444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
Dark fiber networks play a crucial role in the telecommunications industry, providing the backbone infrastructure for high-speed data transmission. With the increasing demand for seamless connectivity and the proliferation of data-intensive applications, the dark fiber network market has witnessed significant growth in recent years. This market overview delves into the meaning of dark fiber networks, key market insights, drivers, restraints, opportunities, and dynamics, along with regional analysis, competitive landscape, segmentation, and more.
Meaning
Dark fiber refers to the unused or unlit optical fiber cables that are laid underground or suspended on utility poles. These fiber cables have not been activated or equipped with the necessary transmission equipment, allowing them to remain “dark.” Dark fiber networks are essentially the physical infrastructure composed of these idle fiber optic cables.
Executive Summary
The dark fiber network market has been witnessing robust growth due to the increasing demand for high-speed connectivity and bandwidth-intensive applications. The market is characterized by the presence of several players, ranging from telecommunication service providers to enterprises. As organizations strive to enhance their network performance and data transfer capabilities, the adoption of dark fiber networks has become a strategic imperative.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The dark fiber network market is highly dynamic, influenced by various factors such as technological advancements, regulatory landscape, and evolving customer demands. Understanding the market dynamics is crucial for stakeholders to make informed decisions and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Technological advancements in fiber optic technology, including higher capacity and improved signal quality, are driving the adoption of dark fiber networks. The continuous evolution of network architecture and the emergence of technologies like 5G and IoT further propel market growth.
Moreover, government initiatives and investments in digital infrastructure and connectivity drive the expansion of dark fiber networks. Funding programs and subsidies aimed at enhancing broadband connectivity in underserved areas create new opportunities for market players.
On the other hand, challenges related to high initial investment, technical expertise, and regulatory compliance can hinder market growth. Overcoming these hurdles requires collaboration among industry participants, regulatory bodies, and government entities to streamline network deployment processes and ensure a favorable operating environment.
Regional Analysis
The dark fiber network market exhibits regional variations in terms of adoption, infrastructure availability, and market players. Key regions analyzed in this report include North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East and Africa.
North America: North America dominates the dark fiber network market, driven by advanced telecommunication infrastructure, high internet penetration, and a robust digital ecosystem. The presence of major technology companies and data centers further fuels the demand for dark fiber networks in this region.
Europe: Europe witnesses significant growth in the dark fiber network market, fueled by initiatives to enhance broadband connectivity and support digital transformation. The European Union’s focus on building a unified digital market and improving digital infrastructure acts as a catalyst for market expansion.
Asia Pacific: The Asia Pacific region presents immense growth potential for the dark fiber network market, attributed to the rapid digitalization across emerging economies, such as China and India. The increasing demand for high-speed connectivity, driven by a growing population and expanding internet penetration, boosts market growth in this region.
Latin America: Latin America is experiencing a gradual adoption of dark fiber networks, driven by initiatives to bridge the digital divide and enhance internet connectivity in underserved areas. The region’s expanding IT and telecommunication sector contributes to market growth.
Middle East and Africa: The Middle East and Africa are witnessing significant growth in the dark fiber network market, fueled by the rapid development of digital infrastructure and increasing investment in advanced telecommunications networks. Government initiatives promoting connectivity and digital transformation further augment market growth.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Dark Fiber Network Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
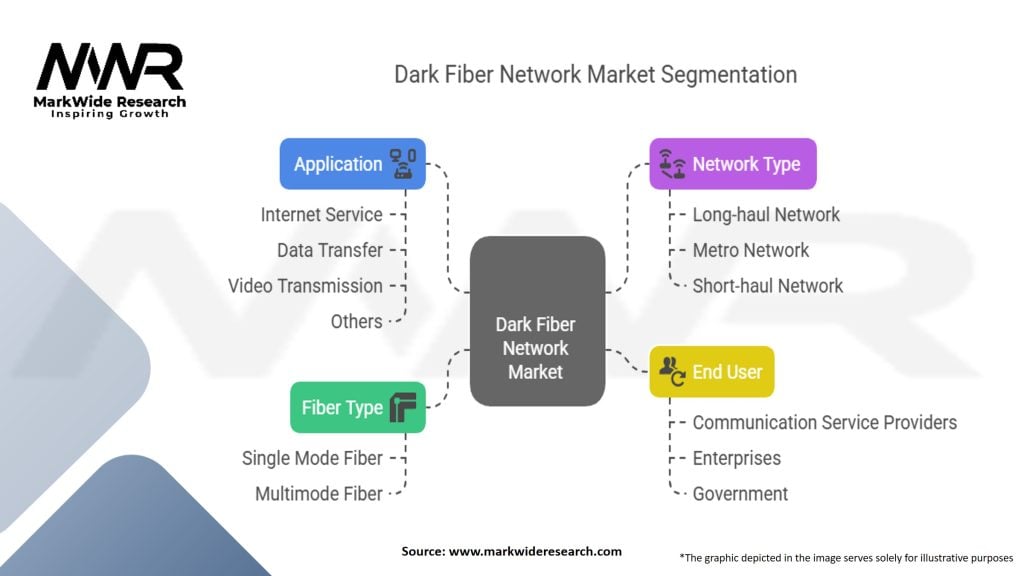
Segmentation
The dark fiber network market can be segmented based on the following criteria:
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
Industry participants and stakeholders in the dark fiber network market can benefit in the following ways:
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the dark fiber network market. On one hand, the surge in remote working, online learning, and video streaming has increased the demand for high-speed connectivity, driving the adoption of dark fiber networks. On the other hand, the economic uncertainties and disruptions caused by the pandemic have led to delays in network infrastructure projects and reduced investments in some regions. However, the long-term potential of dark fiber networks remains strong, as organizations prioritize robust connectivity and infrastructure resilience.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the dark fiber network market appears promising. The increasing demand for high-speed connectivity, fueled by emerging technologies and data-intensive applications, will continue to drive market growth. The rollout of 5G networks, expansion of cloud services, and the proliferation of IoT devices will further fuel the adoption of dark fiber networks. However, challenges such as high initial investment and regulatory complexities need to be addressed to unlock the full potential of the market.
Conclusion
The dark fiber network market is witnessing significant growth driven by the increasing demand for high-speed connectivity, bandwidth-intensive applications, and enhanced network security. With its ability to provide reliable and scalable infrastructure, dark fiber networks are becoming a preferred choice for telecommunication service providers, enterprises, and data centers. While challenges exist, such as high initial investment and regulatory hurdles, the market presents ample opportunities for industry participants. By capitalizing on key trends, collaborating with stakeholders, and addressing customer needs, dark fiber network providers can position themselves for success in the evolving telecommunications landscape.
What is a dark fiber network?
A dark fiber network refers to unused or unlit optical fiber that is available for lease or sale. It is often utilized by telecommunications companies and enterprises to create private networks for data transmission, enhancing bandwidth and security.
Who are the key players in the dark fiber network market?
Key players in the dark fiber network market include companies like Zayo Group, Crown Castle, and Uniti Group, which provide extensive fiber optic infrastructure and services to various industries, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the dark fiber network market?
The growth of the dark fiber network market is driven by increasing demand for high-speed internet, the expansion of data centers, and the rise of cloud computing services. Additionally, the need for secure and private communication channels is propelling market expansion.
What challenges does the dark fiber network market face?
Challenges in the dark fiber network market include high initial investment costs, regulatory hurdles, and competition from alternative technologies such as wireless solutions. These factors can hinder market entry and expansion for new players.
What opportunities exist in the dark fiber network market?
Opportunities in the dark fiber network market include the growing adoption of IoT devices, the increasing need for enhanced connectivity in urban areas, and the potential for partnerships with cloud service providers. These trends can lead to expanded service offerings and customer bases.
What are the current trends in the dark fiber network market?
Current trends in the dark fiber network market include the rise of edge computing, increased investment in fiber infrastructure, and a focus on sustainability in network deployment. These trends are shaping the future of connectivity and data management.
Dark Fiber Network Market
| Segmentation | Details |
|---|---|
| Fiber Type | Single Mode Fiber, Multimode Fiber |
| Network Type | Long-haul Network, Metro Network, Short-haul Network |
| End User | Communication Service Providers, Enterprises, Government |
| Application | Internet Service, Data Transfer, Video Transmission, Others |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Dark Fiber Network Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at