444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The China insulin drugs and delivery devices market represents one of the most dynamic and rapidly expanding healthcare segments in the Asia-Pacific region. With diabetes prevalence reaching unprecedented levels across China, the demand for innovative insulin therapies and advanced delivery systems has experienced remarkable growth. Market dynamics indicate that China’s aging population, combined with lifestyle changes and urbanization trends, has created a substantial patient base requiring comprehensive diabetes management solutions.
Healthcare infrastructure improvements and government initiatives supporting diabetes care have significantly enhanced market accessibility. The market encompasses various insulin formulations, including rapid-acting, long-acting, and intermediate-acting insulin products, alongside sophisticated delivery devices such as insulin pens, pumps, and continuous glucose monitoring systems. Growth projections suggest the market will expand at a robust CAGR of 8.2% through the forecast period, driven by increasing diabetes awareness and technological advancements.
Regional distribution shows concentrated demand in major metropolitan areas, with tier-one cities accounting for approximately 45% of market consumption. The integration of digital health solutions and smart insulin delivery devices has further accelerated market adoption, particularly among tech-savvy urban populations seeking convenient diabetes management options.
The China insulin drugs and delivery devices market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of pharmaceutical products and medical devices designed for diabetes management within the Chinese healthcare landscape. This market encompasses all insulin-based therapeutic solutions, ranging from traditional human insulin to advanced analog formulations, combined with innovative delivery mechanisms that enhance patient compliance and treatment outcomes.
Market scope includes prescription insulin medications, over-the-counter glucose monitoring supplies, and sophisticated delivery systems such as smart insulin pens, automated insulin pumps, and integrated continuous glucose monitoring devices. The market serves millions of diabetic patients across China, providing essential therapeutic interventions that enable effective blood glucose management and improved quality of life.
Stakeholder involvement spans pharmaceutical manufacturers, medical device companies, healthcare providers, regulatory authorities, and patient advocacy groups, all working collaboratively to ensure accessible, affordable, and effective diabetes care solutions throughout China’s diverse healthcare system.
Strategic analysis reveals that China’s insulin drugs and delivery devices market has emerged as a critical healthcare sector, driven by the country’s escalating diabetes epidemic and evolving patient care requirements. The market demonstrates exceptional growth potential, supported by favorable government policies, increasing healthcare expenditure, and rising patient awareness regarding diabetes management importance.
Key market drivers include the growing prevalence of Type 2 diabetes, which affects approximately 11.2% of China’s adult population, alongside increasing adoption of advanced insulin delivery technologies. Market participants are focusing on developing localized solutions that address specific Chinese patient preferences and healthcare system requirements, including cost-effective treatment options and culturally appropriate care delivery models.
Competitive landscape features both international pharmaceutical giants and emerging domestic manufacturers, creating a dynamic environment that promotes innovation while ensuring competitive pricing. The market’s future trajectory appears highly promising, with digital health integration and personalized medicine approaches expected to drive continued expansion and transformation.
Market intelligence indicates several critical insights that define the China insulin drugs and delivery devices landscape:
Primary growth catalysts propelling the China insulin drugs and delivery devices market include the escalating diabetes prevalence, which has reached epidemic proportions across the country. Lifestyle factors such as sedentary behavior, dietary changes, and increased stress levels have contributed to a dramatic rise in Type 2 diabetes cases, particularly among urban populations.
Healthcare infrastructure improvements and government initiatives supporting diabetes care have significantly enhanced market growth prospects. The Chinese government’s commitment to expanding healthcare coverage and improving diabetes management programs has created favorable conditions for market expansion. Reimbursement policies have been progressively enhanced, making insulin therapies more accessible to broader patient populations.
Technological advancement represents another crucial driver, with innovations in insulin delivery devices, continuous glucose monitoring systems, and digital health solutions attracting significant patient interest. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies into diabetes management platforms has created new opportunities for personalized treatment approaches, driving market demand for sophisticated insulin delivery systems.
Demographic trends continue to support market growth, with China’s aging population and increasing life expectancy contributing to higher diabetes incidence rates. Economic development and rising disposable incomes have enabled more patients to access premium insulin products and advanced delivery devices, further stimulating market expansion.
Significant challenges facing the China insulin drugs and delivery devices market include cost barriers and accessibility issues, particularly in rural and economically disadvantaged regions. Despite government efforts to expand healthcare coverage, out-of-pocket expenses for advanced insulin therapies and delivery devices remain substantial for many patients, limiting market penetration in certain demographic segments.
Regulatory complexities and lengthy approval processes for new insulin products and medical devices can delay market entry and increase development costs for manufacturers. The Chinese regulatory environment, while improving, still presents challenges for international companies seeking to introduce innovative diabetes management solutions to the local market.
Healthcare provider training and education gaps represent another constraint, as many healthcare professionals, particularly in rural areas, may lack comprehensive knowledge about advanced insulin delivery systems and optimal diabetes management protocols. This knowledge gap can impact patient outcomes and slow adoption of innovative treatment approaches.
Cultural factors and patient compliance issues also present challenges, as traditional medicine preferences and stigma associated with diabetes can influence treatment acceptance and adherence. Supply chain complexities and cold storage requirements for insulin products create additional logistical challenges, particularly in remote regions with limited healthcare infrastructure.
Emerging opportunities in the China insulin drugs and delivery devices market are substantial, driven by untapped rural markets and increasing government focus on diabetes prevention and management. Rural healthcare expansion initiatives present significant growth potential, as these regions currently have limited access to advanced diabetes care solutions but represent a large patient population.
Digital health integration offers transformative opportunities, with telemedicine, mobile health applications, and remote patient monitoring systems creating new avenues for diabetes management and insulin delivery optimization. The growing acceptance of digital healthcare solutions, accelerated by recent global health events, has created favorable conditions for innovative diabetes management platforms.
Personalized medicine approaches represent another significant opportunity, as advances in genetic testing and biomarker identification enable more targeted insulin therapy selection and dosing optimization. Precision diabetes care solutions that consider individual patient characteristics and preferences are gaining traction among healthcare providers and patients alike.
Partnership opportunities with local healthcare providers, technology companies, and government agencies offer pathways for market expansion and innovation acceleration. Strategic collaborations can help international companies navigate regulatory requirements while leveraging local market knowledge and distribution networks to enhance their competitive positioning.
Complex interactions between various market forces shape the China insulin drugs and delivery devices landscape, creating a dynamic environment characterized by rapid evolution and continuous adaptation. Supply and demand dynamics are influenced by demographic trends, healthcare policy changes, technological innovations, and economic factors that collectively determine market growth trajectories.
Competitive pressures drive continuous innovation and price optimization, as manufacturers strive to differentiate their products while maintaining affordability for Chinese patients. The market experiences ongoing tension between premium, high-tech solutions and cost-effective alternatives, with market segmentation reflecting diverse patient needs and economic capabilities.
Regulatory evolution continues to influence market dynamics, with policy changes affecting product approvals, reimbursement coverage, and market access requirements. Healthcare reform initiatives and diabetes prevention programs create both opportunities and challenges for market participants, requiring adaptive strategies and flexible business models.
Technology convergence between pharmaceutical products and digital health solutions is reshaping market boundaries and creating new competitive landscapes. The integration of insulin delivery devices with smartphone applications and cloud-based data analytics platforms represents a fundamental shift toward comprehensive diabetes management ecosystems that extend beyond traditional product categories.
Comprehensive research approaches employed in analyzing the China insulin drugs and delivery devices market incorporate multiple data sources and analytical methodologies to ensure accuracy and reliability. Primary research activities include extensive interviews with healthcare professionals, diabetes specialists, pharmaceutical executives, and patient advocacy groups to gather firsthand insights about market trends and challenges.
Secondary research encompasses analysis of government health statistics, pharmaceutical industry reports, academic publications, and regulatory documentation to establish market foundations and validate primary findings. Data triangulation techniques ensure consistency across multiple information sources while identifying potential discrepancies or emerging trends.
Market modeling utilizes advanced statistical techniques and forecasting algorithms to project future market scenarios and growth trajectories. Scenario analysis considers various economic, regulatory, and technological factors that could influence market development, providing comprehensive insights for strategic decision-making.
Validation processes include expert panel reviews, industry stakeholder feedback, and cross-reference verification to ensure research findings accurately reflect market realities and provide actionable intelligence for market participants and investors.
Geographic distribution of the China insulin drugs and delivery devices market reveals significant regional variations in demand patterns, accessibility, and growth potential. Eastern coastal regions, including Shanghai, Beijing, and Guangzhou, demonstrate the highest market penetration rates, accounting for approximately 52% of total market consumption due to superior healthcare infrastructure and higher disposable incomes.
Central China regions show moderate market development with growing demand driven by urbanization and healthcare infrastructure improvements. Cities such as Wuhan, Chengdu, and Xi’an are experiencing rapid market expansion as diabetes awareness increases and healthcare access improves. Market growth rates in these regions often exceed 12% annually, reflecting the substantial untapped potential.
Western and rural regions present both challenges and opportunities, with limited healthcare infrastructure constraining market access while representing significant patient populations requiring diabetes management solutions. Government initiatives targeting rural healthcare development are gradually improving market conditions in these areas.
Regional preferences vary considerably, with urban populations showing greater acceptance of advanced insulin delivery devices and digital health solutions, while rural patients often prefer traditional treatment approaches and cost-effective options. Distribution strategies must account for these regional differences to optimize market penetration and patient outcomes.
Market competition in China’s insulin drugs and delivery devices sector features a diverse mix of international pharmaceutical giants and emerging domestic manufacturers, creating a dynamic competitive environment that drives innovation and competitive pricing strategies.
Competitive strategies emphasize product differentiation, pricing optimization, and strategic partnerships with local healthcare providers and distribution networks. Innovation focus areas include smart insulin delivery devices, personalized dosing algorithms, and integrated diabetes management platforms that combine therapeutic products with digital health solutions.
Market segmentation analysis reveals distinct categories within the China insulin drugs and delivery devices market, each characterized by unique growth patterns, customer preferences, and competitive dynamics.
By Product Type:
By Application:
By End User:
Insulin drugs category demonstrates robust growth driven by increasing patient populations and expanding treatment protocols. Analog insulin products are gaining market share over traditional human insulin formulations, with patients and healthcare providers recognizing superior pharmacokinetic profiles and improved glycemic control outcomes. Biosimilar insulin products are emerging as cost-effective alternatives, particularly important in price-sensitive market segments.
Delivery devices category shows exceptional innovation momentum, with smart insulin pens and automated insulin pumps representing the fastest-growing segments. Connected devices that integrate with smartphone applications and cloud-based data platforms are attracting significant patient interest, particularly among younger demographics comfortable with digital health technologies.
Continuous glucose monitoring systems are experiencing rapid adoption as standalone products and integrated components of comprehensive diabetes management systems. Real-time glucose data capabilities enable more precise insulin dosing decisions and improved patient outcomes, driving demand for these advanced monitoring solutions.
Combination products that integrate insulin delivery with glucose monitoring capabilities represent emerging market opportunities, offering patients comprehensive diabetes management solutions in single, convenient devices. Market acceptance of these integrated systems is growing as patients seek simplified treatment regimens and healthcare providers recognize improved compliance benefits.
Pharmaceutical manufacturers benefit from expanding market opportunities driven by growing patient populations and increasing demand for innovative insulin formulations. Revenue growth potential is substantial, particularly for companies developing advanced analog insulin products and biosimilar alternatives that address diverse patient needs and economic requirements.
Medical device companies experience significant opportunities in the rapidly expanding insulin delivery device segment, with smart technology integration creating new product categories and premium pricing opportunities. Innovation leadership in connected devices and automated insulin delivery systems provides competitive advantages and market differentiation.
Healthcare providers gain access to improved treatment tools and patient monitoring capabilities that enhance clinical outcomes and operational efficiency. Digital health integration enables remote patient monitoring and telemedicine capabilities, expanding care delivery options while reducing healthcare system burdens.
Patients benefit from expanded treatment options, improved insulin delivery convenience, and enhanced diabetes management capabilities that support better glycemic control and quality of life improvements. Cost reduction opportunities through generic insulin availability and insurance coverage expansion make treatments more accessible to broader patient populations.
Government stakeholders achieve public health objectives through improved diabetes care outcomes and reduced long-term healthcare costs associated with diabetes complications. Economic benefits include reduced healthcare expenditure and improved population health metrics supporting national development goals.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Digital transformation represents the most significant trend reshaping the China insulin drugs and delivery devices market, with smart insulin pens, mobile health applications, and cloud-based diabetes management platforms gaining widespread adoption. Connected devices that provide real-time data sharing between patients and healthcare providers are becoming standard expectations rather than premium features.
Personalized medicine approaches are gaining momentum, with genetic testing and biomarker analysis enabling more targeted insulin therapy selection and dosing optimization. Precision diabetes care protocols that consider individual patient characteristics, lifestyle factors, and genetic predispositions are becoming increasingly sophisticated and clinically relevant.
Biosimilar adoption continues accelerating as cost-conscious patients and healthcare systems seek affordable alternatives to branded insulin products. Market penetration of biosimilar insulin products is expected to reach 35% market share within the next five years, driven by government initiatives supporting generic medication usage.
Telemedicine integration has become a permanent feature of diabetes care delivery, with remote consultation capabilities and digital patient monitoring systems enabling continuous care management. Virtual care platforms are particularly valuable for patients in rural areas with limited access to specialized diabetes care providers.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning applications are being integrated into insulin dosing algorithms and glucose prediction models, enabling more precise diabetes management and reducing hypoglycemic episodes. AI-powered diabetes management systems are showing 25% improvement in glycemic control outcomes compared to traditional approaches.
Recent developments in the China insulin drugs and delivery devices market reflect accelerating innovation and expanding market access initiatives. Regulatory approvals for several new insulin analog products and advanced delivery devices have enhanced treatment options for Chinese patients, while government reimbursement expansions have improved affordability.
Manufacturing investments by both international and domestic companies have increased local production capacity and reduced supply chain dependencies. Facility expansions and technology transfers are enabling more cost-effective insulin production while meeting growing domestic demand requirements.
Strategic partnerships between pharmaceutical companies and technology firms are accelerating digital health integration and creating comprehensive diabetes management ecosystems. Collaboration initiatives focus on developing culturally appropriate solutions that address specific Chinese patient preferences and healthcare system requirements.
Clinical research activities have intensified, with numerous studies evaluating new insulin formulations, delivery technologies, and treatment protocols specifically designed for Chinese patient populations. Research outcomes are informing product development strategies and regulatory approval pathways for innovative diabetes management solutions.
Market consolidation activities include mergers, acquisitions, and strategic alliances that are reshaping competitive dynamics and creating larger, more capable market participants with enhanced research and development capabilities.
Strategic recommendations for market participants include prioritizing digital health integration and developing comprehensive diabetes management platforms that extend beyond traditional product boundaries. MarkWide Research analysis suggests that companies investing in connected device technologies and data analytics capabilities will achieve superior competitive positioning and customer loyalty.
Market entry strategies should emphasize partnerships with local healthcare providers and distribution networks to navigate regulatory requirements and cultural preferences effectively. Localization efforts that adapt products and services to specific Chinese market needs will enhance acceptance and market penetration rates.
Innovation focus areas should include biosimilar insulin development, smart delivery device technologies, and artificial intelligence applications for diabetes management optimization. Research and development investments in these areas are likely to generate significant returns as market demand continues expanding.
Pricing strategies must balance profitability objectives with accessibility requirements, considering the diverse economic capabilities of Chinese patient populations. Tiered pricing approaches that offer premium and cost-effective options can maximize market coverage while maintaining sustainable business models.
Regulatory engagement should be proactive and collaborative, working closely with Chinese authorities to ensure compliance while advocating for policies that support innovation and patient access. Government relations capabilities are essential for navigating the complex regulatory environment and securing favorable market conditions.
Long-term projections for the China insulin drugs and delivery devices market indicate sustained growth driven by demographic trends, technological advancement, and expanding healthcare access. Market evolution will likely accelerate toward integrated diabetes management ecosystems that combine pharmaceutical products, medical devices, and digital health solutions in comprehensive care platforms.
Technology convergence will create new product categories and business models, with artificial intelligence, machine learning, and Internet of Things technologies becoming standard components of diabetes management solutions. Smart insulin systems that automatically adjust dosing based on real-time glucose levels and patient activity patterns represent the next frontier of diabetes care innovation.
Market accessibility will continue improving through government healthcare reforms, insurance coverage expansions, and cost reduction initiatives that make advanced diabetes management solutions available to broader patient populations. Rural market development will accelerate as healthcare infrastructure improvements and telemedicine capabilities extend specialized care to underserved regions.
Competitive dynamics will intensify as market opportunities attract new entrants and drive innovation acceleration. MWR forecasts suggest that market leadership will increasingly depend on comprehensive solution capabilities rather than individual product excellence, favoring companies with integrated diabetes management platforms.
Patient empowerment trends will continue strengthening, with self-management capabilities and patient education programs becoming integral components of successful diabetes care strategies. Outcome-based care models that tie treatment costs to patient health improvements are expected to gain adoption, creating new value propositions for innovative diabetes management solutions.
The China insulin drugs and delivery devices market represents a transformative healthcare sector characterized by exceptional growth potential, technological innovation, and expanding patient access. Market fundamentals remain robust, supported by increasing diabetes prevalence, favorable government policies, and continuous advancement in treatment technologies and delivery systems.
Strategic opportunities abound for companies capable of developing comprehensive diabetes management solutions that address the diverse needs of Chinese patients while navigating complex regulatory and cultural requirements. Digital health integration and personalized medicine approaches will define competitive success in this evolving market landscape.
Future success will depend on companies’ ability to balance innovation with affordability, ensuring that advanced diabetes management solutions remain accessible to China’s diverse patient population. Collaborative approaches that leverage partnerships with local healthcare providers, technology companies, and government agencies will be essential for sustainable market development and patient outcome optimization.
What is Insulin Drugs And Delivery Devices?
Insulin Drugs And Delivery Devices refer to the medications and tools used to manage diabetes by delivering insulin to patients. This includes various forms of insulin, such as rapid-acting and long-acting types, as well as delivery devices like syringes, pens, and pumps.
What are the key players in the China Insulin Drugs And Delivery Devices Market?
Key players in the China Insulin Drugs And Delivery Devices Market include companies like Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, and Eli Lilly, which are known for their innovative insulin formulations and delivery technologies, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the China Insulin Drugs And Delivery Devices Market?
The growth of the China Insulin Drugs And Delivery Devices Market is driven by the increasing prevalence of diabetes, advancements in insulin delivery technologies, and rising awareness about diabetes management among patients.
What challenges does the China Insulin Drugs And Delivery Devices Market face?
Challenges in the China Insulin Drugs And Delivery Devices Market include regulatory hurdles, high costs of advanced delivery devices, and competition from alternative diabetes management solutions.
What opportunities exist in the China Insulin Drugs And Delivery Devices Market?
Opportunities in the China Insulin Drugs And Delivery Devices Market include the development of smart insulin delivery systems, increasing investment in diabetes care, and the potential for personalized medicine approaches.
What trends are shaping the China Insulin Drugs And Delivery Devices Market?
Trends in the China Insulin Drugs And Delivery Devices Market include the rise of digital health solutions, integration of mobile apps for diabetes management, and the growing demand for user-friendly delivery devices.
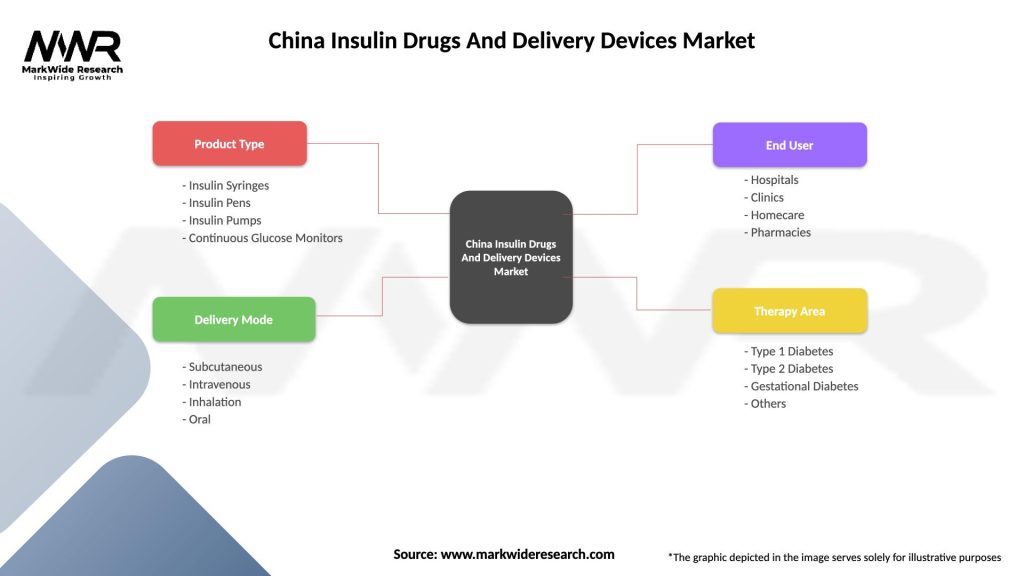
China Insulin Drugs And Delivery Devices Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Insulin Syringes, Insulin Pens, Insulin Pumps, Continuous Glucose Monitors |
| Delivery Mode | Subcutaneous, Intravenous, Inhalation, Oral |
| End User | Hospitals, Clinics, Homecare, Pharmacies |
| Therapy Area | Type 1 Diabetes, Type 2 Diabetes, Gestational Diabetes, Others |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the China Insulin Drugs And Delivery Devices Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at