444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The China Engineering, Procurement, and Construction Management (EPCM) market represents a cornerstone of the nation’s industrial infrastructure development, encompassing comprehensive project management services across multiple sectors. This dynamic market has experienced remarkable transformation, driven by China’s ambitious infrastructure initiatives, urbanization programs, and industrial modernization efforts. The EPCM sector in China demonstrates exceptional growth potential, with industry analysts projecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.2% through the forecast period.
Market dynamics in China’s EPCM sector reflect the country’s strategic focus on sustainable development, technological advancement, and international expansion. The market encompasses diverse project types, from petrochemical facilities and power generation plants to transportation infrastructure and smart city developments. Chinese EPCM companies have evolved from primarily domestic service providers to globally competitive organizations, capturing approximately 35% market share in Asia-Pacific EPCM projects.
Regional distribution within China shows concentrated activity in eastern coastal provinces, with Guangdong, Jiangsu, and Shandong accounting for nearly 45% of total EPCM project volume. The market’s expansion into western regions aligns with government initiatives promoting balanced regional development and resource utilization optimization.
The China Engineering, Procurement, and Construction Management (EPCM) market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of professional services that integrate engineering design, procurement coordination, and construction management activities for large-scale industrial and infrastructure projects across the Chinese mainland. This market encompasses specialized consulting services where EPCM contractors act as project managers and technical advisors, coordinating multiple stakeholders while maintaining cost control and schedule adherence.
EPCM services differ from traditional Engineering, Procurement, and Construction (EPC) contracts by positioning the service provider as the owner’s representative rather than assuming construction risk. This model provides enhanced project control, transparency, and flexibility while leveraging specialized expertise in complex project environments. The Chinese EPCM market has adapted this international model to align with local regulatory requirements, business practices, and cultural considerations.
Service integration within China’s EPCM market includes front-end engineering design, vendor qualification and procurement support, construction supervision, commissioning assistance, and project closeout services. This comprehensive approach enables clients to benefit from streamlined project delivery while maintaining direct contractual relationships with major suppliers and contractors.
China’s EPCM market stands at the forefront of the nation’s industrial transformation, driven by unprecedented infrastructure investment, technological innovation, and international expansion strategies. The market demonstrates robust growth fundamentals, supported by government policies promoting high-quality development and sustainable industrialization. Key growth drivers include the Belt and Road Initiative, domestic industrial upgrading, and increasing adoption of digital project management technologies.
Market segmentation reveals strong performance across multiple sectors, with petrochemicals, power generation, and transportation infrastructure representing the largest application areas. The integration of advanced technologies, including Building Information Modeling (BIM), artificial intelligence, and Internet of Things (IoT) solutions, has enhanced project delivery efficiency by approximately 25% compared to traditional methods.
Competitive dynamics showcase a mix of state-owned enterprises, private companies, and international joint ventures, creating a diverse ecosystem that promotes innovation and best practice adoption. Leading Chinese EPCM providers have expanded their global footprint, participating in major international projects and establishing strategic partnerships with technology leaders.
Strategic insights from comprehensive market analysis reveal several critical trends shaping China’s EPCM landscape:
Market maturation indicators suggest increasing sophistication in service delivery, with clients demanding higher levels of project transparency, cost predictability, and schedule reliability. This evolution has prompted EPCM providers to invest heavily in technology infrastructure and professional development programs.
Government policy support serves as the primary catalyst for China’s EPCM market expansion, with national development strategies emphasizing infrastructure modernization and industrial upgrading. The 14th Five-Year Plan allocates substantial resources for strategic infrastructure projects, creating sustained demand for professional project management services. Additionally, the Carbon Neutrality commitment by 2060 drives investment in renewable energy and clean technology projects requiring specialized EPCM expertise.
Industrial transformation initiatives across traditional manufacturing sectors generate significant EPCM opportunities as companies modernize facilities, implement automation technologies, and enhance environmental compliance. The petrochemical industry’s shift toward higher-value products and cleaner production processes particularly benefits EPCM service providers with specialized technical capabilities.
Urbanization acceleration continues driving infrastructure development in tier-two and tier-three cities, creating demand for transportation systems, utilities, and public facilities. Smart city initiatives incorporate advanced technologies requiring integrated project management approaches that align with EPCM service models.
International expansion through the Belt and Road Initiative provides Chinese EPCM companies with opportunities to apply domestic expertise in international markets, while simultaneously attracting foreign investment in domestic projects that require international standards and best practices.
Regulatory complexity presents ongoing challenges for EPCM providers, particularly regarding environmental compliance, safety standards, and quality assurance requirements. Frequent policy updates and varying local implementation approaches can create project delays and cost overruns, impacting overall market growth momentum.
Talent shortage in specialized project management disciplines constrains market expansion, despite increasing educational investment and professional development programs. The rapid pace of technological advancement requires continuous skill updates, creating pressure on human resource development and retention strategies.
Economic volatility and cyclical downturns in key industries can significantly impact EPCM demand, as clients defer capital investment projects during uncertain economic conditions. The interconnected nature of global supply chains also exposes Chinese EPCM projects to international market fluctuations and geopolitical tensions.
Technology integration costs associated with digital transformation initiatives require substantial upfront investment, potentially limiting adoption among smaller EPCM providers. The need for continuous technology upgrades and cybersecurity measures adds ongoing operational complexity and expense.
Green infrastructure development presents substantial opportunities as China pursues carbon neutrality goals through renewable energy projects, energy efficiency improvements, and environmental remediation initiatives. EPCM providers with expertise in sustainable construction practices and clean technology integration are positioned to capture significant market share in this expanding segment.
Digital infrastructure expansion including 5G networks, data centers, and smart manufacturing facilities creates new EPCM service categories requiring specialized technical knowledge and project management approaches. The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence technologies in industrial projects demands enhanced coordination and systems integration capabilities.
Regional development initiatives focusing on western China and northeastern industrial base revitalization generate substantial infrastructure investment opportunities. These programs emphasize balanced regional development and resource optimization, creating demand for comprehensive project management services across diverse geographic areas.
International market penetration through strategic partnerships and joint ventures enables Chinese EPCM companies to access global projects while bringing international expertise to domestic markets. Cross-border collaboration facilitates knowledge transfer and best practice adoption, enhancing overall service quality and competitiveness.
Supply-demand equilibrium in China’s EPCM market reflects the interplay between massive infrastructure investment programs and the availability of qualified service providers. Current market conditions indicate strong demand growth outpacing service provider capacity expansion, creating opportunities for new market entrants and service diversification strategies.
Competitive intensity varies significantly across market segments, with specialized technical services commanding premium pricing while commodity project management services face increasing price pressure. Market leaders differentiate through technology adoption, international experience, and comprehensive service portfolios that address complete project lifecycles.
Value chain integration trends show EPCM providers expanding service offerings to include financing advisory, regulatory compliance support, and post-construction operations management. This evolution toward comprehensive project solutions enhances client relationships while creating additional revenue streams and competitive barriers.
Technology disruption continues reshaping traditional EPCM service delivery models, with digital platforms enabling remote project monitoring, virtual collaboration, and predictive maintenance capabilities. Early technology adopters report project efficiency improvements of approximately 30% in schedule adherence and cost control metrics.
Comprehensive market analysis employs multiple research methodologies to ensure accurate and reliable insights into China’s EPCM market dynamics. Primary research includes structured interviews with industry executives, project managers, and client organizations across diverse sectors and geographic regions. This qualitative approach provides deep insights into market trends, challenges, and opportunities from stakeholder perspectives.
Secondary research encompasses analysis of government publications, industry reports, company financial statements, and project databases to establish quantitative market parameters and validate primary research findings. Statistical analysis of historical project data enables identification of growth patterns, seasonal variations, and cyclical trends affecting market performance.
Data validation processes include cross-referencing multiple sources, expert panel reviews, and statistical significance testing to ensure research accuracy and reliability. Market sizing methodologies incorporate bottom-up analysis of project volumes and top-down validation through industry capacity assessments and economic indicators.
Forecasting models integrate macroeconomic variables, policy impact assessments, and industry-specific drivers to project future market development scenarios. Sensitivity analysis examines potential variations in key assumptions and their impact on market projections, providing stakeholders with comprehensive risk assessment frameworks.
Eastern China dominates the EPCM market landscape, accounting for approximately 52% of total project activity due to concentrated industrial development, port infrastructure, and international trade facilities. Provinces including Guangdong, Jiangsu, and Zhejiang benefit from advanced manufacturing clusters, technology innovation centers, and proximity to major markets driving sustained EPCM demand.
Northern China represents a significant market segment focused on heavy industry modernization, energy infrastructure, and transportation networks. The region’s emphasis on industrial upgrading and environmental compliance creates opportunities for EPCM providers with expertise in facility retrofits and clean technology implementation.
Western China emerges as a high-growth region supported by government development initiatives and natural resource projects. Infrastructure investment in transportation, energy, and telecommunications creates substantial EPCM opportunities, though geographic challenges and talent availability constraints require specialized service approaches.
Central China benefits from its strategic location as a logistics and manufacturing hub, generating demand for warehouse facilities, transportation infrastructure, and industrial parks. The region’s role in connecting eastern and western markets drives investment in multimodal transportation systems and supply chain infrastructure.
Southern China maintains strong EPCM activity through petrochemical complexes, renewable energy projects, and cross-border infrastructure development. The region’s international connectivity and technology adoption leadership create demand for sophisticated project management services and international standard compliance.
Market leadership in China’s EPCM sector reflects a diverse ecosystem of service providers ranging from large state-owned enterprises to specialized private companies and international joint ventures. The competitive environment promotes innovation, service quality improvements, and technology adoption across the industry.
Competitive differentiation strategies emphasize technology adoption, international experience, specialized technical capabilities, and comprehensive service portfolios. Market leaders invest heavily in digital transformation, talent development, and strategic partnerships to maintain competitive advantages in an evolving marketplace.
By Industry Vertical:
By Service Type:
By Project Size:
Petrochemical EPCM services demonstrate exceptional growth driven by industry consolidation, environmental compliance requirements, and product portfolio optimization. Advanced process technologies and integrated facility designs require specialized engineering expertise and comprehensive project coordination capabilities. The segment benefits from China’s position as a global petrochemical manufacturing hub and increasing domestic demand for high-performance materials.
Power generation EPCM experiences transformation through renewable energy integration and grid modernization initiatives. Solar, wind, and energy storage projects require different technical approaches compared to traditional thermal power facilities, creating opportunities for EPCM providers with clean energy expertise. Smart grid development and distributed energy systems add complexity requiring advanced project management capabilities.
Transportation infrastructure EPCM benefits from continued urbanization and regional connectivity improvements. High-speed rail expansion, urban transit systems, and multimodal logistics hubs require sophisticated engineering and construction management approaches. Integration of intelligent transportation systems and sustainable design principles creates additional technical requirements and service opportunities.
Industrial facility EPCM serves manufacturing sector modernization through automation implementation, environmental compliance upgrades, and capacity expansion projects. Smart manufacturing initiatives incorporating Internet of Things and artificial intelligence technologies require specialized project management approaches and systems integration expertise.
For Project Owners:
For EPCM Service Providers:
For Contractors and Suppliers:
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Digital transformation represents the most significant trend reshaping China’s EPCM market, with providers investing heavily in Building Information Modeling (BIM), artificial intelligence, and Internet of Things technologies. These digital tools enable enhanced project visualization, predictive analytics, and real-time monitoring capabilities that improve decision-making and risk management throughout project lifecycles.
Sustainability integration drives increasing demand for green construction practices, renewable energy expertise, and environmental compliance services. EPCM providers are developing specialized capabilities in sustainable design, carbon footprint reduction, and circular economy principles to meet evolving client requirements and regulatory standards.
International standardization reflects Chinese EPCM companies’ efforts to adopt global best practices and certification standards to compete in international markets. This trend includes investment in international project management certifications, quality management systems, and safety protocols that align with global industry standards.
Service integration shows EPCM providers expanding beyond traditional project management to offer comprehensive solutions including financing advisory, regulatory compliance, and operations support. This evolution toward full-service project delivery creates additional value for clients while establishing stronger competitive positions.
Talent development initiatives focus on building specialized expertise in emerging technologies, international project management, and cross-cultural collaboration. Professional training programs and university partnerships aim to address skill gaps and prepare the workforce for evolving market requirements.
Strategic partnerships between Chinese EPCM providers and international technology companies have accelerated knowledge transfer and capability development. Recent collaborations focus on digital project management platforms, advanced engineering software, and specialized technical services that enhance competitive positioning in global markets.
Technology investments by leading EPCM companies include development of integrated project management platforms, artificial intelligence applications, and virtual reality tools for project visualization and training. These investments demonstrate commitment to digital transformation and competitive differentiation through technology leadership.
International expansion activities show Chinese EPCM providers establishing overseas offices, forming joint ventures with local partners, and participating in major international projects. According to MarkWide Research analysis, Chinese companies now participate in approximately 22% of major international EPCM projects in developing markets.
Regulatory developments include updated project management standards, enhanced safety requirements, and environmental compliance protocols that influence EPCM service delivery approaches. These changes require ongoing adaptation and investment in compliance capabilities across the industry.
Market consolidation trends show larger EPCM providers acquiring specialized companies to expand technical capabilities and geographic coverage. This consolidation creates more comprehensive service providers while potentially reducing competitive intensity in certain market segments.
Technology adoption should remain a top priority for EPCM providers seeking competitive advantages in an evolving marketplace. Investment in digital project management tools, artificial intelligence applications, and data analytics capabilities will enable enhanced service delivery and operational efficiency. Companies should develop comprehensive technology roadmaps aligned with client requirements and industry trends.
Talent development strategies must address critical skill gaps in project management, technical specialization, and international business practices. Partnerships with universities, professional training programs, and international exchange initiatives can help build the expertise needed for market leadership. Retention strategies should emphasize career development opportunities and competitive compensation packages.
International expansion requires careful market selection, local partnership development, and cultural adaptation strategies. Companies should focus on markets with strong infrastructure investment programs and favorable regulatory environments while building relationships with local partners who understand regional business practices and requirements.
Service diversification toward comprehensive project solutions can create competitive advantages and additional revenue streams. EPCM providers should consider expanding into adjacent services such as financing advisory, regulatory compliance, and operations support while maintaining core competencies in project management and technical services.
Sustainability expertise development will become increasingly important as clients prioritize environmental compliance and carbon reduction objectives. Investment in green construction practices, renewable energy technologies, and environmental management capabilities will position providers for growth in emerging market segments.
Market growth prospects for China’s EPCM sector remain robust, supported by continued infrastructure investment, industrial modernization, and international expansion initiatives. MarkWide Research projects sustained growth momentum with particular strength in renewable energy, digital infrastructure, and environmental projects driving demand for specialized EPCM services.
Technology evolution will continue reshaping service delivery models, with artificial intelligence, machine learning, and advanced analytics becoming standard tools for project management and risk assessment. The integration of Internet of Things sensors and real-time monitoring systems will enable predictive maintenance and optimized resource allocation throughout project lifecycles.
International competitiveness of Chinese EPCM providers is expected to strengthen through continued investment in technology, talent development, and global partnerships. The combination of domestic market experience, cost competitiveness, and technological capabilities positions Chinese companies for increased participation in international projects, particularly in developing markets aligned with Belt and Road Initiative objectives.
Regulatory environment evolution will likely emphasize environmental compliance, safety standards, and quality assurance requirements. EPCM providers must maintain adaptability to changing regulations while investing in compliance capabilities that meet both domestic and international standards.
Market maturation indicators suggest increasing client sophistication and demand for value-added services beyond traditional project management. This evolution creates opportunities for providers who can demonstrate measurable value creation through cost optimization, schedule reliability, and quality enhancement while adapting to changing market requirements and technological advancement.
China’s Engineering, Procurement, and Construction Management market represents a dynamic and rapidly evolving sector positioned at the intersection of the nation’s infrastructure development ambitions and industrial modernization objectives. The market demonstrates exceptional growth potential, driven by sustained government investment, technological innovation, and international expansion opportunities that create substantial value for stakeholders across the project delivery ecosystem.
Strategic positioning for success in this market requires comprehensive understanding of evolving client requirements, regulatory environments, and technological capabilities that define competitive advantage. EPCM providers who invest in digital transformation, talent development, and service diversification while maintaining operational excellence will be best positioned to capture growth opportunities and establish market leadership positions.
Future success in China’s EPCM market will depend on the ability to adapt to changing market conditions, embrace technological innovation, and deliver measurable value to clients through enhanced project outcomes. The integration of sustainability principles, international best practices, and advanced project management methodologies will define the next generation of market leaders in this critical sector of China’s economic development infrastructure.
What is Engineering, Procurement, And Construction Management?
Engineering, Procurement, And Construction Management (EPCM) refers to a project delivery method where the contractor is responsible for the design, procurement of materials, and construction of a project. This approach is commonly used in large-scale infrastructure projects, such as power plants, highways, and industrial facilities.
What are the key players in the China Engineering, Procurement, And Construction Management (EPCM) Market?
Key players in the China Engineering, Procurement, And Construction Management (EPCM) Market include China State Construction Engineering Corporation, China Communications Construction Company, and Sinopec Engineering Group, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the China Engineering, Procurement, And Construction Management (EPCM) Market?
The growth of the China Engineering, Procurement, And Construction Management (EPCM) Market is driven by increasing urbanization, government investments in infrastructure, and the rising demand for energy projects. These factors contribute to a robust pipeline of construction projects across various sectors.
What challenges does the China Engineering, Procurement, And Construction Management (EPCM) Market face?
The China Engineering, Procurement, And Construction Management (EPCM) Market faces challenges such as regulatory hurdles, fluctuating material costs, and skilled labor shortages. These issues can impact project timelines and overall project costs.
What opportunities exist in the China Engineering, Procurement, And Construction Management (EPCM) Market?
Opportunities in the China Engineering, Procurement, And Construction Management (EPCM) Market include the expansion of renewable energy projects, smart city initiatives, and advancements in construction technology. These trends are expected to create new avenues for growth and innovation.
What trends are shaping the China Engineering, Procurement, And Construction Management (EPCM) Market?
Trends shaping the China Engineering, Procurement, And Construction Management (EPCM) Market include the adoption of digital technologies, such as Building Information Modeling (BIM), and a focus on sustainability in construction practices. These trends are enhancing project efficiency and reducing environmental impact.
China Engineering, Procurement, And Construction Management (EPCM) Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
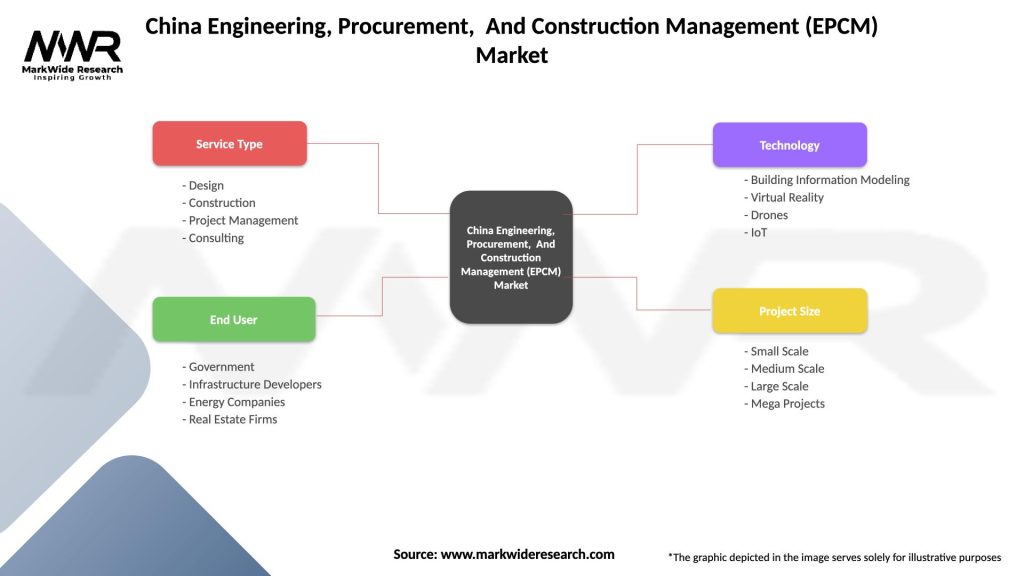
| Service Type | Design, Construction, Project Management, Consulting |
| End User | Government, Infrastructure Developers, Energy Companies, Real Estate Firms |
| Technology | Building Information Modeling, Virtual Reality, Drones, IoT |
| Project Size | Small Scale, Medium Scale, Large Scale, Mega Projects |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the China Engineering, Procurement, And Construction Management (EPCM) Market
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at