444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The cloud technologies in healthcare market has been experiencing significant growth in recent years. Cloud computing has revolutionized the healthcare industry by providing secure storage, data sharing, and advanced analytics capabilities. This technology enables healthcare providers to store and access patient information, collaborate with other professionals, and improve overall efficiency. The market is witnessing rapid adoption of cloud technologies due to their ability to streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance patient care.
Meaning
Cloud technologies refer to the delivery of computing services over the internet. In the healthcare industry, cloud technologies involve storing and managing healthcare data and applications on remote servers instead of local infrastructure. It allows healthcare organizations to access and share information anytime and anywhere, promoting collaboration and facilitating better decision-making.
Executive Summary
The cloud technologies in healthcare market is experiencing remarkable growth globally. The demand for efficient data management and storage solutions in the healthcare industry, along with the growing adoption of electronic health records (EHRs), is driving the market’s expansion. Cloud technologies offer scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, which are vital factors contributing to their adoption. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the adoption of cloud technologies as healthcare providers strive to improve telehealth services and manage large volumes of patient data.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The cloud technologies in healthcare market is highly dynamic, driven by technological advancements, regulatory changes, and evolving patient needs. Healthcare organizations are increasingly recognizing the benefits of cloud technologies in improving efficiency, collaboration, and patient care. The market is witnessing intense competition, with numerous cloud service providers and technology vendors offering specialized solutions tailored to the healthcare industry.
Regional Analysis
The adoption of cloud technologies in healthcare varies across regions. North America leads the market due to the presence of advanced healthcare infrastructure, increasing digitization efforts, and supportive government initiatives. Europe follows closely, with countries like the United Kingdom, Germany, and France embracing cloud technologies to enhance healthcare services. The Asia Pacific region is expected to witness significant growth, driven by the rising healthcare IT expenditure, increasing adoption of EHRs, and a shift towards value-based care models.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Cloud Technologies in Healthcare Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.

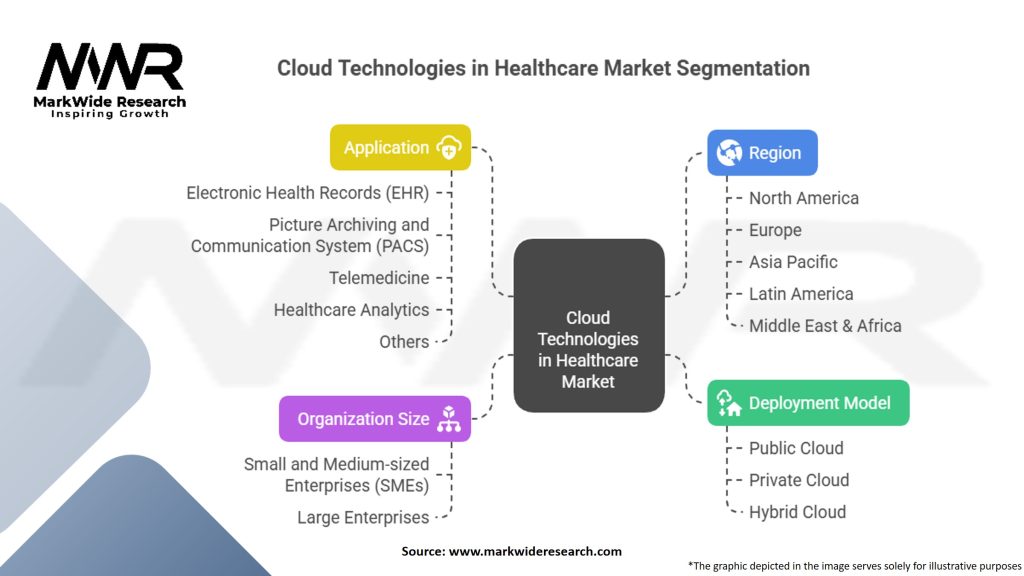
Segmentation
The cloud technologies in healthcare market can be segmented based on deployment models, service types, end-users, and regions. By deployment models, the market can be categorized into public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid cloud. Service types include software as a service (SaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and infrastructure as a service (IaaS). End-users of cloud technologies in healthcare encompass hospitals and clinics, pharmaceutical companies, research institutions, and healthcare payers.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of cloud technologies in healthcare. The need for remote patient monitoring, virtual consultations, and telehealth services has surged during the pandemic, and cloud technologies have played a vital role in enabling these services. Cloud-based EHR systems and telemedicine platforms have allowed healthcare providers to continue delivering care while minimizing in-person interactions. The pandemic has highlighted the importance of secure and accessible cloud infrastructure for healthcare organizations to adapt to rapidly changing circumstances and effectively manage patient data.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future of cloud technologies in healthcare looks promising. The market is expected to witness continued growth due to the increasing digitization of healthcare processes, rising demand for telehealth services, and the need for efficient data management and analytics. Advancements in AI, ML, and IoT will further augment cloud capabilities, enabling personalized medicine, remote monitoring, and predictive analytics. Cloud technologies will continue to play a vital role in transforming the healthcare industry, improving patient outcomes, and driving operational efficiencies.
Conclusion
Cloud technologies have brought about a paradigm shift in the healthcare industry, revolutionizing the way healthcare organizations store, manage, and utilize patient data. The market is witnessing significant growth driven by the need for efficient data management, rising adoption of EHRs, and the demand for cost-effective solutions. While data security and regulatory compliance remain challenges, the benefits of cloud technologies, including scalability, flexibility, and enhanced collaboration, outweigh the concerns. As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, cloud technologies will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of healthcare delivery, improving patient care, and driving innovation.
What is Cloud Technologies in Healthcare?
Cloud technologies in healthcare refer to the use of cloud computing services to store, manage, and analyze healthcare data. This includes applications such as electronic health records, telemedicine, and data analytics, which enhance patient care and operational efficiency.
What are the key players in the Cloud Technologies in Healthcare Market?
Key players in the Cloud Technologies in Healthcare Market include companies like Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, which provide robust cloud solutions tailored for healthcare applications, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Cloud Technologies in Healthcare Market?
The main drivers of growth in the Cloud Technologies in Healthcare Market include the increasing demand for remote patient monitoring, the need for efficient data management, and the rising adoption of telehealth services.
What challenges does the Cloud Technologies in Healthcare Market face?
Challenges in the Cloud Technologies in Healthcare Market include concerns over data security and privacy, regulatory compliance issues, and the need for interoperability between different healthcare systems.
What future opportunities exist in the Cloud Technologies in Healthcare Market?
Future opportunities in the Cloud Technologies in Healthcare Market include advancements in artificial intelligence for predictive analytics, the expansion of telehealth services, and the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices for real-time health monitoring.
What trends are shaping the Cloud Technologies in Healthcare Market?
Trends shaping the Cloud Technologies in Healthcare Market include the increasing use of hybrid cloud solutions, the rise of patient-centric care models, and the growing emphasis on data analytics for improving healthcare outcomes.
Cloud Technologies in Healthcare Market
| Segmentation Details | Details |
|---|---|
| Deployment Model | Public Cloud, Private Cloud, Hybrid Cloud |
| Organization Size | Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs), Large Enterprises |
| Application | Electronic Health Records (EHR), Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS), Telemedicine, Healthcare Analytics, Others |
| Region | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Cloud Technologies in Healthcare Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at