444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The compulsory third-party insurance (CTP) market plays a crucial role in the insurance landscape, providing financial protection to individuals against liabilities arising from third-party injuries or fatalities in motor vehicle accidents. Compulsory third-party insurance is mandatory in many jurisdictions, aiming to ensure that victims of motor vehicle accidents receive adequate compensation for their injuries or losses. The CTP market operates within the broader context of the insurance industry, serving as a vital component of risk management for motorists and society at large.
Meaning
Compulsory third-party insurance, also known as third-party liability insurance or green slip insurance in some regions, is a type of insurance coverage that protects individuals against legal liabilities arising from injuries or fatalities caused to third parties in motor vehicle accidents. Unlike voluntary insurance policies that provide coverage for damage to one’s vehicle, compulsory third-party insurance specifically covers bodily injury or death to third parties, including pedestrians, cyclists, and passengers in other vehicles. This insurance is mandatory in many jurisdictions to ensure that victims of motor vehicle accidents are adequately compensated for their losses.
Executive Summary
The compulsory third-party insurance market is a fundamental aspect of motor vehicle insurance systems worldwide, providing essential protection to individuals against the financial consequences of causing injury or death to third parties in motor vehicle accidents. Key stakeholders in the market include insurers, regulatory authorities, motorists, and accident victims. The market operates under regulatory frameworks that mandate the purchase of CTP insurance as a prerequisite for vehicle registration and road use. While the market faces challenges such as rising claim costs, fraud, and regulatory complexities, it also presents opportunities for innovation, efficiency, and collaboration to enhance the overall effectiveness of CTP insurance systems.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The CTP insurance market operates within a dynamic ecosystem shaped by regulatory, technological, economic, and social factors. These dynamics influence market behaviors, trends, and outcomes, requiring insurers to adapt and innovate continuously to remain competitive and resilient. Understanding the interplay of market dynamics is essential for stakeholders to navigate challenges, capitalize on opportunities, and drive sustainable growth and value creation in the CTP insurance market.
Regional Analysis
The CTP insurance market exhibits regional variations in regulatory frameworks, market structures, and consumer preferences, reflecting differences in legal systems, cultural norms, and socio-economic conditions. Regions with stringent regulatory requirements, robust enforcement mechanisms, and high levels of motor vehicle ownership tend to have well-established CTP insurance markets with extensive coverage and participation. In contrast, regions with limited regulatory oversight, weak enforcement mechanisms, and lower levels of motor vehicle ownership may face challenges in ensuring widespread compliance and adequate protection for accident victims.
Competitive Landscape
Leading companies in the Compulsory Third Party Insurance Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
The CTP insurance market can be segmented based on various criteria, including geographical regions, regulatory frameworks, insurance products, distribution channels, and customer demographics. Segmentation enables insurers to target specific market segments, tailor their products and services to meet diverse needs, and optimize their marketing, distribution, and pricing strategies effectively. Common segmentation variables include age, gender, vehicle type, driving history, and risk profile, allowing insurers to offer customized solutions and value propositions to different customer segments.
Category-wise Insight
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the CTP insurance market, leading to changes in market dynamics, consumer behaviors, and regulatory priorities. Lockdowns, travel restrictions, and remote working arrangements have resulted in changes in vehicle usage patterns, traffic volumes, and accident frequencies, affecting claims experience and risk profiles for insurers. The pandemic has also accelerated digital transformation initiatives in the insurance industry, prompting insurers to adopt digital platforms, remote service delivery models, and contactless claims processes to adapt to changing customer preferences and market conditions.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the compulsory third-party insurance market is promising, driven by factors such as regulatory mandates, technological innovation, consumer demand, and societal expectations. While the market faces challenges such as rising claim costs, fraud, and regulatory complexities, it also presents opportunities for innovation, efficiency, and collaboration to enhance the overall effectiveness and sustainability of CTP insurance systems.
Conclusion
The compulsory third-party insurance market plays a critical role in the insurance landscape, providing essential protection to individuals against the financial consequences of causing injury or death to third parties in motor vehicle accidents. With the increasing prevalence of technological innovation, regulatory evolution, and societal expectations, the CTP insurance market is undergoing significant changes and transformations. By embracing technology, fostering collaboration, and prioritizing regulatory compliance, insurers can navigate challenges, capitalize on opportunities, and drive sustainable growth and value creation in the CTP insurance market.
What is Compulsory Third Party Insurance?
Compulsory Third Party Insurance is a type of insurance that provides coverage for damages or injuries caused to third parties in the event of an accident involving a vehicle. It is mandatory in many jurisdictions to ensure that victims of road accidents receive compensation regardless of the fault.
What are the key players in the Compulsory Third Party Insurance Market?
Key players in the Compulsory Third Party Insurance Market include companies like Allianz, AAMI, and QBE Insurance, which offer various policies to meet regulatory requirements and consumer needs, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Compulsory Third Party Insurance Market?
The main drivers of growth in the Compulsory Third Party Insurance Market include increasing vehicle ownership, rising awareness of road safety, and regulatory mandates that require drivers to have insurance coverage, which collectively enhance market demand.
What challenges does the Compulsory Third Party Insurance Market face?
Challenges in the Compulsory Third Party Insurance Market include fraudulent claims, regulatory changes that can affect policy pricing, and the need for insurers to balance risk management with competitive pricing strategies.
What opportunities exist in the Compulsory Third Party Insurance Market?
Opportunities in the Compulsory Third Party Insurance Market include the potential for digital transformation in policy management, the introduction of usage-based insurance models, and the growing emphasis on customer-centric services that enhance user experience.
What trends are shaping the Compulsory Third Party Insurance Market?
Trends shaping the Compulsory Third Party Insurance Market include the integration of technology for claims processing, the rise of telematics in assessing risk, and an increasing focus on sustainability and ethical practices within the insurance sector.
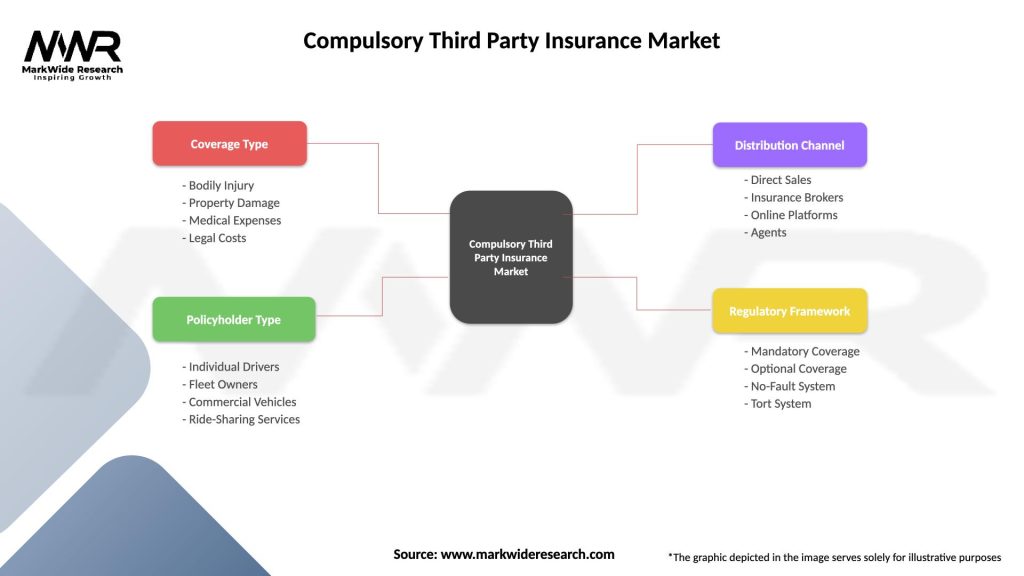
Compulsory Third Party Insurance Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Coverage Type | Bodily Injury, Property Damage, Medical Expenses, Legal Costs |
| Policyholder Type | Individual Drivers, Fleet Owners, Commercial Vehicles, Ride-Sharing Services |
| Distribution Channel | Direct Sales, Insurance Brokers, Online Platforms, Agents |
| Regulatory Framework | Mandatory Coverage, Optional Coverage, No-Fault System, Tort System |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Compulsory Third Party Insurance Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at