the success of emission trading schemes in the long run.
What is Emission Trading Schemes?
Emission Trading Schemes refer to market-based approaches used to control pollution by providing economic incentives for reducing emissions of pollutants. These schemes allow companies to buy and sell emission allowances, creating a financial motivation to lower their carbon footprint.
What are the key players in the Emission Trading Schemes market?
Key players in the Emission Trading Schemes market include companies like European Energy Exchange, California Carbon Market, and the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative, among others. These organizations facilitate trading and compliance with emission reduction targets.
What are the main drivers of the Emission Trading Schemes market?
The main drivers of the Emission Trading Schemes market include increasing regulatory pressure to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, the growing awareness of climate change, and the financial benefits associated with trading carbon credits. These factors encourage companies to participate in emission reduction initiatives.
What challenges does the Emission Trading Schemes market face?
The Emission Trading Schemes market faces challenges such as market volatility, regulatory uncertainty, and the potential for market manipulation. These issues can hinder the effectiveness of trading schemes and create barriers for companies looking to invest in emissions reductions.
What opportunities exist in the Emission Trading Schemes market?
Opportunities in the Emission Trading Schemes market include the expansion of carbon markets in developing countries, advancements in technology for monitoring emissions, and the potential for innovative financial products linked to carbon credits. These factors can enhance market participation and effectiveness.
What trends are shaping the Emission Trading Schemes market?
Trends shaping the Emission Trading Schemes market include the integration of blockchain technology for transparent trading, the rise of voluntary carbon markets, and increasing corporate commitments to net-zero emissions. These trends are influencing how companies approach emissions management.
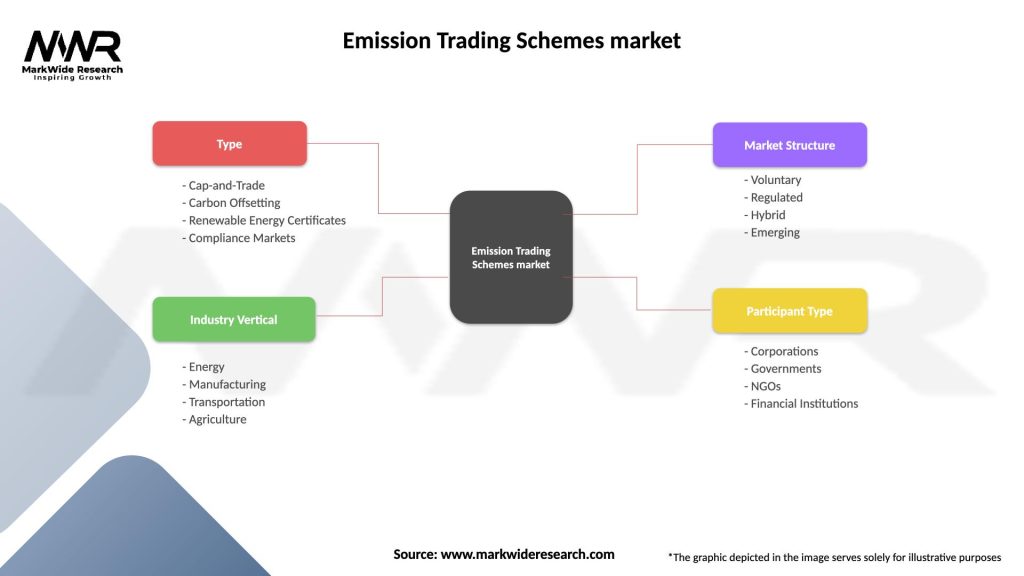
Emission Trading Schemes market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Cap-and-Trade, Carbon Offsetting, Renewable Energy Certificates, Compliance Markets |
| Industry Vertical | Energy, Manufacturing, Transportation, Agriculture |
| Market Structure | Voluntary, Regulated, Hybrid, Emerging |
| Participant Type | Corporations, Governments, NGOs, Financial Institutions |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Emission Trading Schemes Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at