444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
The cloud applications market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing adoption of cloud computing technologies across various industries. Cloud applications refer to software applications that are hosted and accessed through the internet, eliminating the need for on-premises infrastructure and providing scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency to businesses.
Cloud applications, also known as Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) solutions, are web-based applications that allow users to access and use software tools and services without the need for installation or maintenance on their local devices. These applications are hosted on remote servers and are accessed through web browsers, providing businesses with the ability to streamline their operations and enhance productivity.
Executive Summary
The cloud applications market is experiencing rapid growth, driven by factors such as the increasing demand for cost-effective and scalable software solutions, the rising adoption of cloud computing technologies, and the need for seamless collaboration and data accessibility. This market analysis provides insights into the key trends, drivers, restraints, opportunities, and dynamics shaping the cloud applications market.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
3. Data Security: Cloud applications provide robust security measures, including data encryption, regular backups, and multi-factor authentication, ensuring the protection of sensitive information.
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The cloud applications market is highly dynamic and influenced by several factors:
Regional Analysis
The cloud applications market exhibits significant regional variations. North America dominates the market, owing to the presence of major cloud service providers and early adoption of cloud technologies. Europe and Asia Pacific are also witnessing substantial growth, driven by increasing digitalization efforts and growing acceptance of cloud-based solutions.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Cloud Applications Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.

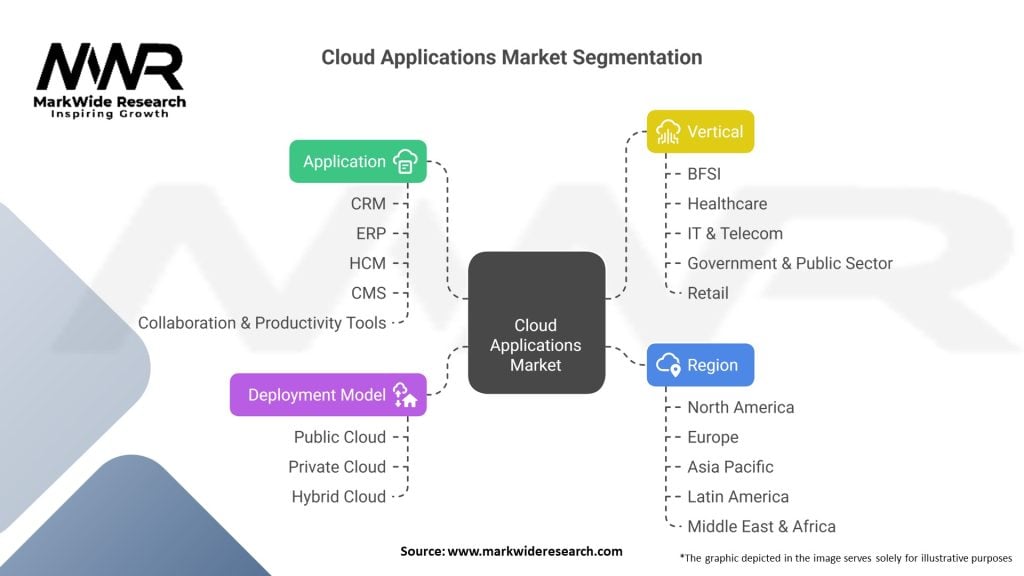
Segmentation
The cloud applications market can be segmented based on deployment model, application type, organization size, and industry vertical. Deployment models include public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid cloud. Application types encompass customer relationship management (CRM), enterprise resource planning (ERP), human resource management (HRM), supply chain management (SCM), and others.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of cloud applications across industries. With remote work becoming the new normal, businesses have increasingly relied on cloud-based tools to ensure continuity and enable collaboration. Cloud applications have facilitated remote access to essential business processes and data, enabling organizations to operate seamlessly amidst lockdowns and social distancing measures.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future of the cloud applications market looks promising, with continued growth expected. Factors such as the increasing adoption of cloud computing, the demand for cost-effective and scalable software solutions, and the need for remote collaboration are likely to drive the market further. Integration with emerging technologies and industry-specific solutions will create new opportunities, while data security and regulatory compliance will remain key challenges for businesses.
Conclusion
The cloud applications market has transformed the way businesses access and utilize software tools and services. With their scalability, cost efficiency, and accessibility, cloud applications have become essential for businesses across industries. The market is witnessing significant growth, driven by factors such as cost savings, scalability, and enhanced collaboration.
However, challenges such as connectivity issues and data security concerns need to be addressed. Businesses must ensure reliable internet connectivity and implement robust security measures to protect sensitive data.
What are cloud applications?
Cloud applications are software programs that run on remote servers and are accessed via the internet. They allow users to utilize applications without needing to install them locally, providing flexibility and scalability for various business needs.
Who are the key players in the Cloud Applications Market?
Key players in the Cloud Applications Market include Salesforce, Microsoft, and Google, which offer a range of cloud-based solutions for customer relationship management, productivity, and collaboration, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Cloud Applications Market?
The main drivers of growth in the Cloud Applications Market include the increasing demand for remote work solutions, the need for scalable IT infrastructure, and the rising adoption of digital transformation strategies across various industries.
What challenges does the Cloud Applications Market face?
Challenges in the Cloud Applications Market include data security concerns, compliance with regulations, and the complexity of integrating cloud solutions with existing on-premises systems.
What opportunities exist in the Cloud Applications Market?
Opportunities in the Cloud Applications Market include the expansion of artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities, the growth of industry-specific applications, and the increasing focus on enhancing user experience through innovative features.
What trends are shaping the Cloud Applications Market?
Trends shaping the Cloud Applications Market include the rise of low-code and no-code development platforms, the integration of advanced analytics, and the growing emphasis on sustainability and energy-efficient cloud solutions.
Cloud Applications Market:
| Segmentation | Details |
|---|---|
| Application | Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Human Capital Management (HCM), Content Management System (CMS), Collaboration & Productivity Tools, Others |
| Deployment Model | Public Cloud, Private Cloud, Hybrid Cloud |
| Vertical | BFSI, Healthcare, IT & Telecom, Government & Public Sector, Retail, Others |
| Region | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Cloud Applications Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at