444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The children’s programming education market is a rapidly expanding sector focused on teaching coding and computer programming skills to young learners. With the increasing importance of technology literacy in the modern world, parents and educators are seeking innovative ways to introduce coding concepts to children in a fun and engaging manner. Children’s programming education programs utilize age-appropriate resources, interactive platforms, and hands-on activities to cultivate computational thinking and problem-solving skills from an early age.
Meaning
Children’s programming education refers to the provision of coding and computer programming instruction tailored specifically to young learners, typically aged between 5 and 18 years old. These educational programs aim to introduce fundamental coding concepts such as algorithms, loops, conditionals, and variables in an accessible and engaging manner. Through interactive lessons, games, projects, and collaborative activities, children develop critical thinking, creativity, and digital literacy skills essential for success in the digital age.
Executive Summary
The children’s programming education market is experiencing exponential growth, fueled by increasing demand for STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) education, parental emphasis on future-ready skills, and advancements in educational technology. Key market players offer a diverse range of programming courses, coding camps, robotics workshops, and online platforms designed to cater to different age groups and skill levels. With the rising importance of coding literacy in the job market and society, the children’s programming education market presents lucrative opportunities for innovation, expansion, and market penetration.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Several factors are driving the growth of the children’s programming education market:
Market Restraints
Despite the market’s growth potential, several challenges hinder its progress:
Market Opportunities
The children’s programming education market offers several growth opportunities:
Market Dynamics
The children’s programming education market is characterized by dynamic trends and evolving pedagogical approaches:
Regional Analysis
The children’s programming education market exhibits regional variations in demand, adoption, and regulatory frameworks:
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Children’s Programming Education Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
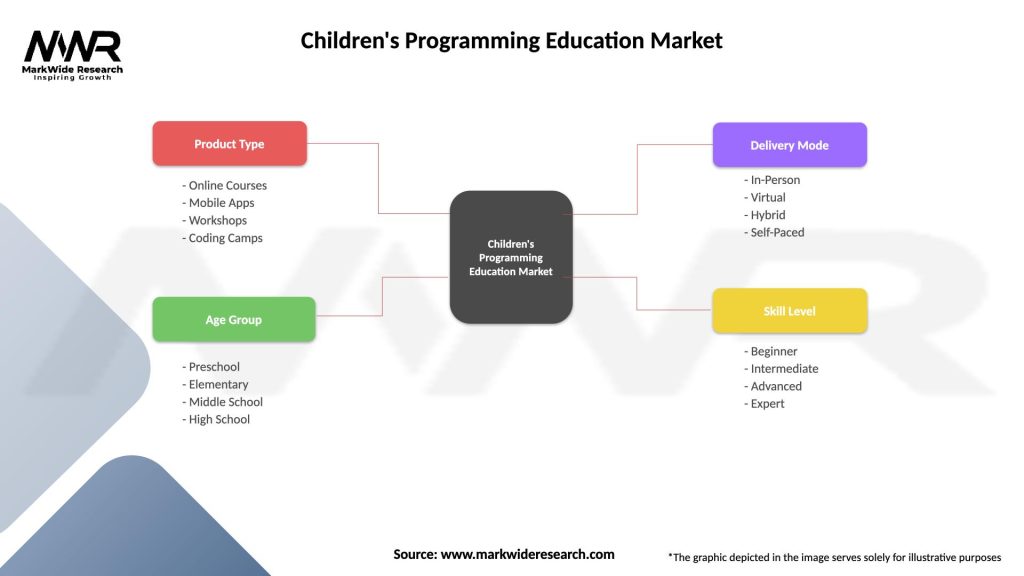
Segmentation
The children’s programming education market can be segmented based on various factors, including:
Category-wise Insights
Each category of children’s programming education offers unique benefits and learning opportunities:
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
The children’s programming education market offers numerous benefits for industry participants and stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Several key trends are shaping the children’s programming education market:
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the children’s programming education market:
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Based on market trends and developments, analysts suggest the following strategies for industry participants:
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the children’s programming education market is highly promising, with sustained growth and innovation anticipated in the coming years. As coding literacy becomes increasingly essential in an interconnected, technology-driven world, the demand for high-quality coding education programs for children will continue to rise. Industry stakeholders that prioritize equity, accessibility, innovation, and collaboration are poised to shape the future of children’s programming education and empower the next generation of digital innovators and problem solvers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the children’s programming education market represents a dynamic and rapidly expanding sector at the intersection of education, technology, and workforce development. With the growing recognition of coding literacy as a critical skill for future success, there is a tremendous opportunity to cultivate computational thinking, creativity, and digital fluency among young learners. By leveraging innovative teaching methodologies, educational technologies, and collaborative partnerships, industry participants can address the challenges and opportunities of the evolving coding education landscape and empower children worldwide to thrive in an increasingly digital society.
What is Children’s Programming Education?
Children’s Programming Education refers to the teaching of programming concepts and skills to children, often through interactive and engaging methods. This education can include coding languages, robotics, and computational thinking, aimed at fostering problem-solving and creativity in young learners.
What are the key players in the Children’s Programming Education Market?
Key players in the Children’s Programming Education Market include companies like Code.org, Tynker, and Scratch, which provide platforms and resources for teaching coding to children. These companies focus on creating engaging content and tools that make learning programming accessible and fun, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Children’s Programming Education Market?
The Children’s Programming Education Market is driven by the increasing demand for STEM education, the rise of technology in everyday life, and the need for digital literacy among young learners. Additionally, the growing popularity of coding camps and online courses contributes to market expansion.
What challenges does the Children’s Programming Education Market face?
Challenges in the Children’s Programming Education Market include a lack of trained educators, varying access to technology among different regions, and the need for curriculum standardization. These factors can hinder the effective implementation of programming education in schools and communities.
What opportunities exist in the Children’s Programming Education Market?
Opportunities in the Children’s Programming Education Market include the development of new educational technologies, partnerships with schools to integrate coding into the curriculum, and the expansion of after-school programs. These initiatives can enhance children’s engagement with programming and prepare them for future careers.
What trends are shaping the Children’s Programming Education Market?
Trends in the Children’s Programming Education Market include the gamification of learning, the use of artificial intelligence in educational tools, and the increasing focus on inclusivity in tech education. These trends aim to make programming more appealing and accessible to a diverse range of children.
Children’s Programming Education Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Online Courses, Mobile Apps, Workshops, Coding Camps |
| Age Group | Preschool, Elementary, Middle School, High School |
| Delivery Mode | In-Person, Virtual, Hybrid, Self-Paced |
| Skill Level | Beginner, Intermediate, Advanced, Expert |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Children’s Programming Education Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at