444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The economic sanctions market refers to the global market for measures taken by governments or international organizations to restrict trade and economic relations with specific countries, entities, or individuals. These sanctions are often imposed as a response to political or security concerns and aim to influence the behavior of targeted parties. The economic sanctions market encompasses various sectors, including finance, energy, technology, defense, and trade, among others. This market plays a crucial role in international relations and has significant implications for businesses, governments, and individuals worldwide.
Meaning
Economic sanctions are punitive measures imposed by governments or international bodies to restrict or prohibit economic activities with a targeted country, entity, or individual. These measures can take various forms, such as trade embargoes, asset freezes, travel bans, or restrictions on financial transactions. The primary purpose of economic sanctions is to exert pressure on the targeted parties, encouraging them to change their behavior, comply with international norms, or resolve disputes peacefully. These sanctions can have wide-ranging impacts on the economies and societies of both the targeted country and the countries imposing the sanctions.
Executive Summary
The economic sanctions market is a complex and dynamic landscape, driven by geopolitical tensions, security concerns, and human rights issues. This market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, as governments and international organizations increasingly resort to sanctions as a tool of diplomacy and foreign policy. The market is characterized by a wide range of stakeholders, including government agencies, financial institutions, multinational corporations, legal firms, and compliance professionals. These stakeholders play a crucial role in facilitating or mitigating the impact of economic sanctions on various industries and economies.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
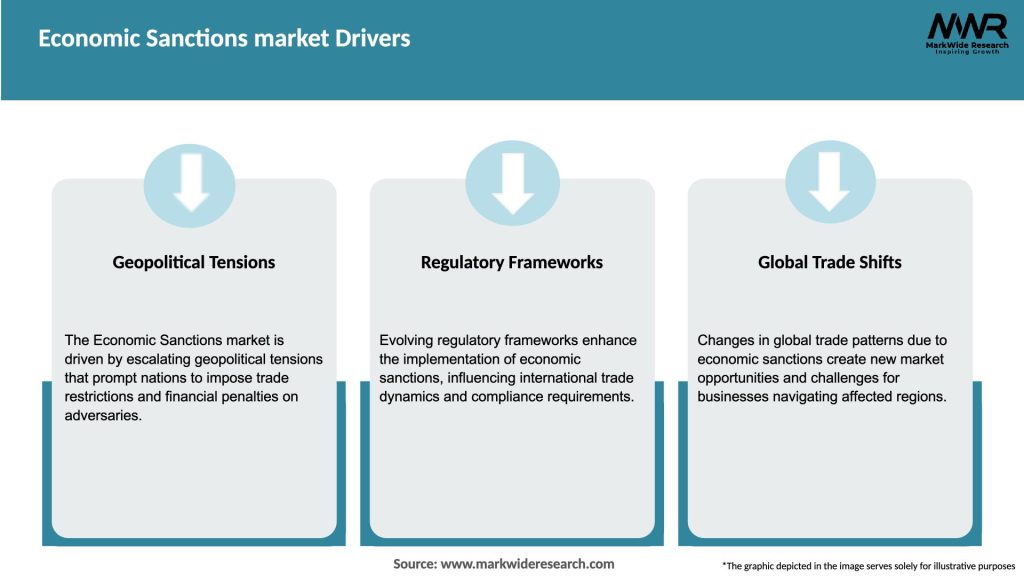
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The economic sanctions market is shaped by a range of dynamic factors, including geopolitical events, international cooperation, technological advancements, and economic considerations. The interplay of these factors determines the scope, impact, and effectiveness of sanctions measures. Additionally, the market is influenced by the responses and countermeasures adopted by targeted entities, including efforts to evade sanctions, seek alternative trade partners, or develop domestic industries. The enforcement and compliance landscape also evolve in response to market dynamics, with regulators and businesses adapting their strategies and technologies to address emerging challenges.
Regional Analysis
The economic sanctions market is a global phenomenon, with sanctions being imposed by various countries and international organizations against different targets worldwide. The regional dynamics of this market vary significantly, reflecting regional conflicts, geopolitical rivalries, and economic interdependencies. Major players in the economic sanctions market include the United States, European Union, United Nations, and other regional bodies. The effectiveness and impact of sanctions measures may differ across regions, depending on factors such as the level of integration with the global economy, regional political dynamics, and the resilience of local economies.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Economic Sanctions Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
The economic sanctions market can be segmented based on various factors, including the target of sanctions, the sector or industry affected, and the geographic scope of the measures. Segmentation allows for a better understanding of the specific dynamics and challenges associated with different types of sanctions. For example, sector-specific sanctions may have a significant impact on industries such as energy or technology, while country-specific sanctions can affect trade and investment flows with specific countries. Geographic segmentation provides insights into regional variations in the application and enforcement of sanctions measures, reflecting different geopolitical interests and priorities.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has had significant implications for the economic sanctions market. The pandemic disrupted global trade, supply chains, and economies, leading to an increased focus on domestic priorities and challenges. In some cases, governments temporarily lifted or relaxed sanctions to facilitate the flow of humanitarian aid and medical supplies. However, the pandemic also highlighted the vulnerabilities of the global financial system, with illicit activities, money laundering, and sanctions evasion continuing amidst the crisis. The long-term impact of the pandemic on the economic sanctions market will depend on factors such as the pace of global economic recovery, geopolitical dynamics, and the evolution of regional alliances and conflicts.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The economic sanctions market is expected to continue evolving in the coming years, driven by geopolitical tensions, changing alliances, technological advancements, and evolving regulatory frameworks. The use of sector-specific sanctions is likely to increase, targeting industries such as technology, energy, and defense. The emphasis on human rights considerations in the imposition of sanctions is expected to grow, reflecting global concerns and public sentiment. The role of technology in compliance and enforcement will continue to expand, enabling more effective monitoring, detection, and prevention of sanctions violations. The future of the economic sanctions market will be shaped by ongoing geopolitical conflicts, emerging technologies, and the response of targeted entities and the international community.
Conclusion
The economic sanctions market is a complex and dynamic landscape, shaped by geopolitical tensions, security concerns, and human rights considerations. Economic sanctions are used as a tool to exert pressure, influence behavior, and address international conflicts and disputes. The market involves a diverse range of stakeholders, including governments, regulatory bodies, financial institutions, multinational corporations, legal firms, and compliance professionals. Compliance with sanctions regulations and the ability to navigate the evolving market dynamics are crucial for businesses operating in multiple jurisdictions. The future of the economic sanctions market will be influenced by geopolitical developments, technological advancements, and the ongoing efforts to balance the desired impact of sanctions with the potential unintended consequences.
What is Economic Sanctions?
Economic sanctions are restrictive measures imposed by countries or international organizations to influence the behavior of a target nation, often in response to political or economic issues. They can include trade barriers, tariffs, and restrictions on financial transactions.
What are the key players in the Economic Sanctions market?
Key players in the Economic Sanctions market include government agencies, international organizations like the United Nations, and private sector firms that specialize in compliance and risk management, such as Control Risks and Stratfor, among others.
What are the main drivers of the Economic Sanctions market?
The main drivers of the Economic Sanctions market include geopolitical tensions, the need for countries to enforce international law, and the desire to promote human rights. These factors often lead to the implementation of sanctions as a tool for foreign policy.
What challenges does the Economic Sanctions market face?
The Economic Sanctions market faces challenges such as the potential for unintended consequences on civilian populations, the difficulty in enforcing sanctions effectively, and the risk of retaliatory measures from targeted nations.
What opportunities exist in the Economic Sanctions market?
Opportunities in the Economic Sanctions market include the development of advanced compliance technologies, increased demand for consulting services to navigate sanctions, and the potential for new sanctions regimes in response to emerging global threats.
What trends are shaping the Economic Sanctions market?
Trends shaping the Economic Sanctions market include the growing use of targeted sanctions, the rise of digital currencies complicating enforcement, and an increasing focus on multilateral sanctions efforts among nations.
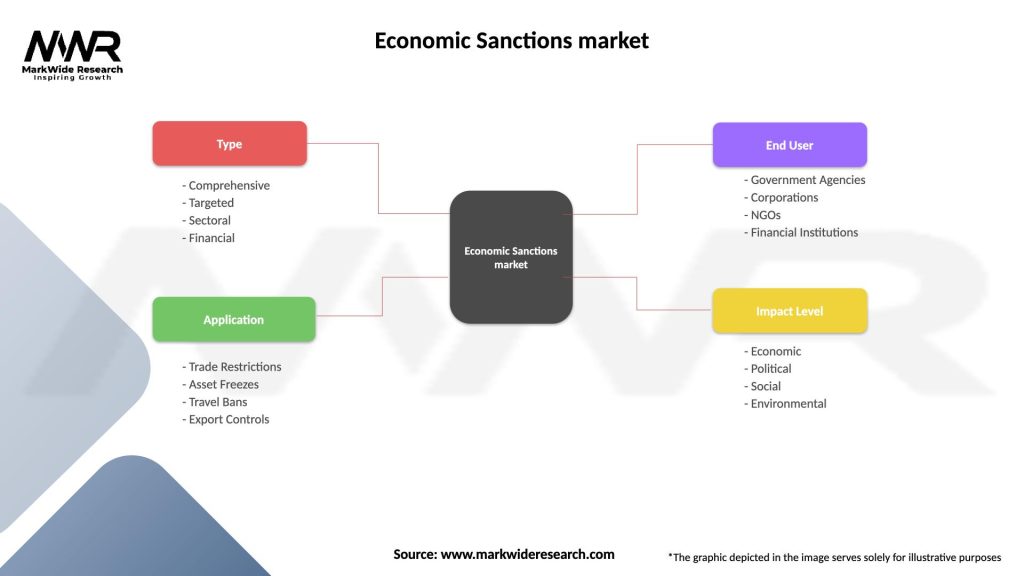
Economic Sanctions market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Comprehensive, Targeted, Sectoral, Financial |
| Application | Trade Restrictions, Asset Freezes, Travel Bans, Export Controls |
| End User | Government Agencies, Corporations, NGOs, Financial Institutions |
| Impact Level | Economic, Political, Social, Environmental |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Economic Sanctions Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at