444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
Electron Probe Microanalyzers (EPMA) are advanced scientific instruments used in various industries for elemental analysis and imaging of solid materials. EPMA combines the capabilities of scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) to provide high-resolution imaging and quantitative chemical analysis at the microscale. These instruments play a crucial role in research and development, quality control, and failure analysis across sectors such as materials science, geology, metallurgy, electronics, and pharmaceuticals.
Meaning
Electron Probe Microanalyzers (EPMA) are sophisticated analytical tools that use an electron beam to probe the surface of a sample and collect information about its elemental composition. By exciting the atoms in the sample, EPMA generates characteristic X-rays that are detected and analyzed to determine the presence and concentration of different elements. This technique enables researchers to obtain detailed elemental maps and perform accurate quantitative analysis at the micro- and nanoscale.
Executive Summary
The Electron Probe Microanalyzers (EPMA) market has been experiencing steady growth in recent years. The increasing demand for high-resolution imaging and precise elemental analysis in various industries is driving the market’s expansion. EPMA offers numerous advantages, such as enhanced sensitivity, improved spatial resolution, and the ability to analyze a wide range of materials. These factors, coupled with technological advancements and ongoing research and development activities, are expected to fuel the market’s growth in the coming years.
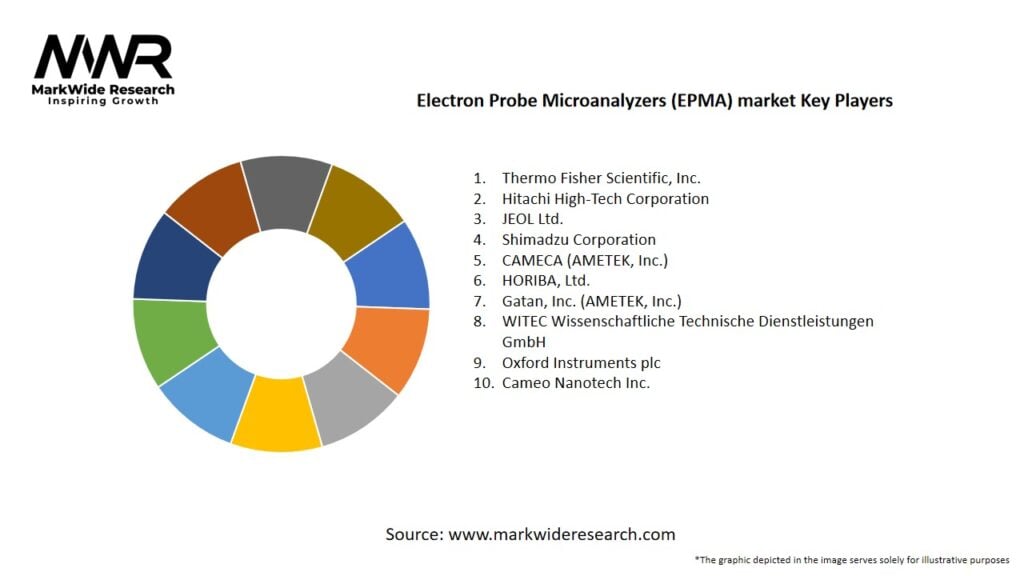
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities

Market Dynamics
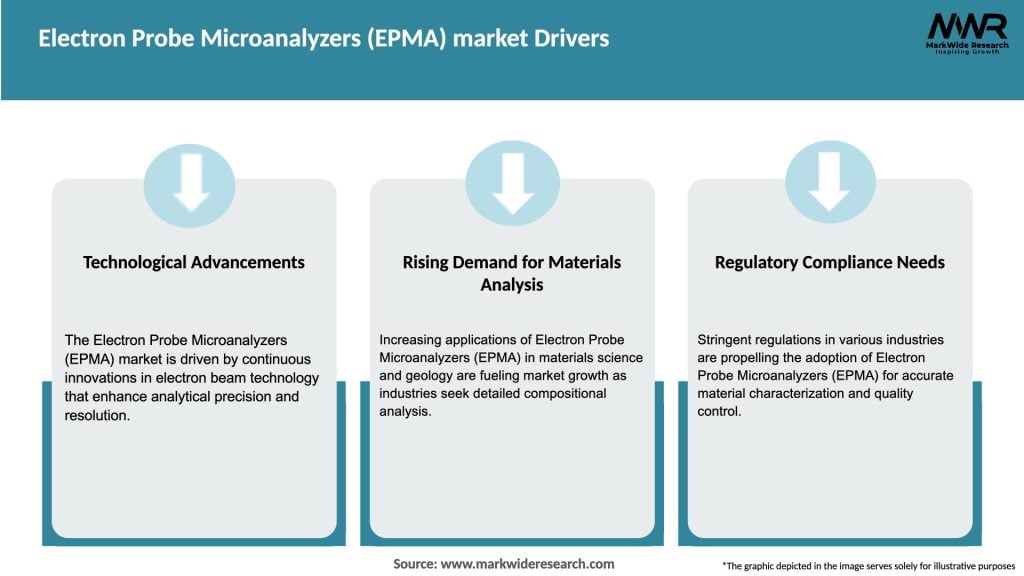
The Electron Probe Microanalyzers (EPMA) market is driven by a combination of factors, including technological advancements, industry demand, and research and development activities. The increasing need for high-resolution imaging and accurate elemental analysis in various industries is a significant driver for market growth. The integration of EPMA with other analytical techniques and the development of advanced detectors and software algorithms are enhancing the capabilities of these instruments, opening up new opportunities for their application.
However,there are certain restraints that can hinder market growth. The high cost associated with EPMA instruments makes them less accessible to small and medium-sized enterprises. Moreover, the complex operation and maintenance requirements of EPMA instruments necessitate skilled personnel, which can be a challenge for some organizations. Additionally, the lack of awareness about the benefits and capabilities of EPMA among potential end-users poses a barrier to market expansion. Overcoming these challenges and addressing the limitations in elemental detection sensitivity and accurate quantitative analysis will be crucial for the sustained growth of the EPMA market.
Regional Analysis
The global Electron Probe Microanalyzers (EPMA) market can be analyzed based on different regions, including North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East and Africa.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Electron Probe Microanalyzers (EPMA) Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
The Electron Probe Microanalyzers (EPMA) market can be segmented based on various factors, including instrument type, application, end-user industry, and region.
By instrument type:
By application:
By end-user industry:
By region:
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic had asignificant impact on various industries, including the Electron Probe Microanalyzers (EPMA) market. The initial phase of the pandemic led to disruptions in manufacturing, supply chain, and research activities, affecting the demand for EPMA instruments. However, as the world adapted to the new normal, the market started recovering, driven by the growing need for research and development related to the pandemic and the increased focus on quality control and failure analysis in industries such as healthcare and pharmaceuticals.
During the pandemic, EPMA instruments played a crucial role in the analysis of materials and particles related to the virus, such as studying the structural properties of the virus itself, analyzing the composition of personal protective equipment (PPE), and investigating the effectiveness of disinfectants. EPMA was also utilized in studying the impact of the pandemic on various materials, such as the corrosion of medical equipment and the stability of pharmaceutical formulations.
The pandemic highlighted the importance of accurate and precise analysis in various industries, leading to an increased recognition of the capabilities of EPMA instruments. As a result, the market witnessed a surge in demand from sectors such as healthcare, pharmaceuticals, and materials science.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The Electron Probe Microanalyzers (EPMA) market is expected to continue its growth trajectory in thecoming years. The increasing demand for high-resolution imaging and precise elemental analysis across industries such as materials science, geology, and electronics will drive market expansion. Technological advancements, integration with complementary analytical techniques, and the development of advanced detectors and software algorithms will further enhance the capabilities of EPMA instruments.
The Asia Pacific region is projected to dominate the EPMA market, driven by rapid industrialization, research and development activities, and the presence of key market players. The region’s growing investments in emerging economies such as China, Japan, and South Korea will contribute to market growth.
To maintain a competitive edge, companies should focus on research and development, expand their applications and market reach, and invest in customer education and support. Strategic partnerships and collaborations will also play a crucial role in driving innovation and accessing new market opportunities.
Despite challenges such as instrument cost, complexity, and competition from alternative analytical techniques, the EPMA market is poised for growth. The continued advancements in EPMA technology and the increasing demand for accurate elemental analysis and imaging capabilities will propel the market forward.
Conclusion
The Electron Probe Microanalyzers (EPMA) market is witnessing steady growth due to the increasing demand for high-resolution imaging and precise elemental analysis in various industries. EPMA instruments play a critical role in research and development, quality control, and failure analysis across sectors such as materials science, geology, metallurgy, electronics, and pharmaceuticals.
The market’s future looks promising, with technological advancements, integration with other analytical techniques, and expanding applications in emerging sectors such as life sciences and environmental analysis. The Asia Pacific region is expected to dominate the market, driven by rapid industrialization and research activities.
What is Electron Probe Microanalyzers (EPMA)?
Electron Probe Microanalyzers (EPMA) are sophisticated analytical instruments used to determine the elemental composition of materials at a microscopic scale. They utilize focused electron beams to excite atoms in a sample, allowing for precise measurement of elemental concentrations.
What are the key players in the Electron Probe Microanalyzers (EPMA) market?
Key players in the Electron Probe Microanalyzers (EPMA) market include JEOL Ltd., Thermo Fisher Scientific, and Hitachi High-Technologies Corporation, among others. These companies are known for their innovative technologies and extensive product offerings in the field of microanalysis.
What are the growth factors driving the Electron Probe Microanalyzers (EPMA) market?
The Electron Probe Microanalyzers (EPMA) market is driven by increasing demand for high-precision material analysis in industries such as semiconductor manufacturing, materials science, and geology. Additionally, advancements in technology and the growing need for quality control in production processes are contributing to market growth.
What challenges does the Electron Probe Microanalyzers (EPMA) market face?
The Electron Probe Microanalyzers (EPMA) market faces challenges such as high initial investment costs and the need for skilled personnel to operate these complex instruments. Furthermore, competition from alternative analytical techniques can also pose a challenge to market growth.
What opportunities exist in the Electron Probe Microanalyzers (EPMA) market?
Opportunities in the Electron Probe Microanalyzers (EPMA) market include the expansion of applications in emerging fields like nanotechnology and biomaterials. Additionally, the increasing focus on research and development in various scientific disciplines presents significant growth potential.
What trends are shaping the Electron Probe Microanalyzers (EPMA) market?
Trends in the Electron Probe Microanalyzers (EPMA) market include the integration of automation and artificial intelligence to enhance analysis efficiency and accuracy. Moreover, there is a growing emphasis on miniaturization and portability of EPMA systems to cater to diverse research environments.
Electron Probe Microanalyzers (EPMA) market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Wavelength Dispersive, Energy Dispersive, Scanning Electron, Transmission Electron |
| End User | Research Institutions, Semiconductor Manufacturers, Material Science Labs, Academic Institutions |
| Application | Metallurgy, Geology, Nanotechnology, Forensics |
| Technology | Electron Beam, X-Ray Fluorescence, Scanning Probe, Laser Ablation |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Electron Probe Microanalyzers (EPMA) Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at