444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
Market Overview
The Canada student loan market plays a crucial role in financing higher education for students across the country, providing access to funding for tuition, fees, living expenses, and other educational costs. The market encompasses various loan programs offered by federal and provincial governments, as well as private lenders, credit unions, and financial institutions. With the rising cost of education and increasing demand for post-secondary credentials, the Canada student loan market serves as a key financial resource for students and families seeking to pursue their educational goals and aspirations.
Meaning
The Canada student loan market refers to the financial ecosystem encompassing the origination, servicing, and repayment of loans taken out by students to finance their post-secondary education expenses. Student loans are available through government-sponsored programs, including the Canada Student Loans Program (CSLP) and provincial student loan programs, as well as private lenders and financial institutions. These loans typically feature favorable terms such as low interest rates, flexible repayment options, and borrower assistance programs to support students in financing their education.
Executive Summary
The Canada student loan market is a critical component of the higher education financing landscape, providing essential financial support to students pursuing post-secondary education. The market offers a range of loan programs and financing options to accommodate diverse student needs and financial circumstances. While government-sponsored loan programs play a central role in providing access to affordable education, private lenders and financial institutions also play a significant role in offering additional financing options and services. Understanding the complexities of the Canada student loan market is essential for policymakers, educational institutions, lenders, and borrowers to promote access, affordability, and equity in higher education.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The Canada student loan market operates in a dynamic and evolving environment shaped by factors such as government policies, economic conditions, demographic trends, and technological innovations. Understanding market dynamics and emerging trends is essential for stakeholders, including policymakers, educational institutions, lenders, and borrowers, to effectively navigate the complexities of the student loan landscape and promote access to affordable and quality higher education.
Regional Analysis
The Canada student loan market exhibits regional variations in terms of loan origination volumes, default rates, repayment outcomes, and socioeconomic factors. Key regional differences include disparities in college affordability, access to financial aid, and employment opportunities, influencing borrowers’ financial circumstances and repayment experiences across different provinces and territories.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies for Canada Student Loan Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
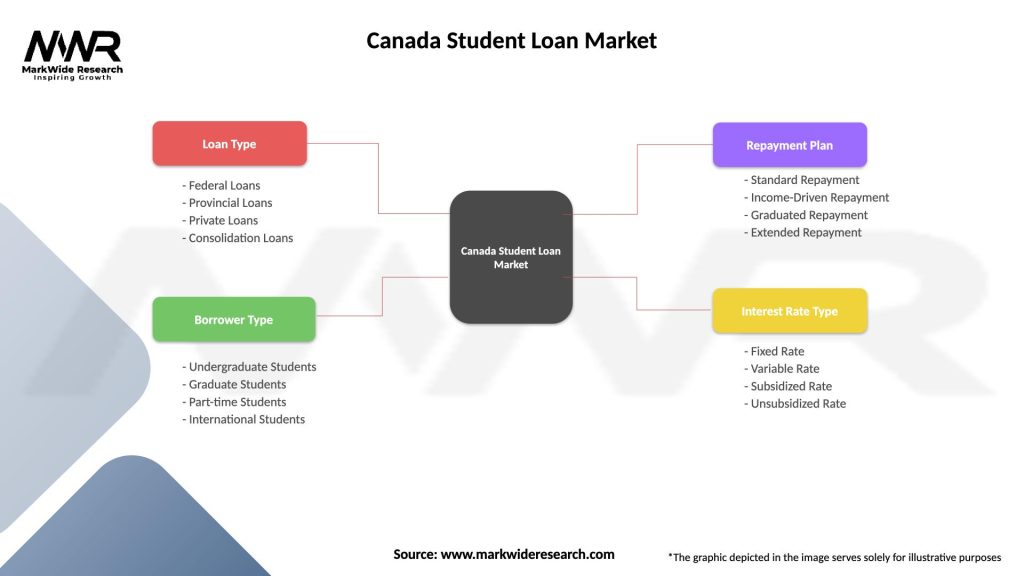
Segmentation
The Canada student loan market can be segmented based on factors such as loan type, borrower demographics, repayment status, and loan terms. Segmentation allows lenders, policymakers, and educational institutions to target specific borrower segments with tailored loan products, services, and support initiatives.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
The Canada student loan market offers several benefits for industry participants and stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis provides insights into the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats facing the Canada student loan market:
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the Canada student loan market, disrupting higher education operations, employment opportunities, and borrower repayment capabilities. The pandemic has led to changes in student enrollment patterns, increased demand for financial aid, and challenges in loan servicing and repayment. Government relief measures such as loan forbearance, interest waivers, and emergency grants have provided temporary relief to borrowers affected by the pandemic but have also raised concerns about long-term financial sustainability and borrower support.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the Canada student loan market is influenced by factors such as government policies, economic conditions, demographic trends, and technological advancements. While the market faces challenges such as rising student debt levels, repayment difficulties, and affordability concerns, opportunities for innovation, reform, and collaboration offer potential avenues for positive change and improvement. By addressing systemic challenges, promoting financial literacy, and advocating for policy reforms, stakeholders can contribute to a more sustainable, accessible, and equitable higher education financing system in Canada.
Conclusion
The Canada student loan market is a vital component of the higher education financing landscape, providing essential funding to students pursuing post-secondary education. While the market offers opportunities for access and affordability, it also faces challenges such as rising student debt levels, repayment difficulties, and concerns about equity and accessibility. By promoting financial education, expanding loan repayment options, advocating for policy reform, and enhancing collaboration among stakeholders, the Canada student loan market can evolve to better serve the needs of students and families, promote economic mobility, and ensure the long-term sustainability of higher education financing in Canada.
What is Canada Student Loan?
Canada Student Loan refers to financial assistance provided to students in Canada to help cover the costs of their post-secondary education. These loans are typically offered by the government and are designed to support students in paying for tuition, books, and living expenses.
What are the key players in the Canada Student Loan Market?
Key players in the Canada Student Loan Market include the Government of Canada, provincial governments, and financial institutions such as banks and credit unions that offer student loan products. These entities work together to provide funding and support for students pursuing higher education, among others.
What are the main drivers of the Canada Student Loan Market?
The main drivers of the Canada Student Loan Market include the rising cost of post-secondary education, increasing enrollment rates in colleges and universities, and the growing demand for skilled labor in various industries. These factors contribute to a higher reliance on student loans among Canadian students.
What challenges does the Canada Student Loan Market face?
The Canada Student Loan Market faces challenges such as rising student debt levels, concerns about loan repayment rates, and the impact of economic fluctuations on students’ ability to repay loans. Additionally, there are ongoing discussions about the accessibility and fairness of student loan programs.
What opportunities exist in the Canada Student Loan Market?
Opportunities in the Canada Student Loan Market include the potential for innovative loan products tailored to specific demographics, partnerships between educational institutions and financial organizations, and the development of financial literacy programs to help students manage their loans effectively.
What trends are shaping the Canada Student Loan Market?
Trends shaping the Canada Student Loan Market include the increasing use of technology in loan applications and management, a shift towards income-driven repayment plans, and a growing emphasis on mental health support for students dealing with financial stress. These trends reflect the evolving needs of students in Canada.
Canada Student Loan Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Loan Type | Federal Loans, Provincial Loans, Private Loans, Consolidation Loans |
| Borrower Type | Undergraduate Students, Graduate Students, Part-time Students, International Students |
| Repayment Plan | Standard Repayment, Income-Driven Repayment, Graduated Repayment, Extended Repayment |
| Interest Rate Type | Fixed Rate, Variable Rate, Subsidized Rate, Unsubsidized Rate |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies for Canada Student Loan Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at