444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
The desktop virtualization in manufacturing market represents a transformative technology segment that is revolutionizing how manufacturing enterprises manage their IT infrastructure and workforce productivity. This innovative approach enables manufacturers to deliver virtual desktop environments to employees across production floors, engineering departments, and administrative offices, creating unprecedented flexibility and operational efficiency.
Manufacturing organizations are increasingly adopting desktop virtualization solutions to address critical challenges including remote workforce management, security compliance, and cost optimization. The technology allows companies to centralize desktop management while providing secure access to manufacturing applications, CAD software, and enterprise resource planning systems from any location or device.
Market dynamics indicate robust growth driven by the increasing digitalization of manufacturing processes and the growing need for flexible work arrangements. According to industry analysis, the adoption rate of desktop virtualization in manufacturing environments has increased by 42% annually over the past three years, reflecting the technology’s strategic importance in modern manufacturing operations.
Key market segments include automotive manufacturing, aerospace and defense, electronics production, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and industrial machinery sectors. Each segment presents unique requirements for desktop virtualization, from high-performance computing needs in engineering applications to stringent security requirements in regulated industries.
The desktop virtualization in manufacturing market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of technologies, solutions, and services that enable manufacturing companies to create, deploy, and manage virtual desktop environments for their workforce. This technology separates the desktop operating system and applications from the physical hardware, allowing users to access their personalized desktop experience from various devices and locations.
Virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) in manufacturing environments encompasses hosted virtual machines running desktop operating systems, application virtualization platforms, and cloud-based desktop services specifically tailored for manufacturing workflows. The technology enables manufacturers to maintain centralized control over desktop environments while providing employees with flexible access to critical manufacturing applications and data.
Manufacturing-specific implementations often include specialized features such as support for industrial software applications, integration with manufacturing execution systems, and compatibility with shop floor devices. The technology addresses unique manufacturing challenges including shift-based operations, multi-site coordination, and the need for secure access to proprietary design and production data.
Desktop virtualization technology is experiencing unprecedented adoption across manufacturing sectors, driven by the convergence of digital transformation initiatives, remote work requirements, and operational efficiency demands. Manufacturing companies are leveraging virtual desktop solutions to modernize their IT infrastructure while maintaining the specialized computing requirements essential for production operations.
Strategic implementation of desktop virtualization in manufacturing environments delivers significant benefits including reduced IT management overhead, enhanced security posture, and improved workforce flexibility. Organizations report achieving 35% reduction in desktop management costs and 28% improvement in application deployment speed through virtualization initiatives.
Market evolution is characterized by increasing integration with cloud platforms, enhanced support for graphics-intensive manufacturing applications, and improved compatibility with Internet of Things (IoT) devices used in smart manufacturing environments. The technology is becoming integral to Industry 4.0 initiatives and digital factory transformations.
Competitive landscape features established virtualization vendors expanding their manufacturing-focused offerings alongside specialized providers developing industry-specific solutions. Innovation focuses on performance optimization for CAD applications, enhanced security features for intellectual property protection, and seamless integration with manufacturing software ecosystems.
Manufacturing industry adoption of desktop virtualization is accelerating due to several converging factors that make virtual desktop infrastructure increasingly attractive for production environments. Key insights reveal fundamental shifts in how manufacturers approach desktop computing and workforce management.
Digital transformation initiatives across manufacturing industries serve as the primary catalyst for desktop virtualization adoption. Manufacturers are modernizing their IT infrastructure to support advanced manufacturing technologies, requiring flexible and scalable desktop computing solutions that can adapt to evolving operational requirements.
Remote work requirements have fundamentally changed how manufacturing companies approach workforce management. The need to provide secure access to manufacturing applications and data from remote locations has accelerated virtualization adoption, with organizations reporting 58% increase in remote access requirements for engineering and administrative functions.
Security concerns related to intellectual property protection and regulatory compliance drive significant investment in desktop virtualization solutions. Manufacturing companies handling sensitive design data, proprietary processes, and regulated information require centralized security controls that virtual desktop environments provide effectively.
Cost reduction pressures motivate manufacturers to seek more efficient IT management approaches. Desktop virtualization enables organizations to extend hardware lifecycles, reduce support overhead, and optimize software licensing, delivering measurable cost benefits that align with operational efficiency objectives.
Workforce mobility demands reflect changing employee expectations and operational requirements. Manufacturing professionals increasingly require access to desktop applications from multiple locations, including production floors, remote sites, and home offices, driving adoption of flexible virtualization solutions.
Implementation complexity presents significant challenges for manufacturing organizations considering desktop virtualization adoption. The technical requirements for deploying virtual desktop infrastructure, including network optimization, storage configuration, and application compatibility testing, can overwhelm internal IT resources and delay implementation timelines.
Performance concerns related to graphics-intensive manufacturing applications create hesitation among potential adopters. CAD software, simulation tools, and visualization applications require substantial computing resources, and organizations worry about performance degradation in virtualized environments affecting productivity and user satisfaction.
Initial investment requirements for desktop virtualization infrastructure can strain manufacturing budgets, particularly for smaller organizations. The costs associated with server hardware, storage systems, networking upgrades, and software licensing create financial barriers that slow adoption rates in cost-sensitive manufacturing segments.
Change management challenges emerge as manufacturing employees adapt to virtualized desktop environments. Training requirements, workflow adjustments, and user resistance to new technology interfaces can impact implementation success and require significant organizational change management efforts.
Network dependency risks concern manufacturers operating in locations with limited connectivity options. Desktop virtualization requires reliable, high-bandwidth network connections, and organizations in remote manufacturing locations may face connectivity challenges that affect solution viability and user experience quality.
Industry 4.0 integration presents substantial opportunities for desktop virtualization vendors to develop specialized solutions supporting smart manufacturing initiatives. The convergence of IoT devices, artificial intelligence, and advanced analytics in manufacturing environments creates demand for flexible desktop platforms that can support emerging technologies and workflows.
Cloud-based deployment models offer significant growth potential as manufacturing companies seek to reduce infrastructure complexity and operational overhead. Desktop-as-a-Service (DaaS) solutions specifically designed for manufacturing applications can address scalability requirements while minimizing capital investment and technical management burdens.
Edge computing integration represents an emerging opportunity as manufacturers deploy computing resources closer to production environments. Virtual desktop solutions optimized for edge deployment can support real-time manufacturing applications while maintaining centralized management and security controls.
Artificial intelligence enhancement creates opportunities for intelligent desktop virtualization platforms that can optimize resource allocation, predict performance issues, and automate management tasks. AI-powered solutions can improve user experience while reducing administrative overhead for manufacturing IT departments.
Vertical market specialization enables solution providers to develop industry-specific offerings tailored to unique manufacturing requirements. Specialized solutions for automotive, aerospace, pharmaceutical, and other manufacturing sectors can command premium pricing while delivering superior value through targeted functionality and compliance features.
Technology evolution continues to reshape the desktop virtualization landscape in manufacturing, with advances in graphics processing, network optimization, and cloud computing enhancing solution capabilities and user experience. These technological improvements address historical performance limitations and expand the range of manufacturing applications suitable for virtualization.
Competitive intensity is increasing as established virtualization vendors compete with cloud service providers and specialized manufacturing technology companies. This competition drives innovation in pricing models, feature development, and customer support, ultimately benefiting manufacturing organizations through improved solution options and value propositions.
Regulatory influences shape market development as manufacturing industries face evolving compliance requirements related to data security, privacy protection, and operational transparency. Desktop virtualization solutions must adapt to support regulatory compliance while maintaining operational efficiency and user productivity.
Economic factors including manufacturing sector growth, capital investment trends, and technology spending patterns influence market dynamics. Economic uncertainty can slow adoption decisions, while periods of growth accelerate investment in modernization initiatives that include desktop virtualization components.
User expectations continue to evolve as manufacturing professionals become more familiar with consumer technology experiences. The demand for intuitive interfaces, mobile device support, and seamless application access drives solution development and influences purchasing decisions across manufacturing organizations.
Comprehensive market analysis employs multiple research methodologies to ensure accurate and reliable insights into the desktop virtualization in manufacturing market. The research approach combines quantitative data collection with qualitative analysis to provide a complete understanding of market dynamics, trends, and opportunities.
Primary research activities include structured interviews with manufacturing IT executives, desktop virtualization vendors, and industry consultants. These interviews provide firsthand insights into adoption drivers, implementation challenges, and future requirements that shape market development and solution evolution.
Secondary research sources encompass industry reports, vendor documentation, regulatory filings, and academic studies related to manufacturing technology adoption and virtualization trends. This comprehensive data collection ensures broad market coverage and validates primary research findings through multiple information sources.
Market sizing methodologies utilize bottom-up and top-down approaches to estimate market scope and growth potential. Analysis includes examination of manufacturing industry segments, technology adoption rates, and spending patterns to develop accurate market assessments and growth projections.
Data validation processes ensure research accuracy through cross-referencing multiple sources, expert review panels, and statistical analysis techniques. Quality assurance measures maintain research integrity and provide confidence in market insights and recommendations presented to stakeholders.
North American markets lead desktop virtualization adoption in manufacturing, driven by advanced technology infrastructure, regulatory compliance requirements, and significant investment in digital transformation initiatives. The region accounts for approximately 38% market share globally, with strong growth in automotive, aerospace, and electronics manufacturing sectors.
European manufacturing demonstrates robust adoption of desktop virtualization solutions, particularly in Germany, France, and the United Kingdom. European organizations prioritize data sovereignty and regulatory compliance, driving demand for on-premises and hybrid virtualization deployments that maintain local data control while enabling operational flexibility.
Asia-Pacific regions exhibit the highest growth rates in desktop virtualization adoption, with manufacturing expansion in China, India, and Southeast Asian countries creating substantial demand for scalable IT solutions. The region’s focus on manufacturing modernization and workforce development supports 45% annual growth in virtualization implementations.
Latin American markets show increasing interest in desktop virtualization as manufacturing operations expand and modernize. Countries including Mexico, Brazil, and Argentina are investing in technology infrastructure to support manufacturing competitiveness, creating opportunities for virtualization solution providers.
Middle East and Africa represent emerging markets for desktop virtualization in manufacturing, with growing industrial sectors and government initiatives supporting technology adoption. Regional growth is driven by diversification efforts away from resource-based economies toward manufacturing and technology-intensive industries.
Market leadership in desktop virtualization for manufacturing is characterized by a mix of established virtualization vendors, cloud service providers, and specialized manufacturing technology companies. Competition focuses on performance optimization, industry-specific features, and comprehensive support for manufacturing workflows and applications.
Innovation strategies among competitive players include development of manufacturing-specific features, enhanced graphics processing capabilities, and improved integration with industrial software applications. Companies are investing in research and development to address unique manufacturing requirements and differentiate their offerings in competitive markets.
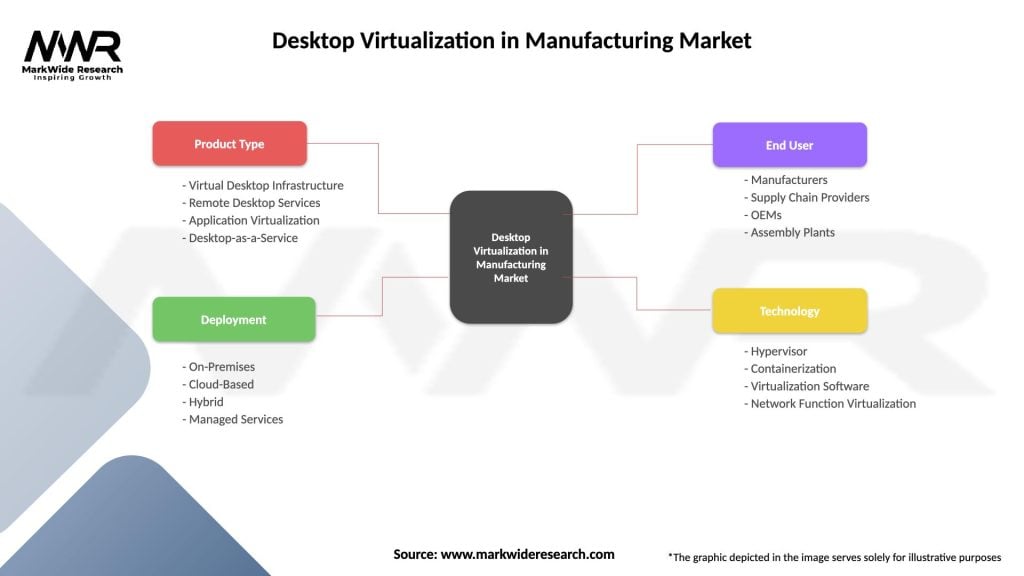
Technology-based segmentation divides the desktop virtualization in manufacturing market into distinct categories based on deployment models and technical architectures. Each segment serves different manufacturing requirements and organizational preferences for technology implementation and management.
By Deployment Model:
By Manufacturing Sector:
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) represents the largest segment within desktop virtualization for manufacturing, providing comprehensive desktop environments hosted on centralized server infrastructure. This category appeals to manufacturers requiring maximum control over desktop configurations and data security while supporting resource-intensive applications common in manufacturing environments.
Desktop-as-a-Service (DaaS) demonstrates the highest growth rates as manufacturing companies seek to reduce infrastructure complexity and operational overhead. Cloud-based desktop services offer scalability advantages and simplified management, particularly attractive to smaller manufacturers and organizations with distributed operations requiring flexible access solutions.
Application virtualization serves as a complementary technology enabling manufacturers to deliver specific applications without full desktop virtualization. This approach suits organizations with limited virtualization requirements or those seeking to modernize specific manufacturing applications while maintaining existing desktop infrastructure.
Graphics-intensive solutions address the unique requirements of manufacturing applications including CAD software, simulation tools, and visualization platforms. These specialized offerings command premium pricing while delivering essential performance capabilities for engineering and design workflows in manufacturing environments.
Mobile device management integration enables manufacturers to extend desktop virtualization benefits to tablets, smartphones, and ruggedized devices used in production environments. This category supports mobility requirements while maintaining security and management controls essential for manufacturing operations.
Manufacturing organizations realize substantial operational benefits through desktop virtualization implementation, including enhanced workforce flexibility, improved security posture, and reduced IT management complexity. These advantages translate into measurable improvements in productivity, cost efficiency, and competitive positioning within manufacturing markets.
IT departments benefit from centralized desktop management capabilities that simplify software deployment, security updates, and user support processes. Virtualization reduces the complexity of managing diverse hardware configurations while providing consistent desktop experiences across manufacturing facilities and remote locations.
Manufacturing employees gain access to familiar desktop environments from multiple devices and locations, supporting flexible work arrangements and improving work-life balance. The technology enables secure access to manufacturing applications and data regardless of physical location or device type.
Solution vendors capitalize on growing demand for manufacturing-specific virtualization capabilities, creating opportunities for specialized product development and premium pricing. The market expansion enables vendors to develop long-term customer relationships and recurring revenue streams through ongoing support and services.
System integrators benefit from increased demand for virtualization implementation and support services. The complexity of manufacturing environments creates opportunities for specialized consulting, implementation, and managed services that support ongoing virtualization operations and optimization.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Cloud-first strategies are reshaping desktop virtualization adoption in manufacturing as organizations prioritize operational flexibility and reduced infrastructure complexity. MarkWide Research analysis indicates that cloud-based desktop services adoption has increased by 52% annually among manufacturing companies seeking scalable and cost-effective virtualization solutions.
Artificial intelligence integration represents a significant trend as virtualization platforms incorporate AI capabilities for performance optimization, predictive maintenance, and automated resource management. These intelligent features enhance user experience while reducing administrative overhead for manufacturing IT departments.
Edge computing adoption drives development of distributed virtualization architectures that bring desktop computing resources closer to manufacturing operations. This trend addresses latency requirements for real-time applications while maintaining centralized management and security controls essential for manufacturing environments.
Zero trust security models influence virtualization solution development as manufacturers implement comprehensive security frameworks that verify every access request regardless of user location or device type. This approach enhances protection for sensitive manufacturing data and intellectual property.
Sustainability initiatives motivate manufacturers to adopt virtualization solutions that reduce energy consumption and hardware requirements. Desktop virtualization supports environmental goals by extending hardware lifecycles and optimizing resource utilization across manufacturing operations.
Strategic partnerships between virtualization vendors and manufacturing software providers are creating integrated solutions that address specific industry requirements. These collaborations result in optimized performance for CAD applications, manufacturing execution systems, and other critical manufacturing software platforms.
Technology acquisitions enable established virtualization companies to expand their manufacturing-focused capabilities and market reach. Recent acquisitions have strengthened vendor portfolios with specialized graphics processing, security features, and industry-specific functionality essential for manufacturing environments.
Product innovations focus on addressing manufacturing-specific challenges including support for industrial devices, enhanced graphics performance, and improved integration with manufacturing software ecosystems. These developments expand the range of manufacturing applications suitable for virtualization deployment.
Regulatory compliance enhancements help virtualization solutions meet evolving manufacturing industry requirements related to data protection, audit trails, and operational transparency. Compliance features become increasingly important for manufacturers in regulated industries including pharmaceuticals, aerospace, and automotive sectors.
Market expansion initiatives by leading vendors include establishment of regional data centers, local support organizations, and partnerships with manufacturing-focused system integrators. These efforts improve solution accessibility and support quality for manufacturing customers in diverse geographic markets.
Implementation planning should prioritize comprehensive assessment of manufacturing application requirements, network infrastructure capabilities, and user workflow analysis before virtualization deployment. Organizations benefit from phased implementation approaches that minimize operational disruption while demonstrating value through pilot programs and gradual expansion.
Vendor selection requires careful evaluation of manufacturing-specific capabilities, performance benchmarks, and long-term support commitments. MWR recommends focusing on vendors with proven manufacturing industry experience and comprehensive solution portfolios that address current and future requirements.
Change management strategies should address user training, workflow optimization, and organizational culture adaptation to maximize virtualization benefits. Successful implementations invest significantly in user education and support programs that ensure smooth transition to virtualized desktop environments.
Security considerations must encompass comprehensive risk assessment, multi-layered protection strategies, and ongoing monitoring capabilities. Manufacturing organizations should implement zero trust security models and regular security audits to protect sensitive data and intellectual property in virtualized environments.
Performance optimization requires ongoing monitoring, capacity planning, and infrastructure tuning to maintain user satisfaction and application performance. Organizations should establish performance baselines and implement proactive management practices that prevent performance degradation and user productivity issues.
Market evolution will be characterized by continued integration with emerging technologies including artificial intelligence, edge computing, and Internet of Things platforms. These technological convergences will create new opportunities for desktop virtualization in manufacturing while addressing evolving operational requirements and user expectations.
Adoption acceleration is expected as manufacturing companies recognize the strategic value of flexible desktop computing solutions for supporting hybrid work models, operational resilience, and digital transformation initiatives. Growth projections indicate sustained expansion across all manufacturing sectors and geographic regions.
Technology advancement will focus on performance improvements for graphics-intensive applications, enhanced security features, and simplified management capabilities. Innovation priorities include reducing implementation complexity while expanding functionality to support emerging manufacturing technologies and workflows.
Market consolidation may occur as larger technology companies acquire specialized virtualization vendors to expand their manufacturing industry capabilities. This consolidation could accelerate solution development while providing customers with more comprehensive technology platforms and support services.
Regulatory evolution will influence solution development as manufacturing industries face new compliance requirements related to data protection, cybersecurity, and operational transparency. Virtualization solutions must adapt to support regulatory compliance while maintaining operational efficiency and user productivity in manufacturing environments.
Desktop virtualization in manufacturing represents a critical technology transformation that enables organizations to modernize their IT infrastructure while supporting evolving workforce requirements and operational demands. The market demonstrates strong growth potential driven by digital transformation initiatives, security requirements, and cost optimization objectives across manufacturing industries.
Strategic implementation of desktop virtualization solutions delivers measurable benefits including improved operational efficiency, enhanced security posture, and increased workforce flexibility. Manufacturing companies that successfully deploy virtualization technologies gain competitive advantages through reduced IT complexity, optimized resource utilization, and improved user productivity.
Future success in this market will depend on continued innovation in performance optimization, security enhancement, and integration capabilities that address unique manufacturing requirements. Organizations and solution providers that prioritize user experience, operational efficiency, and strategic alignment with manufacturing objectives will realize the greatest value from desktop virtualization investments and market opportunities.
What is Desktop Virtualization in Manufacturing?
Desktop virtualization in manufacturing refers to the technology that allows users to access a virtual desktop environment hosted on a centralized server. This approach enables manufacturers to streamline operations, enhance collaboration, and improve data security across various production processes.
What are the key players in the Desktop Virtualization in Manufacturing Market?
Key players in the Desktop Virtualization in Manufacturing Market include VMware, Citrix Systems, and Microsoft. These companies provide solutions that enhance productivity and efficiency in manufacturing environments, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Desktop Virtualization in Manufacturing Market?
The main drivers of growth in the Desktop Virtualization in Manufacturing Market include the increasing need for remote access to manufacturing systems, the demand for improved data security, and the rising trend of digital transformation in manufacturing processes.
What challenges does the Desktop Virtualization in Manufacturing Market face?
Challenges in the Desktop Virtualization in Manufacturing Market include concerns over data privacy, the complexity of integration with existing systems, and the need for significant initial investment in infrastructure.
What opportunities exist in the Desktop Virtualization in Manufacturing Market?
Opportunities in the Desktop Virtualization in Manufacturing Market include the growing adoption of cloud-based solutions, advancements in virtualization technologies, and the increasing focus on Industry Four Point Zero initiatives that promote automation and connectivity.
What trends are shaping the Desktop Virtualization in Manufacturing Market?
Trends shaping the Desktop Virtualization in Manufacturing Market include the rise of edge computing, the integration of artificial intelligence for enhanced analytics, and the shift towards hybrid work environments that require flexible access to manufacturing resources.
Desktop Virtualization in Manufacturing Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Virtual Desktop Infrastructure, Remote Desktop Services, Application Virtualization, Desktop-as-a-Service |
| Deployment | On-Premises, Cloud-Based, Hybrid, Managed Services |
| End User | Manufacturers, Supply Chain Providers, OEMs, Assembly Plants |
| Technology | Hypervisor, Containerization, Virtualization Software, Network Function Virtualization |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Desktop Virtualization in Manufacturing Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at