444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
The construction repair and rehabilitation chemicals market represents a dynamic and rapidly evolving sector within the global construction industry. This specialized market encompasses a comprehensive range of chemical solutions designed to restore, strengthen, and extend the lifespan of existing concrete structures and infrastructure. Market growth is driven by increasing infrastructure deterioration, urbanization pressures, and the growing emphasis on sustainable construction practices that prioritize repair over replacement.
Infrastructure aging across developed nations has created substantial demand for advanced chemical solutions that can effectively address structural deficiencies. The market includes various product categories such as concrete repair mortars, protective coatings, waterproofing compounds, structural adhesives, and corrosion inhibitors. Growth projections indicate the market is expanding at a robust 6.8% CAGR, reflecting the critical need for infrastructure maintenance and rehabilitation globally.
Regional dynamics show significant variation in market adoption, with North America and Europe leading in terms of technological advancement and regulatory compliance. Asia-Pacific emerges as the fastest-growing region, driven by rapid industrialization and increasing infrastructure investments. The market benefits from continuous innovation in chemical formulations that offer enhanced performance characteristics including faster curing times, improved durability, and environmental sustainability.
The construction repair and rehabilitation chemicals market refers to the specialized segment of chemical products specifically formulated to restore, strengthen, and protect existing concrete and masonry structures. These advanced chemical solutions address various structural issues including concrete deterioration, steel corrosion, water infiltration, and structural weakening caused by environmental factors, aging, or inadequate initial construction practices.
Chemical formulations in this market are engineered to provide specific performance characteristics such as high bond strength, chemical resistance, thermal stability, and long-term durability. The products serve as cost-effective alternatives to complete structural replacement, enabling property owners and infrastructure managers to extend asset lifecycles while maintaining structural integrity and safety standards.
Market scope encompasses both preventive and corrective applications, ranging from routine maintenance procedures to major rehabilitation projects. These chemicals play a crucial role in preserving critical infrastructure including bridges, tunnels, parking structures, industrial facilities, and residential buildings, contributing significantly to sustainable construction practices and resource conservation.
Market dynamics in the construction repair and rehabilitation chemicals sector reflect a mature yet rapidly evolving industry driven by infrastructure aging and sustainability imperatives. The market demonstrates strong growth potential with increasing adoption of advanced chemical solutions that offer superior performance compared to traditional repair methods. Key growth drivers include stringent building codes, environmental regulations, and the economic advantages of repair over replacement strategies.
Product innovation continues to shape market evolution, with manufacturers developing eco-friendly formulations that reduce environmental impact while maintaining high performance standards. The market benefits from technological advancements in polymer chemistry, nanotechnology, and smart materials that enhance product effectiveness and application versatility. Market penetration varies significantly across regions, with developed markets showing 75% adoption rates for advanced repair chemicals compared to 45% in emerging markets.
Competitive landscape features a mix of global chemical giants and specialized manufacturers, creating a dynamic environment that fosters innovation and competitive pricing. The market outlook remains positive, supported by increasing infrastructure investments, growing awareness of lifecycle cost benefits, and regulatory requirements that mandate regular maintenance and rehabilitation of critical structures.
Market analysis reveals several critical insights that define the current state and future trajectory of the construction repair and rehabilitation chemicals market:
Infrastructure aging stands as the primary driver propelling market growth, with millions of concrete structures worldwide approaching or exceeding their design lifecycles. This phenomenon is particularly pronounced in developed nations where post-World War II construction boom has resulted in widespread infrastructure deterioration requiring immediate attention. Structural assessments indicate that preventive maintenance using advanced chemical solutions can extend infrastructure lifecycles by 20-30 years.
Economic considerations significantly influence market adoption, as repair and rehabilitation typically require substantially lower capital investment compared to complete reconstruction. Property owners and infrastructure managers increasingly recognize the long-term cost benefits of proactive maintenance strategies that utilize specialized chemical solutions. Lifecycle cost analysis demonstrates that early intervention with quality repair chemicals can reduce total ownership costs by up to 40%.
Environmental sustainability concerns drive demand for chemical solutions that minimize construction waste and reduce carbon footprints associated with demolition and reconstruction activities. Modern repair chemicals enable structures to achieve extended service lives while consuming fewer natural resources and generating less environmental impact. Regulatory frameworks increasingly mandate sustainable construction practices, further supporting market growth.
Urbanization pressures create additional market drivers as densely populated areas require infrastructure maintenance with minimal disruption to daily activities. Chemical repair solutions enable rapid application and curing, reducing project timelines and minimizing inconvenience to building occupants and surrounding communities. Smart city initiatives worldwide emphasize infrastructure resilience and longevity, creating favorable conditions for advanced repair chemical adoption.
High initial costs associated with premium repair chemicals can deter adoption, particularly in price-sensitive markets where immediate cost considerations outweigh long-term benefits. Many property owners and contractors remain focused on short-term expenses rather than lifecycle cost advantages, creating resistance to higher-priced advanced chemical solutions. Budget constraints in public infrastructure projects often favor lower-cost alternatives despite inferior long-term performance.
Technical complexity in application procedures requires specialized knowledge and training, limiting market accessibility for smaller contractors and maintenance teams. Proper surface preparation, mixing ratios, environmental conditions, and curing requirements demand expertise that may not be readily available in all markets. Application errors can result in product failure and costly remediation, creating reluctance among inexperienced users.
Limited awareness regarding advanced repair chemical capabilities and benefits constrains market growth in emerging regions where traditional repair methods remain prevalent. Educational initiatives and technical support programs are essential to overcome knowledge gaps and demonstrate product value propositions. Cultural resistance to new technologies and methods can slow adoption rates in conservative construction markets.
Regulatory variations across different regions create compliance challenges for manufacturers and users, potentially limiting product availability and increasing costs. Inconsistent standards and approval processes can delay market entry and complicate product selection for international projects. Environmental regulations may restrict certain chemical formulations, requiring continuous product reformulation and testing.
Emerging markets present substantial growth opportunities as developing nations invest heavily in infrastructure development and begin addressing maintenance needs of existing structures. Countries in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa demonstrate increasing awareness of repair chemical benefits and growing capacity for advanced construction technologies. Infrastructure investments in these regions create favorable conditions for market expansion and technology transfer.
Smart materials integration offers significant opportunities for product differentiation and premium positioning. Self-healing concrete additives, shape-memory polymers, and responsive chemical systems represent frontier technologies that can command higher margins while delivering superior performance. Research partnerships between chemical manufacturers and academic institutions accelerate innovation and create competitive advantages.
Digital transformation in construction creates opportunities for integrated solutions that combine repair chemicals with monitoring systems and predictive maintenance technologies. Internet of Things (IoT) sensors embedded in repair materials can provide real-time performance data and optimize maintenance schedules. Data analytics capabilities enable more precise product formulations and application recommendations.
Sustainability mandates drive demand for eco-friendly formulations that meet stringent environmental standards while maintaining high performance characteristics. Bio-based chemicals, recycled content incorporation, and carbon-neutral production processes represent growing market segments with premium pricing potential. Green building certifications increasingly recognize advanced repair chemicals as contributing factors to sustainable construction practices.
Supply chain dynamics in the construction repair chemicals market reflect complex interactions between raw material suppliers, chemical manufacturers, distributors, and end users. Recent global supply chain disruptions have highlighted the importance of supply chain resilience and regional manufacturing capabilities. Raw material volatility affects product pricing and availability, requiring manufacturers to develop flexible sourcing strategies and alternative formulations.
Technology evolution continues to reshape market dynamics through introduction of advanced chemical formulations with enhanced performance characteristics. Nanotechnology applications, polymer modifications, and hybrid systems create new product categories while potentially obsoleting traditional solutions. Innovation cycles are accelerating, requiring continuous investment in research and development to maintain competitive positioning.
Customer behavior patterns show increasing sophistication in product selection criteria, with buyers evaluating total cost of ownership, environmental impact, and long-term performance rather than focusing solely on initial purchase price. Specification processes increasingly involve multiple stakeholders including architects, engineers, sustainability consultants, and facility managers, creating more complex decision-making dynamics.
Competitive pressures intensify as market maturity increases and new entrants challenge established players with innovative products and aggressive pricing strategies. Market consolidation through mergers and acquisitions creates larger entities with enhanced research capabilities and global reach, while specialized niche players focus on specific applications or regional markets.
Comprehensive analysis of the construction repair and rehabilitation chemicals market employs multiple research methodologies to ensure accuracy and reliability of findings. Primary research involves extensive interviews with industry executives, technical specialists, contractors, and end users across different regions and market segments. Survey methodologies capture quantitative data regarding market size, growth rates, pricing trends, and competitive positioning.
Secondary research encompasses analysis of industry publications, technical literature, patent databases, regulatory documents, and company financial reports. Market intelligence gathering includes monitoring of trade shows, conferences, and industry forums to identify emerging trends and technological developments. Data triangulation techniques validate findings across multiple sources and methodologies to ensure research integrity.
Market modeling utilizes statistical analysis and forecasting techniques to project future market trends and growth trajectories. Econometric models incorporate macroeconomic indicators, construction activity levels, infrastructure spending patterns, and demographic trends to develop robust market projections. Scenario analysis evaluates potential market outcomes under different economic and regulatory conditions.
Expert validation processes involve review of research findings by industry experts, academic researchers, and technical specialists to ensure accuracy and relevance. Peer review mechanisms and advisory panels provide additional quality assurance and help identify potential research gaps or biases. Continuous monitoring systems track market developments and update research findings as new information becomes available.
North America maintains market leadership in the construction repair and rehabilitation chemicals sector, driven by extensive aging infrastructure and stringent regulatory requirements. The region demonstrates 65% market penetration for advanced repair chemicals, reflecting high awareness levels and established distribution networks. United States infrastructure investments focus heavily on bridge rehabilitation, tunnel maintenance, and parking structure repairs, creating sustained demand for specialized chemical solutions.
Europe represents the second-largest market with strong emphasis on sustainability and environmental compliance. European Union regulations promote eco-friendly construction practices and mandate regular infrastructure maintenance, supporting market growth. Germany and United Kingdom lead regional adoption with sophisticated specification processes and high-performance requirements. Market maturity in Western Europe contrasts with growth opportunities in Eastern European countries undergoing infrastructure modernization.
Asia-Pacific emerges as the fastest-growing regional market, driven by rapid urbanization and increasing infrastructure investments. China and India demonstrate particularly strong growth potential as construction activities expand and maintenance awareness increases. The region shows 45% adoption rates for advanced repair chemicals, indicating substantial room for market expansion. Technology transfer from developed markets accelerates product adoption and local manufacturing capabilities.
Latin America and Middle East & Africa represent emerging markets with growing recognition of repair chemical benefits. These regions face infrastructure challenges related to climate conditions, seismic activity, and resource constraints that create opportunities for specialized chemical solutions. Government initiatives promoting infrastructure development and maintenance create favorable market conditions for international suppliers and local manufacturers.
Market leadership in the construction repair and rehabilitation chemicals sector is distributed among several global chemical companies and specialized manufacturers, each with distinct competitive advantages and market positioning strategies:
Competitive strategies emphasize product innovation, technical support services, and regional market expansion. Companies invest heavily in research and development to create differentiated products with superior performance characteristics and environmental benefits. Strategic partnerships with distributors, contractors, and engineering firms enhance market reach and customer relationships.
Product segmentation in the construction repair and rehabilitation chemicals market reflects diverse application requirements and performance specifications:
By Product Type:
By Application:
By Technology:
Concrete repair mortars represent the largest product category, accounting for approximately 35% of market share due to widespread concrete deterioration issues and established application methods. These products range from simple patching compounds to high-performance structural repair systems with specific strength and durability requirements. Innovation focus includes rapid-setting formulations, fiber-reinforced systems, and self-consolidating properties that improve application efficiency.
Protective coatings demonstrate strong growth potential as preventive maintenance strategies gain acceptance among property owners and infrastructure managers. This category includes various coating systems such as penetrating sealers, surface hardeners, and barrier coatings that protect concrete from environmental damage. Technology advancement emphasizes smart coatings with self-healing properties and integrated monitoring capabilities.
Structural adhesives serve critical applications in seismic retrofitting, structural strengthening, and composite material bonding. These high-performance products require extensive testing and certification to meet structural engineering requirements. Market growth is driven by increasing adoption of external reinforcement systems and post-installed anchoring applications that demand reliable bonding performance.
Waterproofing compounds address fundamental moisture protection needs across all construction sectors. Product categories include crystalline waterproofing, membrane systems, and penetrating sealers that provide different levels of protection and application methods. Sustainability trends favor water-based formulations and bio-compatible systems that minimize environmental impact while maintaining effectiveness.
Property owners benefit significantly from advanced repair chemicals through extended asset lifecycles, reduced maintenance costs, and improved structural performance. These solutions enable proactive maintenance strategies that prevent costly emergency repairs and minimize business disruption. Return on investment typically ranges from 300-500% over the extended service life of repaired structures.
Contractors and applicators gain competitive advantages through access to high-performance products that enable faster project completion and superior results. Advanced repair chemicals often feature improved workability, extended working time, and predictable curing characteristics that reduce application risks and rework requirements. Technical support from manufacturers enhances contractor capabilities and project success rates.
Engineers and specifiers benefit from comprehensive product data, performance warranties, and technical expertise that support confident specification decisions. Modern repair chemicals undergo extensive testing and certification processes that provide reliable performance data for engineering calculations and lifecycle assessments. Design flexibility increases through availability of products with specific performance characteristics tailored to unique project requirements.
Manufacturers and suppliers participate in a growing market with opportunities for product differentiation and premium positioning. Innovation in chemical formulations, application methods, and performance characteristics creates competitive advantages and higher profit margins. Market expansion opportunities exist in emerging regions and new application areas that require specialized chemical solutions.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Sustainability integration emerges as a dominant trend shaping product development and market positioning strategies. Manufacturers increasingly focus on bio-based raw materials, reduced volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, and recyclable packaging to meet environmental requirements and customer preferences. Life cycle assessment methodologies help quantify environmental benefits and support green building certification programs.
Smart material development represents a transformative trend incorporating sensors, self-healing capabilities, and responsive properties into repair chemical formulations. These advanced materials can monitor structural health, automatically repair minor damage, and adapt to changing environmental conditions. Digital integration enables real-time performance monitoring and predictive maintenance scheduling.
Application technology advancement focuses on improving ease of use, reducing application time, and minimizing skill requirements. Innovations include pre-mixed systems, spray-applied formulations, and self-leveling products that simplify installation procedures. Robotic application systems are being developed for hazardous or difficult-to-access repair locations.
Performance enhancement continues through development of products with superior strength, durability, and chemical resistance characteristics. Nanotechnology applications enable creation of materials with unprecedented performance properties while maintaining workability and cost-effectiveness. Hybrid systems combining different chemical technologies provide optimized solutions for specific applications.
Product launches in recent years demonstrate industry commitment to innovation and market expansion. Major manufacturers have introduced eco-friendly formulations that meet stringent environmental standards while maintaining high performance characteristics. Bio-based repair mortars and carbon-neutral protective coatings represent significant technological achievements that address sustainability concerns without compromising effectiveness.
Strategic partnerships between chemical manufacturers and technology companies accelerate development of smart repair materials with integrated monitoring capabilities. These collaborations combine chemical expertise with sensor technology and data analytics to create comprehensive structural health monitoring solutions. University partnerships advance fundamental research in polymer chemistry and materials science.
Manufacturing expansion activities focus on establishing regional production facilities to serve growing markets and reduce transportation costs. Companies are investing in automated production systems that improve quality consistency and reduce manufacturing costs. Capacity additions in Asia-Pacific and Latin America reflect confidence in regional market growth potential.
Regulatory approvals for new product formulations enable market entry and expand application possibilities. Recent approvals include products for potable water contact applications, food processing facilities, and seismic retrofitting projects. Certification programs provide third-party validation of product performance and quality standards.
Market participants should prioritize sustainability initiatives and eco-friendly product development to align with evolving customer preferences and regulatory requirements. MarkWide Research analysis indicates that companies investing in green chemistry and sustainable manufacturing practices achieve higher market growth rates and premium pricing opportunities. Investment in bio-based raw materials and carbon-neutral production processes will become increasingly important for competitive positioning.
Technology integration represents a critical success factor for future market leadership. Companies should explore partnerships with technology firms to develop smart materials with monitoring and self-healing capabilities. Digital transformation initiatives including mobile applications for product selection, augmented reality training tools, and IoT-enabled performance monitoring will differentiate market leaders from traditional suppliers.
Regional expansion strategies should focus on emerging markets with growing infrastructure needs and increasing construction activity. Establishing local manufacturing capabilities, distribution partnerships, and technical support services will be essential for capturing market share in these regions. Localization efforts should include product formulations adapted to regional climate conditions and construction practices.
Customer education programs will be crucial for market development, particularly in regions where awareness of advanced repair chemicals remains limited. Technical training, demonstration projects, and case study development help build confidence and drive adoption among contractors and specifiers. Value proposition communication should emphasize total cost of ownership benefits rather than focusing solely on initial product costs.
Market projections indicate sustained growth in the construction repair and rehabilitation chemicals sector, driven by infrastructure aging, urbanization pressures, and increasing emphasis on sustainable construction practices. MarkWide Research forecasts suggest the market will maintain robust growth rates exceeding 6% annually through the next decade, with emerging markets contributing disproportionately to overall expansion.
Technology evolution will continue reshaping the market through introduction of smart materials, nanotechnology applications, and bio-based formulations. These innovations will create new product categories while potentially displacing traditional solutions that cannot match advanced performance characteristics. Research investments in universities and corporate laboratories will accelerate the pace of technological advancement.
Regulatory landscape changes will increasingly favor environmentally responsible products and mandate higher performance standards for critical infrastructure applications. Building codes will likely incorporate more stringent requirements for repair material performance and durability, creating opportunities for premium products while challenging low-cost alternatives. International harmonization of standards may simplify global market access for qualified products.
Market consolidation through mergers and acquisitions will likely continue as companies seek to achieve scale advantages and expand geographic reach. Smaller specialized manufacturers may become acquisition targets for larger chemical companies seeking to enhance their construction chemicals portfolios. Innovation partnerships between established manufacturers and technology startups will become increasingly common as the industry embraces digital transformation and smart materials development.
The construction repair and rehabilitation chemicals market represents a dynamic and essential sector within the global construction industry, addressing critical infrastructure maintenance needs while supporting sustainable building practices. Market growth is driven by fundamental factors including infrastructure aging, urbanization pressures, and increasing recognition of repair cost advantages over replacement strategies. Technological advancement continues to enhance product performance and create new application opportunities, while regulatory support strengthens market foundations.
Regional dynamics show significant variation in market maturity and growth potential, with developed markets demonstrating high adoption rates and emerging markets offering substantial expansion opportunities. The competitive landscape features both global chemical giants and specialized manufacturers, creating a dynamic environment that fosters innovation and competitive pricing. Market segmentation across product types, applications, and technologies provides multiple avenues for growth and specialization.
Future prospects remain highly favorable, supported by massive global infrastructure requiring maintenance and rehabilitation, increasing environmental consciousness, and continuous technological innovation. Companies that successfully integrate sustainability initiatives, embrace digital transformation, and expand into emerging markets will be best positioned to capitalize on growth opportunities. The market’s evolution toward smart materials and integrated monitoring systems will create new value propositions and competitive advantages for forward-thinking participants in this essential industry sector.
What is Construction Repair and Rehabilitation Chemicals?
Construction Repair and Rehabilitation Chemicals refer to a range of products used to restore and enhance the structural integrity of buildings and infrastructure. These chemicals include adhesives, sealants, and coatings that are essential for repairing concrete, masonry, and other materials.
What are the key players in the Construction Repair and Rehabilitation Chemicals Market?
Key players in the Construction Repair and Rehabilitation Chemicals Market include BASF SE, Sika AG, and Dow Inc. These companies are known for their innovative solutions and extensive product portfolios that cater to various construction needs, among others.
What are the main drivers of the Construction Repair and Rehabilitation Chemicals Market?
The main drivers of the Construction Repair and Rehabilitation Chemicals Market include the increasing demand for infrastructure development and maintenance, the need for sustainable building practices, and the growing awareness of safety standards in construction. These factors contribute to the rising adoption of advanced repair solutions.
What challenges does the Construction Repair and Rehabilitation Chemicals Market face?
The Construction Repair and Rehabilitation Chemicals Market faces challenges such as fluctuating raw material prices and stringent regulatory requirements. Additionally, the need for skilled labor to apply these chemicals effectively can hinder market growth.
What opportunities exist in the Construction Repair and Rehabilitation Chemicals Market?
Opportunities in the Construction Repair and Rehabilitation Chemicals Market include the development of eco-friendly products and the expansion into emerging markets. Innovations in chemical formulations that enhance durability and performance also present significant growth potential.
What trends are shaping the Construction Repair and Rehabilitation Chemicals Market?
Trends shaping the Construction Repair and Rehabilitation Chemicals Market include the increasing use of smart materials and the integration of technology in construction processes. Additionally, there is a growing focus on sustainability and the use of recycled materials in chemical formulations.
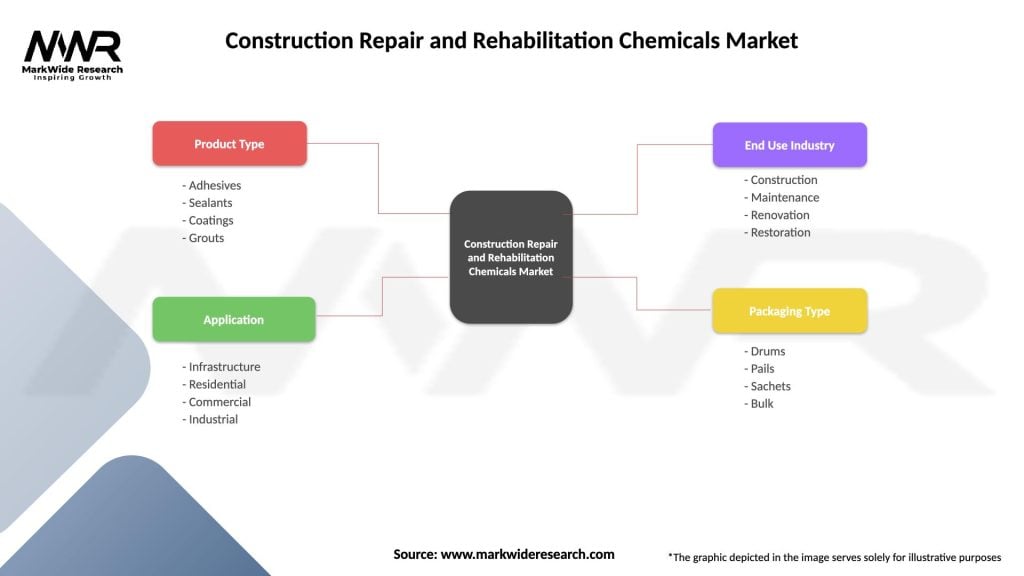
Construction Repair and Rehabilitation Chemicals Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Adhesives, Sealants, Coatings, Grouts |
| Application | Infrastructure, Residential, Commercial, Industrial |
| End Use Industry | Construction, Maintenance, Renovation, Restoration |
| Packaging Type | Drums, Pails, Sachets, Bulk |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Construction Repair and Rehabilitation Chemicals Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at