444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The China plant based food & beverage industry market represents one of the most dynamic and rapidly evolving sectors in the global alternative protein landscape. China’s plant-based market has experienced unprecedented growth, driven by increasing health consciousness, environmental awareness, and changing dietary preferences among Chinese consumers. The market encompasses a diverse range of products including plant-based meat alternatives, dairy substitutes, protein beverages, and innovative food products derived from soy, wheat, pea protein, and other plant sources.
Market expansion in China has been particularly notable in urban centers where younger demographics are increasingly adopting flexitarian lifestyles. The industry benefits from China’s strong agricultural foundation and advanced food processing capabilities, positioning the country as both a significant consumer and producer of plant-based alternatives. Growth rates in the sector have consistently outpaced traditional food categories, with the market experiencing a compound annual growth rate of approximately 20.2% over recent years.
Consumer adoption patterns indicate a shift from traditional soy-based products toward more sophisticated alternatives that closely mimic conventional animal products. The market’s evolution reflects broader trends in sustainable consumption, health optimization, and food innovation that are reshaping China’s massive food and beverage landscape.
The China plant based food & beverage industry market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of companies, products, and services focused on developing, manufacturing, and distributing food and beverage products derived entirely from plant sources as alternatives to conventional animal-based products. This market encompasses meat substitutes, dairy alternatives, plant-based beverages, and innovative protein products designed to replicate the taste, texture, and nutritional profile of traditional animal products.
Plant-based alternatives in the Chinese market include products made from soybeans, wheat gluten, mushrooms, pea protein, rice protein, and other plant sources. The industry represents a convergence of traditional Chinese food culture, which has long incorporated plant-based proteins, with modern food technology and changing consumer preferences toward healthier and more sustainable dietary choices.
Market participants range from established food manufacturers expanding their portfolios to specialized startups focused exclusively on plant-based innovation. The industry encompasses the entire value chain from ingredient sourcing and product development to manufacturing, distribution, and retail, creating a comprehensive alternative food ecosystem within China’s broader food industry.
China’s plant-based food and beverage market has emerged as a critical component of the country’s evolving food landscape, driven by demographic shifts, health consciousness, and environmental concerns. The market demonstrates robust growth potential with urban penetration rates reaching approximately 35% among millennials and Gen Z consumers. Key market drivers include rising disposable incomes, increasing awareness of health benefits associated with plant-based diets, and growing environmental consciousness among Chinese consumers.
Product innovation has accelerated significantly, with companies developing increasingly sophisticated alternatives that appeal to Chinese taste preferences. The market benefits from strong government support for sustainable food production and food security initiatives. Investment activity in the sector has intensified, with both domestic and international investors recognizing the long-term potential of China’s plant-based market.
Competitive dynamics feature a mix of international brands adapting to local preferences and domestic companies leveraging traditional plant-based food knowledge. The market’s growth trajectory suggests continued expansion across multiple product categories, with retail penetration expected to increase substantially in tier-two and tier-three cities. MarkWide Research analysis indicates that the sector’s development aligns with broader trends in China’s food industry modernization and consumer preference evolution.
Consumer behavior analysis reveals several critical insights driving market development in China’s plant-based sector:
Market maturation indicators suggest the industry is transitioning from early adoption to mainstream acceptance, with implications for product development, marketing strategies, and distribution approaches across different consumer segments and geographic regions.
Health consciousness represents the primary driver propelling China’s plant-based food and beverage market forward. Chinese consumers increasingly recognize the connection between diet and health outcomes, with chronic disease prevention becoming a significant motivator for dietary changes. The growing prevalence of lifestyle-related health issues has created heightened awareness of nutrition’s role in long-term wellness, driving demand for healthier food alternatives.
Environmental sustainability concerns have gained prominence among Chinese consumers, particularly in urban areas where air quality and environmental degradation are visible daily concerns. The connection between food production methods and environmental impact resonates with environmentally conscious consumers who view plant-based alternatives as contributing to reduced carbon footprints and more sustainable consumption patterns.
Government policy support for sustainable agriculture and food security initiatives creates a favorable regulatory environment for plant-based food development. Policy frameworks encouraging agricultural innovation and sustainable food production methods provide indirect support for the plant-based industry’s growth and development.
Technological advancement in food processing and product development enables the creation of increasingly sophisticated plant-based alternatives that better replicate conventional products. Improvements in texture, taste, and nutritional profiles address previous consumer concerns about plant-based alternatives, expanding market acceptance and adoption rates.
Rising disposable incomes among China’s growing middle class enable consumers to prioritize health and sustainability considerations in food purchasing decisions. Economic prosperity allows for premium product experimentation and supports market expansion beyond basic necessity-driven consumption patterns.
Cultural food traditions present significant challenges for plant-based market expansion in China. Deep-rooted culinary practices and preferences for traditional animal-based proteins create resistance to alternative products, particularly among older demographic segments. Traditional Chinese cuisine emphasizes specific textures, flavors, and preparation methods that plant-based alternatives struggle to replicate authentically.
Price premium challenges limit market accessibility for price-sensitive consumer segments. Many plant-based alternatives carry higher retail prices compared to conventional products, creating barriers for widespread adoption across diverse economic demographics. Cost considerations particularly impact market penetration in lower-tier cities and among budget-conscious consumers.
Supply chain limitations constrain market growth potential, particularly for specialized ingredients and processing technologies required for advanced plant-based products. Infrastructure gaps in cold chain logistics and specialized storage facilities limit distribution efficiency and product quality maintenance across China’s vast geographic market.
Consumer education needs represent ongoing challenges as many consumers lack understanding of plant-based nutrition, preparation methods, and product benefits. Knowledge gaps about protein quality, nutritional completeness, and cooking techniques create hesitation among potential consumers considering plant-based alternatives.
Regulatory uncertainty in labeling standards and product classification creates compliance challenges for manufacturers and may confuse consumers about product characteristics and benefits. Standardization issues across different product categories and manufacturing processes create additional complexity for market participants.
Product innovation opportunities abound in developing plant-based alternatives specifically tailored to Chinese taste preferences and culinary traditions. Companies can capitalize on localization strategies that incorporate traditional Chinese flavors, spices, and cooking methods into modern plant-based formulations, creating products that resonate more strongly with local consumers.
Tier-two and tier-three city expansion represents substantial growth potential as urbanization continues and disposable incomes rise in secondary markets. These markets offer first-mover advantages for companies establishing early presence and building brand recognition before competition intensifies.
E-commerce platform integration provides opportunities for direct consumer engagement and market education through digital channels. Online platforms enable targeted marketing, consumer education initiatives, and personalized product recommendations that can accelerate adoption among digitally native consumer segments.
Partnership opportunities with established food service providers, restaurant chains, and institutional buyers can drive volume growth and market penetration. B2B market development through foodservice channels provides alternative distribution pathways and helps normalize plant-based consumption through familiar dining experiences.
Export market development leverages China’s manufacturing capabilities to serve growing international demand for plant-based products. Global market expansion opportunities allow Chinese companies to diversify revenue streams while building international brand recognition and market presence.
Technology licensing and joint venture opportunities with international companies provide access to advanced processing technologies and product formulations while offering local market knowledge and distribution capabilities to foreign partners.
Supply and demand dynamics in China’s plant-based market reflect the interplay between growing consumer interest and evolving production capabilities. Demand growth consistently outpaces supply expansion, creating opportunities for new market entrants while challenging existing players to scale production efficiently. The market demonstrates seasonal variations with increased consumption during health-focused periods and traditional festivals.
Competitive intensity has increased significantly as both domestic and international companies recognize market potential. Market consolidation trends suggest larger players are acquiring innovative startups to expand product portfolios and technological capabilities. Competition drives continuous innovation in product development, marketing approaches, and distribution strategies.
Price dynamics reflect ongoing tensions between premium positioning and mass market accessibility. Cost reduction initiatives through improved manufacturing efficiency and economies of scale gradually make plant-based alternatives more price-competitive with conventional products. Premium segments maintain higher margins while volume segments focus on cost optimization.
Distribution channel evolution shows increasing sophistication with multi-channel approaches becoming standard. Omnichannel strategies integrate online and offline touchpoints to maximize market reach and consumer convenience. Traditional retail partnerships complement direct-to-consumer initiatives and foodservice distribution.
Innovation cycles have accelerated with companies introducing new products and formulations at increasing frequency. Product lifecycle management becomes critical as market saturation increases and consumer preferences continue evolving toward more sophisticated alternatives.
Primary research methodologies employed in analyzing China’s plant-based food and beverage market include comprehensive consumer surveys, in-depth interviews with industry stakeholders, and focus group discussions across multiple demographic segments. Data collection encompasses both quantitative metrics and qualitative insights to provide holistic market understanding.
Secondary research incorporates analysis of industry reports, government statistics, trade publications, and company financial disclosures to establish market context and validate primary research findings. Cross-referencing multiple data sources ensures accuracy and reliability of market insights and projections.
Geographic sampling covers first-tier, second-tier, and third-tier cities to capture regional variations in consumer behavior, market development, and competitive dynamics. Urban and rural market segments receive appropriate weighting based on their relative market importance and growth potential.
Industry expert consultations with manufacturers, distributors, retailers, and technology providers offer insider perspectives on market trends, challenges, and opportunities. Stakeholder interviews provide context for quantitative data and reveal emerging trends not yet reflected in published statistics.
Analytical frameworks employ statistical modeling, trend analysis, and scenario planning to project future market development under various conditions. Validation processes ensure research conclusions align with observable market behaviors and industry expert opinions.
Eastern China dominates the plant-based food and beverage market, accounting for approximately 52% of national consumption. Cities like Shanghai, Beijing, and Shenzhen lead adoption rates due to higher disposable incomes, international exposure, and health consciousness. Premium product segments perform particularly well in these markets where consumers demonstrate willingness to pay higher prices for quality and innovation.
Southern China represents approximately 23% of market share, with Guangzhou and surrounding areas showing strong growth in plant-based beverage consumption. The region’s culinary diversity creates opportunities for specialized products that cater to local taste preferences and cooking traditions.
Central China accounts for roughly 15% of market activity, with cities like Wuhan and Chengdu emerging as secondary growth centers. Market penetration in these areas focuses on value-oriented products and gradual consumer education initiatives to build awareness and acceptance.
Western and Northern China represent developing markets with approximately 10% combined market share. These regions show potential for future expansion as urbanization continues and distribution networks improve. Market entry strategies in these areas emphasize affordability and cultural adaptation to local preferences.
Rural market development remains limited but shows emerging potential as e-commerce platforms expand reach and rural incomes increase. Distribution challenges and price sensitivity require specialized approaches for rural market penetration and development.
Market leadership in China’s plant-based food and beverage industry features a diverse mix of domestic and international companies competing across multiple product categories and market segments:
Competitive strategies emphasize product localization, distribution network development, and consumer education initiatives. Market differentiation occurs through technology innovation, brand positioning, and strategic partnerships with retailers and foodservice providers.
By Product Type:
By Source Material:
By Distribution Channel:
Plant-Based Meat Alternatives represent the fastest-growing segment with increasing sophistication in texture and flavor profiles. Consumer acceptance has improved significantly as products better replicate conventional meat characteristics. Innovation focuses on traditional Chinese preparations including dumplings, buns, and stir-fry applications that align with local culinary preferences.
Dairy Alternative Products benefit from existing consumer familiarity with soy milk and other traditional plant-based beverages. Market expansion includes yogurt alternatives, cheese substitutes, and ice cream products that appeal to younger demographics seeking healthier dessert options. Functional benefits including probiotics and added nutrients drive premium segment growth.
Plant-Based Beverages lead market penetration with high consumer acceptance and frequent purchase patterns. Product innovation includes protein-enhanced beverages, functional drinks targeting specific health benefits, and convenient ready-to-drink formats. Flavor variety and seasonal offerings maintain consumer interest and drive repeat purchases.
Snack and Convenience Categories show strong growth potential as busy lifestyles drive demand for convenient plant-based options. Product development focuses on portable formats, extended shelf life, and appealing taste profiles that compete effectively with conventional snack foods. Health positioning appeals to consumers seeking better-for-you convenience options.
Manufacturers benefit from expanding market opportunities and premium pricing potential in the growing plant-based segment. Diversification advantages include reduced dependence on traditional food categories and access to health-conscious consumer segments willing to pay higher prices for innovative products.
Retailers gain competitive differentiation through comprehensive plant-based product offerings that attract health-conscious consumers. Category management opportunities include dedicated plant-based sections that drive store traffic and increase basket sizes among target demographics.
Consumers access healthier food alternatives that support personal wellness goals while aligning with environmental sustainability values. Product variety continues expanding, providing more choices and better taste experiences that make plant-based eating more enjoyable and convenient.
Investors participate in a high-growth market segment with strong long-term fundamentals driven by demographic trends and changing consumer preferences. Investment opportunities span the entire value chain from ingredient suppliers to finished product manufacturers and distribution companies.
Environmental stakeholders benefit from reduced environmental impact associated with plant-based food production compared to conventional animal agriculture. Sustainability outcomes include lower carbon emissions, reduced water usage, and decreased land requirements for food production.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Localization trend dominates product development strategies as companies adapt international plant-based concepts to Chinese taste preferences and culinary traditions. Cultural integration includes incorporating traditional Chinese flavors, cooking methods, and presentation styles that resonate with local consumers and reduce barriers to adoption.
Premium positioning has emerged as a successful strategy for establishing brand credibility and justifying higher price points. Quality emphasis through superior ingredients, advanced processing technologies, and attractive packaging appeals to affluent consumers willing to pay premiums for perceived value and health benefits.
Functional food integration combines plant-based alternatives with additional health benefits including probiotics, vitamins, minerals, and specialized nutrients. Health optimization appeals to consumers seeking comprehensive wellness solutions rather than simple protein substitution.
Convenience factor drives product development toward ready-to-eat formats, easy preparation methods, and portable packaging that fits busy urban lifestyles. Time-saving solutions address consumer demands for healthy options that don’t compromise convenience or taste satisfaction.
Sustainability messaging has become increasingly important in marketing communications as environmental consciousness grows among Chinese consumers. Eco-friendly positioning emphasizes reduced environmental impact and supports brand differentiation in competitive markets.
Technology advancement continues improving product quality through better texture replication, flavor enhancement, and nutritional optimization. Innovation focus on processing techniques and ingredient combinations creates more convincing alternatives that satisfy traditional taste expectations.
Investment activity has intensified significantly with both domestic and international investors recognizing the long-term potential of China’s plant-based market. Funding rounds for innovative startups have increased in size and frequency, enabling accelerated product development and market expansion initiatives.
Strategic partnerships between plant-based companies and established food manufacturers have become common as traditional companies seek to diversify portfolios and access growing alternative protein markets. Collaboration benefits include shared distribution networks, manufacturing capabilities, and market expertise.
Retail expansion has accelerated with major supermarket chains dedicating increased shelf space to plant-based alternatives and creating specialized sections for alternative protein products. Distribution improvements enhance product visibility and consumer accessibility across multiple retail formats.
Technology licensing agreements between Chinese companies and international plant-based leaders facilitate knowledge transfer and accelerate local product development capabilities. Technology adoption enables faster market entry and improved product quality for domestic manufacturers.
Regulatory developments include clearer guidelines for plant-based product labeling and safety standards that provide industry clarity and consumer confidence. Standardization efforts support market growth by establishing consistent quality expectations and competitive frameworks.
Export initiatives by Chinese plant-based companies target international markets, leveraging manufacturing cost advantages and growing global demand for alternative protein products. Global expansion strategies diversify revenue sources and build international brand recognition.
Market entry strategies should prioritize localization and cultural adaptation over direct translation of international products. Success factors include understanding regional taste preferences, traditional cooking methods, and local ingredient availability to create products that resonate with Chinese consumers.
Distribution channel optimization requires multi-channel approaches that integrate online and offline touchpoints effectively. Omnichannel strategies should leverage e-commerce platforms for consumer education and convenience while maintaining retail presence for product trial and impulse purchases.
Consumer education initiatives represent critical investments for long-term market development. Educational programs should focus on nutritional benefits, preparation methods, and taste experiences that address common misconceptions and barriers to adoption.
Price positioning strategies must balance premium positioning with accessibility concerns to maximize market penetration. Tiered pricing approaches can serve different consumer segments while building brand equity and market share across multiple price points.
Innovation focus should emphasize texture improvement and flavor authenticity to address primary consumer concerns about plant-based alternatives. Product development investments in processing technology and ingredient optimization will drive competitive advantages and consumer acceptance.
Partnership development with established food companies, retailers, and foodservice providers can accelerate market penetration and reduce distribution barriers. Strategic alliances provide access to existing networks and consumer relationships while sharing market development costs and risks.
Market expansion is projected to continue at robust rates with compound annual growth rates expected to maintain double-digit levels through the next five years. Growth drivers include increasing health consciousness, expanding distribution networks, and continued product innovation that improves taste and texture characteristics.
Geographic expansion into tier-two and tier-three cities represents the next major growth phase as urbanization continues and disposable incomes rise in secondary markets. Market penetration in these areas will require adapted strategies focusing on affordability and cultural relevance.
Product category diversification will expand beyond current offerings to include more specialized applications, functional foods, and culturally specific products. Innovation pipeline suggests continued advancement in processing technologies and ingredient combinations that enhance product appeal and nutritional profiles.
Competitive landscape evolution will likely feature increased consolidation as successful companies acquire innovative startups and expand market presence. Market maturation will drive efficiency improvements and cost reductions that make plant-based alternatives more price-competitive with conventional products.
MarkWide Research projections indicate that the industry will achieve mainstream acceptance within the next decade, transitioning from niche health food category to standard grocery offerings. Long-term outlook suggests plant-based alternatives will capture increasing market share across multiple food categories as consumer preferences continue evolving toward healthier and more sustainable options.
Export market development will position China as a significant global supplier of plant-based products, leveraging manufacturing capabilities and cost advantages to serve international demand. Global market participation will enhance industry scale and technological advancement while diversifying revenue sources for Chinese companies.
China’s plant-based food and beverage industry market represents a transformative opportunity within the country’s evolving food landscape. The market demonstrates strong fundamentals driven by health consciousness, environmental awareness, and changing demographic preferences that support sustained long-term growth. Market dynamics favor continued expansion across multiple product categories and geographic regions as consumer acceptance increases and distribution networks expand.
Industry development has reached a critical inflection point where product quality improvements and cultural adaptation strategies are driving mainstream consumer adoption. The combination of traditional Chinese plant-based food knowledge with modern processing technologies creates unique competitive advantages for domestic companies while attracting international investment and partnership opportunities.
Future success in China’s plant-based market will depend on companies’ abilities to balance innovation with cultural sensitivity, premium positioning with accessibility, and rapid growth with sustainable business practices. The market’s evolution from niche health food category to mainstream alternative protein source reflects broader trends in Chinese consumer behavior and food industry modernization that will continue shaping market development for years to come.
What is Plant Based Food & Beverage?
Plant Based Food & Beverage refers to products made primarily from plants, including fruits, vegetables, grains, nuts, and seeds, designed to provide alternatives to traditional animal-based food and drink options.
What are the key players in the China Plant Based Food & Beverage Industry Market?
Key players in the China Plant Based Food & Beverage Industry Market include Beyond Meat, Oatly, and Tofurky, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the China Plant Based Food & Beverage Industry Market?
The main drivers of growth in the China Plant Based Food & Beverage Industry Market include increasing health consciousness among consumers, rising demand for sustainable food options, and the growing trend of veganism and vegetarianism.
What challenges does the China Plant Based Food & Beverage Industry Market face?
Challenges in the China Plant Based Food & Beverage Industry Market include competition from traditional meat and dairy products, consumer skepticism regarding taste and texture, and regulatory hurdles related to labeling and health claims.
What opportunities exist in the China Plant Based Food & Beverage Industry Market?
Opportunities in the China Plant Based Food & Beverage Industry Market include expanding product lines to cater to diverse consumer preferences, leveraging e-commerce for distribution, and increasing collaboration with food service providers.
What trends are shaping the China Plant Based Food & Beverage Industry Market?
Trends shaping the China Plant Based Food & Beverage Industry Market include the rise of innovative plant-based protein sources, the incorporation of functional ingredients for health benefits, and the growing popularity of ready-to-eat plant-based meals.
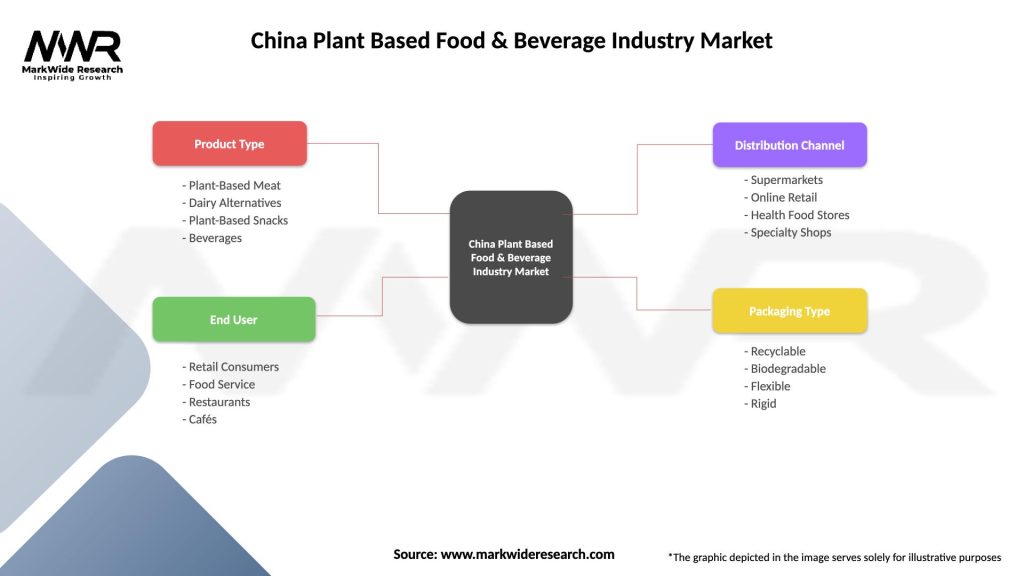
China Plant Based Food & Beverage Industry Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Plant-Based Meat, Dairy Alternatives, Plant-Based Snacks, Beverages |
| End User | Retail Consumers, Food Service, Restaurants, Cafés |
| Distribution Channel | Supermarkets, Online Retail, Health Food Stores, Specialty Shops |
| Packaging Type | Recyclable, Biodegradable, Flexible, Rigid |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the China Plant Based Food & Beverage Industry Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at