444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2750
The Latin America diabetes drugs market represents a critical healthcare segment experiencing unprecedented growth driven by rising diabetes prevalence and expanding access to innovative treatments. Latin American countries are witnessing significant demographic shifts, with urbanization and lifestyle changes contributing to increased diabetes incidence across the region. The market encompasses a comprehensive range of therapeutic solutions including insulin products, oral antidiabetic medications, and emerging biosimilar alternatives.
Regional dynamics indicate substantial variations in market penetration and treatment accessibility across different Latin American nations. Brazil and Mexico dominate the regional landscape, accounting for approximately 65% of total market share, while countries like Argentina, Colombia, and Chile represent emerging opportunities for pharmaceutical companies. The market demonstrates robust growth potential with projected expansion at a compound annual growth rate of 8.2% through the forecast period.
Healthcare infrastructure improvements and government initiatives promoting diabetes awareness have created favorable conditions for market expansion. Public health programs across Latin America are increasingly focusing on diabetes prevention and management, leading to enhanced diagnostic capabilities and treatment accessibility. The integration of digital health solutions and telemedicine platforms has further accelerated market growth, particularly in remote and underserved regions.
The diabetes drugs market in Latin America refers to the comprehensive pharmaceutical landscape encompassing all therapeutic interventions designed to manage and treat diabetes mellitus across Latin American countries. This market includes various medication categories such as insulin formulations, oral hypoglycemic agents, injectable non-insulin therapies, and combination drug products specifically developed for diabetes management.
Market scope extends beyond traditional pharmaceutical products to include biosimilar medications, generic alternatives, and innovative drug delivery systems. The definition encompasses both prescription and over-the-counter diabetes management solutions available through various distribution channels including hospitals, retail pharmacies, online platforms, and specialized diabetes care centers throughout the Latin American region.
Therapeutic classifications within this market include Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes medications, gestational diabetes treatments, and preventive therapies for prediabetic conditions. The market definition also incorporates emerging therapeutic areas such as continuous glucose monitoring systems, smart insulin delivery devices, and personalized medicine approaches tailored to Latin American patient populations.
Latin America’s diabetes drugs market stands at a pivotal juncture characterized by substantial growth opportunities and evolving healthcare landscapes. The region faces a mounting diabetes epidemic with prevalence rates reaching approximately 9.4% among adults, creating unprecedented demand for effective therapeutic interventions. Market transformation is being driven by demographic transitions, urbanization trends, and increasing healthcare awareness among Latin American populations.
Key market drivers include expanding healthcare infrastructure, government policy reforms, and growing pharmaceutical industry investments in the region. Brazil and Mexico continue to lead market development, while countries like Colombia, Peru, and Chile present significant growth potential. The market benefits from increasing adoption of modern diabetes management approaches and rising patient awareness about treatment options.
Competitive dynamics reveal a landscape dominated by international pharmaceutical giants alongside emerging regional players. Innovation trends focus on biosimilar development, combination therapies, and patient-centric drug delivery systems. The market demonstrates resilience despite economic challenges, with healthcare prioritization driving sustained investment in diabetes care solutions across Latin American healthcare systems.
Strategic market insights reveal several critical trends shaping the Latin American diabetes drugs landscape. Demographic analysis indicates that diabetes prevalence is increasing most rapidly among urban populations aged 45-65, creating targeted opportunities for pharmaceutical companies. The market demonstrates strong correlation between economic development and diabetes drug accessibility across different Latin American countries.
Rising diabetes prevalence serves as the primary catalyst driving market expansion across Latin America. Epidemiological trends indicate that diabetes incidence is increasing at alarming rates, particularly in urban centers where lifestyle factors contribute to higher disease occurrence. The combination of genetic predisposition, dietary changes, and reduced physical activity creates a perfect storm for diabetes development among Latin American populations.
Healthcare infrastructure development represents another significant market driver, with governments across the region investing heavily in medical facilities and healthcare accessibility. Public health initiatives focusing on diabetes prevention and management have created supportive environments for pharmaceutical market growth. These programs include screening campaigns, patient education efforts, and subsidized medication access programs that expand the treatable patient population.
Economic growth in key Latin American countries has improved healthcare spending capacity and insurance coverage for diabetes treatments. Middle-class expansion has created a larger population segment capable of affording advanced diabetes therapies, while government healthcare programs increasingly cover diabetes medications for lower-income populations. The growing awareness of diabetes complications and long-term health consequences motivates patients to seek appropriate treatment interventions.
Technological advancement in diabetes care has revolutionized treatment approaches and patient outcomes. Innovation in drug delivery systems, continuous glucose monitoring, and telemedicine platforms has enhanced treatment effectiveness and patient compliance. These technological improvements have made diabetes management more convenient and effective, driving increased adoption of pharmaceutical interventions across the Latin American market.
Economic constraints pose significant challenges to diabetes drug market growth across Latin America. Healthcare affordability remains a critical barrier for many patients, particularly in countries with limited insurance coverage or high out-of-pocket medication costs. Economic instability in certain Latin American nations creates uncertainty in healthcare spending and pharmaceutical market investment decisions.
Regulatory complexities across different Latin American countries create obstacles for pharmaceutical companies seeking regional market expansion. Varying approval processes, pricing regulations, and import restrictions can delay product launches and increase market entry costs. The lack of harmonized regulatory frameworks across the region complicates strategic planning for international pharmaceutical companies.
Healthcare infrastructure limitations in rural and remote areas restrict access to diabetes care and medication distribution. Geographic barriers and limited healthcare facility coverage prevent many patients from receiving appropriate diabetes treatment. The shortage of specialized healthcare professionals and diabetes educators further constrains market growth potential in underserved regions.
Cultural and educational barriers impact diabetes awareness and treatment adherence across Latin American populations. Traditional medicine preferences and skepticism toward pharmaceutical interventions can limit market penetration. Limited health literacy and diabetes education programs in certain regions contribute to delayed diagnosis and suboptimal treatment outcomes, restricting overall market expansion.
Biosimilar development presents substantial opportunities for market expansion and cost reduction across Latin America. Patent expirations of major diabetes drugs create openings for generic and biosimilar manufacturers to enter the market with more affordable alternatives. This trend particularly benefits price-sensitive market segments and government healthcare programs seeking cost-effective treatment solutions.
Digital health integration offers transformative opportunities for diabetes care delivery and patient engagement. Telemedicine platforms can extend specialist care to remote areas, while mobile health applications can improve medication adherence and glucose monitoring. The growing smartphone penetration across Latin America creates favorable conditions for digital diabetes management solution adoption.
Public-private partnerships represent significant opportunities for market expansion and improved patient access. Collaboration between pharmaceutical companies and government healthcare programs can create sustainable models for diabetes drug distribution and affordability. These partnerships can leverage public health infrastructure while providing pharmaceutical companies with stable market access and volume commitments.
Emerging market segments in smaller Latin American countries offer untapped growth potential for pharmaceutical companies. Countries like Uruguay, Paraguay, and Ecuador represent developing markets with improving healthcare systems and growing diabetes awareness. Early market entry in these regions can establish competitive advantages and long-term market positioning for forward-thinking pharmaceutical companies.
Competitive intensity within the Latin American diabetes drugs market continues to escalate as international pharmaceutical giants compete with regional players and emerging biosimilar manufacturers. Market consolidation trends are evident as larger companies acquire regional distributors and local pharmaceutical manufacturers to strengthen their Latin American presence. This dynamic creates both opportunities and challenges for different market participants.
Pricing pressures represent a dominant market dynamic affecting all therapeutic categories and market segments. Government price controls and healthcare budget constraints force pharmaceutical companies to develop innovative pricing strategies and value-based care models. The balance between affordability and innovation drives continuous market evolution and strategic adaptation among industry participants.
Supply chain optimization has become increasingly critical for market success in Latin America. Distribution challenges related to geography, infrastructure, and regulatory requirements necessitate sophisticated logistics solutions. Companies that successfully navigate these complexities gain significant competitive advantages in market penetration and customer service delivery.
Patient-centric approaches are reshaping market dynamics as healthcare systems increasingly focus on treatment outcomes and quality of life improvements. Value-based healthcare models emphasize medication effectiveness and patient satisfaction over traditional volume-based metrics. This shift influences product development priorities, marketing strategies, and partnership approaches throughout the Latin American diabetes drugs market.
Comprehensive market analysis employs multiple research methodologies to ensure accurate and reliable insights into the Latin American diabetes drugs market. Primary research activities include extensive interviews with healthcare professionals, pharmaceutical industry executives, regulatory officials, and patient advocacy groups across major Latin American countries. These qualitative insights provide deep understanding of market dynamics, challenges, and opportunities.
Secondary research components encompass analysis of government healthcare statistics, pharmaceutical industry reports, clinical trial databases, and regulatory filing information. Data triangulation methods validate findings across multiple sources to ensure research accuracy and reliability. Market sizing and forecasting models incorporate demographic trends, epidemiological data, and economic indicators specific to Latin American countries.
Regional market assessment involves country-specific analysis of healthcare systems, regulatory environments, and competitive landscapes. Stakeholder mapping identifies key decision-makers, influencers, and market participants across the diabetes care value chain. This comprehensive approach ensures thorough understanding of market complexities and regional variations throughout Latin America.
Analytical frameworks include Porter’s Five Forces analysis, SWOT assessment, and competitive positioning studies tailored to the Latin American healthcare context. Forecasting methodologies incorporate multiple scenario planning approaches to account for economic, political, and healthcare policy uncertainties affecting the regional diabetes drugs market.
Brazil dominates the Latin American diabetes drugs market with approximately 38% regional market share, driven by its large population, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and robust pharmaceutical industry presence. Brazilian market characteristics include strong government healthcare programs, active biosimilar development, and significant international pharmaceutical company investments. The country’s diabetes prevalence continues rising, creating sustained demand for therapeutic interventions.
Mexico represents the second-largest regional market with 27% market share, benefiting from proximity to the United States and established pharmaceutical manufacturing capabilities. Mexican healthcare reforms have improved diabetes drug accessibility through expanded insurance coverage and government procurement programs. The country serves as a strategic hub for pharmaceutical companies targeting the broader Latin American region.
Argentina, Colombia, and Chile collectively account for 22% of regional market share, each presenting unique opportunities and challenges. Argentina’s market faces economic volatility but maintains strong healthcare infrastructure and diabetes awareness programs. Colombia’s expanding economy and healthcare reforms create favorable conditions for market growth, while Chile’s stable political environment attracts international pharmaceutical investments.
Smaller Latin American markets including Peru, Ecuador, Uruguay, and Central American countries represent emerging opportunities with improving healthcare systems and growing diabetes awareness. MarkWide Research analysis indicates these markets collectively show 12.5% annual growth potential, driven by economic development and healthcare infrastructure investments. Regional integration initiatives may facilitate market access and distribution efficiency across these developing markets.
International pharmaceutical giants maintain dominant positions in the Latin American diabetes drugs market through comprehensive product portfolios and established distribution networks. Market leadership is characterized by companies offering complete diabetes care solutions including insulin products, oral medications, and innovative drug delivery systems.
Regional pharmaceutical companies and biosimilar manufacturers are gaining market share through cost-effective alternatives and localized market strategies. Competitive differentiation increasingly focuses on patient support programs, healthcare professional education, and integrated diabetes care solutions rather than solely on product features.
By Drug Type: The market segmentation reveals distinct therapeutic categories with varying growth patterns and market dynamics. Insulin products maintain the largest market segment, encompassing rapid-acting, long-acting, and combination insulin formulations. Oral antidiabetic medications represent the second-largest segment with metformin-based therapies leading adoption rates across Latin American markets.
By Diabetes Type: Type 2 diabetes treatments dominate market demand due to higher disease prevalence and diverse therapeutic options. Type 1 diabetes medications represent a smaller but critical market segment with specific insulin requirements and specialized care needs. Gestational diabetes treatments constitute an emerging segment with growing awareness and screening programs.
By Distribution Channel: Hospital pharmacies account for the largest distribution segment, particularly for insulin products and specialized diabetes medications. Retail pharmacies serve as primary access points for oral diabetes medications and routine prescription refills. Online pharmacies represent a rapidly growing segment with 18% annual growth in urban markets.
By End User: Adult patients aged 45-65 represent the primary market segment with highest treatment utilization rates. Elderly populations constitute a growing segment requiring specialized medication management and monitoring. Pediatric diabetes patients represent a specialized segment with unique therapeutic requirements and family-centered care approaches.
Insulin Category Analysis: The insulin segment demonstrates robust growth driven by increasing Type 1 diabetes diagnoses and advanced Type 2 diabetes progression. Long-acting insulin formulations show particular strength due to improved patient compliance and convenience. Biosimilar insulin products are gaining traction with 23% adoption rate among cost-conscious patients and healthcare systems seeking budget-friendly alternatives.
Oral Medication Insights: Metformin-based therapies maintain market leadership due to proven efficacy, safety profile, and cost-effectiveness. Combination oral therapies are experiencing increased adoption as healthcare providers seek simplified treatment regimens for improved patient adherence. SGLT-2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists represent premium segments with growing market acceptance despite higher costs.
Injectable Non-Insulin Category: GLP-1 receptor agonists demonstrate strong growth potential with cardiovascular and weight management benefits appealing to Latin American patients. Weekly injection formulations improve patient convenience and compliance compared to daily alternatives. This category benefits from increasing physician awareness and patient education about advanced diabetes treatment options.
Combination Therapy Trends: Fixed-dose combinations are gaining popularity as they simplify treatment regimens and improve medication adherence. Insulin-oral combination products represent an emerging category addressing the needs of patients transitioning from oral-only therapy to insulin treatment. These products offer clinical benefits while reducing treatment complexity for patients and healthcare providers.
Pharmaceutical Companies benefit from expanding market opportunities and diverse revenue streams across multiple Latin American countries. Market diversification reduces dependence on single-country performance while providing access to growing patient populations. Strategic partnerships with local distributors and healthcare systems create sustainable competitive advantages and market penetration opportunities.
Healthcare Providers gain access to comprehensive diabetes treatment options enabling personalized patient care approaches. Clinical outcome improvements result from advanced therapeutic options and integrated care solutions. Professional development opportunities through pharmaceutical company education programs enhance diabetes care capabilities and patient management skills.
Patients and Caregivers benefit from improved treatment accessibility, effectiveness, and convenience. Quality of life enhancements result from better glucose control and reduced diabetes complications. Patient support programs provided by pharmaceutical companies offer education, monitoring tools, and financial assistance for medication access.
Government Healthcare Systems achieve better population health outcomes through effective diabetes management programs. Healthcare cost reductions result from preventing diabetes complications and hospitalizations. Economic benefits include reduced disability claims and increased workforce productivity through better diabetes care and management.
Insurance Providers benefit from reduced long-term healthcare costs through effective diabetes prevention and management. Risk management improvements result from better patient outcomes and reduced complications. Partnership opportunities with pharmaceutical companies create value-based care models that align financial incentives with patient health outcomes.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Personalized Medicine Evolution represents a transformative trend reshaping diabetes treatment approaches across Latin America. Pharmacogenomic testing and individualized therapy selection are gaining acceptance among healthcare providers seeking optimal patient outcomes. This trend drives demand for diverse therapeutic options and specialized diagnostic services supporting personalized treatment decisions.
Digital Health Integration continues accelerating with smartphone applications, continuous glucose monitoring, and telemedicine platforms becoming standard diabetes care components. Remote patient monitoring capabilities enable healthcare providers to manage larger patient populations while improving treatment outcomes. Artificial intelligence applications in glucose prediction and medication adjustment represent emerging technological frontiers.
Biosimilar Market Expansion is transforming the competitive landscape as patent expirations create opportunities for cost-effective alternatives. Regulatory pathway improvements across Latin American countries facilitate biosimilar approvals and market entry. This trend particularly benefits government healthcare programs and price-sensitive patient populations seeking affordable diabetes treatments.
Combination Therapy Adoption reflects clinical evidence supporting multi-mechanism approaches to diabetes management. Fixed-dose combinations simplify treatment regimens while addressing multiple pathophysiological aspects of diabetes. Healthcare provider education about combination therapy benefits drives increased prescription patterns and patient acceptance across Latin American markets.
Value-Based Care Models are emerging as healthcare systems seek to optimize outcomes while controlling costs. Risk-sharing agreements between pharmaceutical companies and healthcare payers create innovative market access approaches. Outcome-based pricing models align pharmaceutical company revenues with patient health improvements and healthcare system cost savings.
Regulatory Harmonization Initiatives across Latin American countries are streamlining pharmaceutical approval processes and reducing market entry barriers. Regional regulatory cooperation facilitates faster product launches and improved market access for diabetes medications. These developments particularly benefit international pharmaceutical companies seeking efficient regional expansion strategies.
Manufacturing Capacity Expansion within Latin America reduces import dependence and improves supply chain reliability. Local production facilities for insulin and oral diabetes medications enhance market stability and reduce costs. Technology transfer agreements between international companies and regional manufacturers create sustainable local production capabilities.
Healthcare Infrastructure Investments by governments and private organizations improve diabetes care accessibility across the region. Specialized diabetes centers and integrated care facilities enhance treatment quality and patient outcomes. Healthcare professional training programs supported by pharmaceutical companies improve clinical expertise and treatment standards.
Digital Health Platform Launches by pharmaceutical companies and technology firms create comprehensive diabetes management ecosystems. Integrated care platforms combine medication management, glucose monitoring, and healthcare provider communication. Patient engagement tools improve treatment adherence and clinical outcomes while reducing healthcare system costs.
Strategic Partnership Development between international pharmaceutical companies and regional distributors strengthens market presence and operational efficiency. Acquisition activities consolidate market positions and expand therapeutic portfolios. Joint venture formations combine international expertise with local market knowledge for enhanced competitive positioning.
Market Entry Strategies should prioritize countries with stable healthcare policies and growing diabetes awareness programs. Brazil and Mexico offer the most immediate opportunities for significant market penetration, while Colombia and Chile represent attractive secondary markets with favorable growth trajectories. Partnership approaches with established local distributors can accelerate market access and reduce operational complexities.
Product Portfolio Optimization should balance innovative premium products with cost-effective alternatives addressing diverse market segments. Biosimilar development represents a critical opportunity for companies seeking to compete in price-sensitive segments. Combination therapy products can differentiate offerings while addressing clinical needs for simplified treatment regimens.
Digital Health Investment should focus on smartphone-based solutions compatible with Latin American technology infrastructure and user preferences. Telemedicine capabilities can extend market reach to underserved rural populations while reducing healthcare delivery costs. Patient engagement platforms should incorporate cultural considerations and language preferences specific to different Latin American markets.
Regulatory Strategy Development should anticipate continued harmonization efforts while maintaining flexibility for country-specific requirements. Early engagement with regulatory authorities can facilitate smoother approval processes and faster market entry. Clinical trial strategies should consider regional patient populations and healthcare system characteristics to support regulatory submissions.
Pricing Strategy Formulation must balance affordability requirements with innovation investment recovery needs. Value-based pricing models can demonstrate medication benefits while addressing healthcare system budget constraints. Patient assistance programs can improve access while maintaining premium pricing for innovative products in appropriate market segments.
Market expansion prospects remain highly favorable with diabetes prevalence projected to increase significantly across Latin America over the next decade. Demographic trends including population aging and urbanization will continue driving diabetes incidence and treatment demand. MarkWide Research projections indicate sustained market growth with compound annual growth rates exceeding 8% in most major Latin American countries.
Innovation trajectories point toward increasingly sophisticated diabetes management solutions incorporating artificial intelligence, continuous monitoring, and personalized medicine approaches. Next-generation insulin formulations and novel therapeutic mechanisms will expand treatment options and improve patient outcomes. Digital health integration will become standard practice, transforming diabetes care delivery and patient engagement across the region.
Market consolidation trends are expected to continue as larger pharmaceutical companies acquire regional players and specialized diabetes care companies. Biosimilar competition will intensify, creating pricing pressures while improving treatment accessibility for broader patient populations. Strategic partnerships between pharmaceutical companies and healthcare systems will become increasingly important for market success.
Regulatory evolution will likely favor streamlined approval processes and increased harmonization across Latin American countries. Healthcare policy developments will continue emphasizing diabetes prevention and management, creating supportive environments for pharmaceutical market growth. Economic stability improvements in key markets will enhance healthcare spending capacity and insurance coverage expansion.
Long-term market sustainability will depend on successful balance between innovation, affordability, and accessibility across diverse Latin American populations. Public health initiatives focusing on diabetes prevention may moderate future treatment demand while creating opportunities in preventive care segments. Technology advancement will continue reshaping diabetes care paradigms and market competitive dynamics throughout the forecast period.
The Latin America diabetes drugs market presents compelling growth opportunities driven by rising disease prevalence, improving healthcare infrastructure, and increasing treatment accessibility across the region. Market dynamics favor companies that can successfully navigate regulatory complexities while delivering innovative, affordable solutions tailored to diverse Latin American patient populations and healthcare systems.
Strategic success factors include comprehensive market entry approaches, balanced product portfolios addressing various price points, and strong local partnerships facilitating distribution and market penetration. Digital health integration and personalized medicine approaches represent key differentiators for companies seeking competitive advantages in this evolving market landscape.
Future market evolution will be shaped by continued demographic transitions, technological advancement, and healthcare policy developments across Latin American countries. Companies positioning themselves to capitalize on biosimilar opportunities, digital health trends, and emerging market segments will be best positioned for sustained growth and market leadership in this dynamic and expanding healthcare sector.
What is Diabetes Drugs?
Diabetes drugs are medications used to manage blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes. They include various classes such as insulin, sulfonylureas, and GLP-1 receptor agonists, each targeting different aspects of glucose regulation.
What are the key players in the Diabetes Drugs in Latin America Market?
Key players in the Diabetes Drugs in Latin America Market include Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, and Merck, which are known for their innovative diabetes treatments and extensive distribution networks in the region, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Diabetes Drugs in Latin America Market?
The growth of the Diabetes Drugs in Latin America Market is driven by increasing diabetes prevalence, rising healthcare expenditure, and advancements in drug formulations. Additionally, greater awareness and education about diabetes management contribute to market expansion.
What challenges does the Diabetes Drugs in Latin America Market face?
The Diabetes Drugs in Latin America Market faces challenges such as high drug costs, varying regulatory environments, and limited access to healthcare in rural areas. These factors can hinder the availability and affordability of essential diabetes medications.
What opportunities exist in the Diabetes Drugs in Latin America Market?
Opportunities in the Diabetes Drugs in Latin America Market include the development of biosimilars, increasing investment in healthcare infrastructure, and the potential for digital health solutions to enhance patient management. These factors can lead to improved access and treatment outcomes.
What trends are shaping the Diabetes Drugs in Latin America Market?
Trends shaping the Diabetes Drugs in Latin America Market include the rise of personalized medicine, the integration of technology in diabetes management, and a focus on preventive care. These trends are influencing how diabetes treatments are developed and delivered.
Diabetes Drugs in Latin America Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
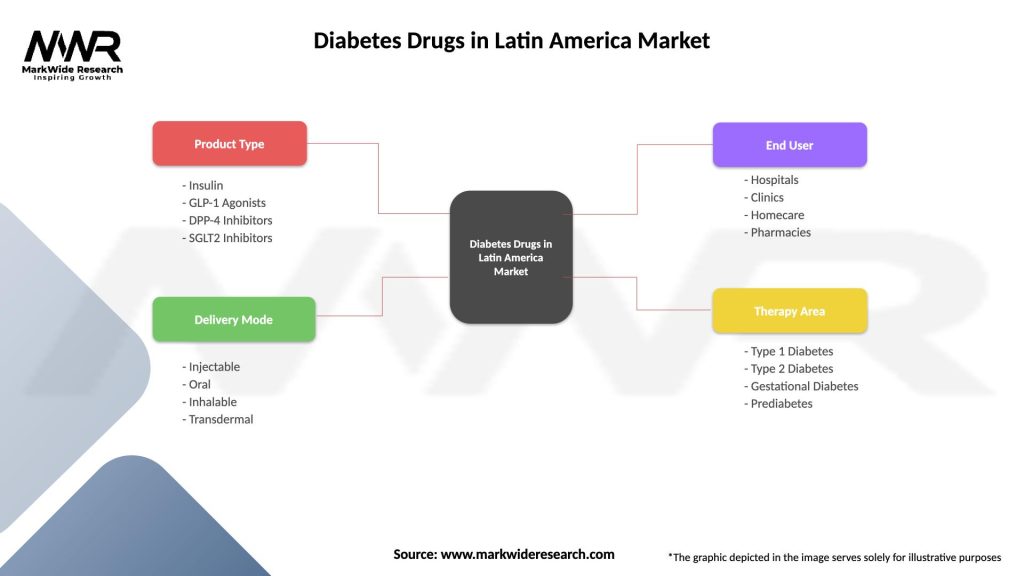
| Product Type | Insulin, GLP-1 Agonists, DPP-4 Inhibitors, SGLT2 Inhibitors |
| Delivery Mode | Injectable, Oral, Inhalable, Transdermal |
| End User | Hospitals, Clinics, Homecare, Pharmacies |
| Therapy Area | Type 1 Diabetes, Type 2 Diabetes, Gestational Diabetes, Prediabetes |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Diabetes Drugs in Latin America Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at