444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The Cameroon agriculture market represents a cornerstone of the nation’s economy, contributing significantly to employment, food security, and export revenues. Agriculture sector activities encompass diverse farming systems ranging from smallholder subsistence farming to large-scale commercial plantations. The market demonstrates remarkable diversity with crops including cocoa, coffee, cotton, bananas, palm oil, rubber, and various food crops that sustain both domestic consumption and international trade.
Market dynamics indicate substantial growth potential driven by favorable climatic conditions, fertile soils, and increasing government support for agricultural modernization. The sector employs approximately 62% of the active population and contributes around 23% to the national GDP, highlighting its critical importance to Cameroon’s socioeconomic development. Agricultural productivity improvements through mechanization, improved seed varieties, and enhanced farming techniques continue to drive market expansion.
Regional variations across Cameroon’s diverse agro-ecological zones create opportunities for specialized crop production, from cocoa cultivation in the humid forest zones to cotton production in the northern savanna regions. The market benefits from strategic geographical positioning, providing access to both Atlantic and Central African markets through established trade corridors.
The Cameroon agriculture market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of agricultural production, processing, distribution, and trade activities within Cameroon’s borders. This market encompasses all aspects of crop cultivation, livestock farming, fisheries, forestry, and related value-added activities that contribute to the nation’s food security and economic development.
Agricultural market scope includes both subsistence farming practiced by smallholder farmers and commercial agriculture operations managed by agribusiness companies. The market integrates traditional farming methods with modern agricultural technologies, creating a dynamic environment where indigenous knowledge meets contemporary farming innovations. Value chain activities span from input supply and production to post-harvest handling, processing, marketing, and export operations.
Market participants include smallholder farmers, commercial agricultural enterprises, cooperatives, agro-processors, input suppliers, financial institutions, and government agencies working collectively to enhance agricultural productivity and market access. The market serves dual purposes of ensuring domestic food security while generating foreign exchange through agricultural exports.
Cameroon’s agricultural sector demonstrates robust growth potential underpinned by favorable natural endowments and strategic government initiatives aimed at modernizing farming practices. The market exhibits strong performance across multiple crop categories, with cocoa and coffee maintaining positions as leading export commodities while food crops ensure domestic nutritional security.
Key market drivers include increasing population demand, rising urbanization rates, and growing export opportunities to regional and international markets. The sector benefits from climate diversity that enables year-round production of various crops across different agro-ecological zones. Government policies promoting agricultural mechanization and value addition are expected to drive productivity improvements of approximately 15-20% annually in targeted subsectors.
Investment opportunities abound in areas such as irrigation infrastructure, post-harvest processing facilities, and agricultural technology adoption. The market faces challenges including limited access to modern farming inputs, inadequate rural infrastructure, and climate variability, yet these challenges present opportunities for innovative solutions and strategic partnerships.
Future prospects remain optimistic with projected growth in agricultural output driven by enhanced productivity measures, expanded cultivated areas, and improved market linkages. The sector’s contribution to poverty reduction and rural development continues to position agriculture as a priority area for national development strategies.
Strategic insights reveal several critical factors shaping Cameroon’s agricultural market landscape:
Population growth serves as a fundamental driver for Cameroon’s agricultural market, with increasing demographic pressure creating sustained demand for food products and agricultural commodities. Urbanization trends are reshaping consumption patterns, driving demand for processed and value-added agricultural products while creating market opportunities for commercial farming operations.
Government policy support through initiatives such as the Agricultural Investment and Market Development Project (PIDMA) and various agricultural modernization programs provides crucial momentum for market expansion. Infrastructure development including rural road networks, irrigation systems, and storage facilities enhances market access and reduces post-harvest losses significantly.
Export market opportunities continue expanding through regional trade agreements and international market access initiatives. Climate advantages including favorable rainfall patterns, diverse agro-ecological zones, and fertile soils create natural competitive advantages for agricultural production. Technology adoption through mobile banking, digital extension services, and precision farming techniques is gradually transforming traditional farming practices.
Private sector investment in agricultural value chains, including input supply, mechanization services, and agro-processing facilities, drives market modernization and efficiency improvements. Youth engagement in agriculture through entrepreneurship programs and modern farming techniques brings innovation and energy to traditional agricultural practices.
Infrastructure limitations pose significant challenges to agricultural market development, with inadequate rural road networks, limited storage facilities, and insufficient processing capacity constraining market efficiency. Access to finance remains a critical bottleneck, with many smallholder farmers lacking collateral and credit history required for agricultural loans and investment capital.
Climate variability and increasing weather unpredictability affect crop yields and farming schedules, creating uncertainty for agricultural planning and investment decisions. Limited mechanization keeps productivity levels below potential, with manual farming methods predominating across most agricultural operations.
Post-harvest losses estimated at significant percentages reduce market efficiency and farmer incomes, particularly affecting perishable crops and remote farming areas. Market information gaps limit farmers’ ability to make informed production and marketing decisions, often resulting in oversupply or undersupply situations.
Land tenure issues and unclear property rights create uncertainty for long-term agricultural investments and limit access to formal credit facilities. Skills gaps in modern farming techniques, business management, and technology adoption constrain productivity improvements and market competitiveness.
Agro-processing development presents substantial opportunities for value addition and market expansion, with current processing capacity utilization remaining well below potential. Export market diversification through quality improvement and certification programs can access premium international markets for Cameroon’s agricultural products.
Digital agriculture solutions including precision farming, drone technology, and mobile-based extension services offer pathways for productivity enhancement and market efficiency improvements. Irrigation infrastructure development can unlock year-round production potential and reduce dependency on rainfall patterns.
Cooperative strengthening and farmer organization development create opportunities for collective bargaining, bulk input procurement, and shared mechanization services. Youth entrepreneurship in agriculture through modern farming techniques and agribusiness ventures can drive innovation and market transformation.
Regional trade integration through CEMAC and other regional economic partnerships provides expanded market access for agricultural products. Climate-smart agriculture adoption offers opportunities for sustainable production increases while building resilience to climate change impacts.
Public-private partnerships in agricultural development can leverage combined resources and expertise for large-scale infrastructure and technology deployment projects.
Supply-side dynamics in Cameroon’s agricultural market are influenced by seasonal production patterns, weather conditions, and input availability. Demand patterns reflect both domestic consumption needs and export market requirements, creating complex market interactions that drive pricing and production decisions.
Price volatility remains a characteristic feature of agricultural markets, influenced by global commodity prices, local supply conditions, and seasonal variations. Market integration between rural production areas and urban consumption centers continues improving through infrastructure development and transportation network expansion.
Technology adoption rates are gradually increasing, with mobile phone penetration reaching rural areas and enabling access to market information, weather forecasts, and extension services. Value chain coordination is strengthening through improved linkages between producers, processors, and marketers.
Competition dynamics include both domestic competition among producers and international competition in export markets. Market efficiency improvements through reduced transaction costs, better information flow, and enhanced logistics capabilities continue driving market development.
Regulatory environment evolution through policy reforms and institutional strengthening creates more conducive conditions for agricultural market development and private sector participation.
Comprehensive market analysis employs multiple research approaches to ensure accurate and reliable insights into Cameroon’s agricultural market dynamics. Primary research involves extensive field surveys, farmer interviews, and stakeholder consultations across different agro-ecological zones and farming systems.
Secondary data analysis incorporates government statistics, international organization reports, and academic research to provide comprehensive market understanding. Quantitative analysis utilizes statistical methods to identify trends, correlations, and market patterns from collected data sets.
Qualitative research methods including focus group discussions and key informant interviews provide deeper insights into market challenges, opportunities, and stakeholder perspectives. Market surveys conducted across urban and rural areas capture consumption patterns, price trends, and market preferences.
Data validation processes ensure accuracy and reliability through cross-referencing multiple sources and expert verification. Analytical frameworks applied include value chain analysis, market structure assessment, and competitive landscape evaluation to provide comprehensive market insights.
Northern regions including Adamawa, North, and Far North provinces dominate cereal production, contributing approximately 55% of national grain output through extensive savanna farming systems. Cotton cultivation in these regions supports both domestic textile industries and export markets, with mechanized farming becoming increasingly prevalent.
Southern forest zones encompassing Centre, South, and East regions specialize in cash crop production, particularly cocoa and coffee cultivation. Cocoa production in these areas accounts for roughly 42% of national agricultural export revenues, with smallholder farmers predominating in production systems.
Coastal regions including Littoral and Southwest provinces focus on plantation agriculture, producing bananas, palm oil, and rubber for both domestic and international markets. Agro-industrial development is most advanced in these regions, with processing facilities and export infrastructure concentrated along the coast.
Western highlands demonstrate intensive farming systems with high population density and diversified crop production including coffee, vegetables, and food crops. Market gardening and horticultural production serve urban markets with fresh produce and high-value crops.
Regional specialization based on agro-ecological advantages creates complementary production systems that enhance national food security and market efficiency through inter-regional trade flows.
Market structure in Cameroon’s agriculture sector features diverse participants ranging from smallholder farmers to large agribusiness corporations. Key players include:
Competitive advantages vary among players, with large corporations leveraging economies of scale, technology, and market access while smallholder farmers benefit from local knowledge, flexibility, and community networks. Market consolidation trends are emerging in certain subsectors, particularly in agro-processing and export-oriented production.
By Crop Type:
By Farming System:
By Market Destination:
Cocoa Sector: Remains Cameroon’s flagship agricultural export, with production concentrated in humid forest zones. Quality improvement initiatives and farmer training programs are enhancing market competitiveness and premium pricing access. Sustainability certification programs are gaining traction among international buyers, creating opportunities for value addition.
Coffee Production: Both Arabica and Robusta varieties are cultivated, with Arabica commanding premium prices in international markets. Cooperative organizations play crucial roles in quality control and market access for smallholder coffee farmers. Processing improvements are enhancing product quality and market positioning.
Cotton Industry: Concentrated in northern regions with strong institutional support through UNVDA and cooperative systems. Mechanization adoption is increasing productivity while maintaining quality standards for textile industry requirements. Integrated pest management practices are improving sustainability and reducing production costs.
Food Crop Sector: Dominated by smallholder farmers producing for domestic markets and food security. Cassava processing is expanding through small-scale enterprises and cooperative initiatives. Rice production is receiving increased attention through irrigation development and improved varieties.
Palm Oil Industry: Large-scale plantations dominate production, with increasing focus on sustainable practices and certification. Smallholder integration programs are expanding to include small farmers in value chains while maintaining quality standards.
For Farmers:
For Agribusiness Companies:
For Government:
For International Partners:
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Sustainable Agriculture Adoption: Increasing focus on environmentally friendly farming practices, organic production methods, and certification programs responding to international market demands. Climate-smart agriculture techniques are gaining acceptance among farmers seeking resilience to climate variability.
Digital Technology Integration: Mobile phone penetration in rural areas is enabling access to market information, weather forecasts, and extension services. Precision agriculture tools including GPS technology and drone applications are beginning to emerge in commercial farming operations.
Value Chain Development: Emphasis on strengthening linkages between producers, processors, and markets through improved coordination and partnership arrangements. Contract farming arrangements are expanding, providing farmers with guaranteed markets and technical support.
Youth Participation: Growing interest among young people in agricultural entrepreneurship and modern farming techniques. Agribusiness ventures led by youth are introducing innovation and technology to traditional farming systems.
Cooperative Strengthening: Farmer organizations and cooperatives are becoming more sophisticated in providing services including input supply, marketing, and financial services. Collective bargaining power is improving farmer access to better prices and market opportunities.
Processing Expansion: Increasing investment in agro-processing facilities to add value to raw agricultural products. Small-scale processing enterprises are emerging at community levels, creating employment and reducing post-harvest losses.
Infrastructure Investments: Major road construction and rehabilitation projects are improving rural connectivity and market access. Irrigation infrastructure development is expanding in northern regions to support year-round production and reduce climate dependency.
Technology Initiatives: Introduction of improved seed varieties and modern farming techniques through research institutions and extension programs. Mechanization programs are providing farmers with access to tractors and other agricultural equipment through rental and cooperative arrangements.
Market Development Projects: Construction of modern markets and storage facilities in key agricultural areas to reduce post-harvest losses and improve market efficiency. Cold storage facilities are being established to extend shelf life of perishable products.
Financial Services Expansion: Microfinance institutions and mobile banking services are expanding to rural areas, improving farmer access to credit and financial services. Agricultural insurance products are being developed to protect farmers against production risks.
Quality Certification Programs: Implementation of quality standards and certification systems to meet international market requirements. Traceability systems are being established for export crops to ensure product quality and safety.
Research and Development: Strengthening of agricultural research institutions and development of climate-resilient crop varieties. Extension service modernization is improving farmer access to technical knowledge and best practices.
MarkWide Research analysis indicates that strategic focus on infrastructure development and technology adoption will be crucial for unlocking Cameroon’s agricultural potential. Investment priorities should emphasize rural road networks, storage facilities, and processing capacity to reduce post-harvest losses and improve market efficiency.
Policy recommendations include strengthening agricultural extension services, improving access to credit, and developing market information systems. Public-private partnerships should be leveraged to accelerate agricultural modernization and value chain development.
Capacity building initiatives focusing on farmer training, cooperative development, and youth engagement in agriculture will be essential for sustainable sector growth. Technology transfer programs should prioritize appropriate technologies that can be adopted by smallholder farmers.
Market development strategies should focus on quality improvement, certification programs, and export market diversification. Regional trade integration opportunities should be maximized through improved cross-border infrastructure and harmonized standards.
Sustainability considerations must be integrated into all agricultural development initiatives to ensure long-term viability and environmental protection. Climate adaptation measures should be prioritized to build resilience against climate change impacts.
Growth projections for Cameroon’s agricultural sector remain optimistic, with expected productivity improvements of 12-15% annually in key subsectors through technology adoption and infrastructure development. Export potential is expected to expand significantly as quality improvements and certification programs enhance market access.
Technological transformation will accelerate with increasing adoption of digital agriculture tools, precision farming techniques, and modern processing equipment. MWR projections indicate that mechanization levels could reach 35-40% within the next decade through targeted support programs.
Market integration will strengthen through improved infrastructure, better information systems, and enhanced value chain coordination. Regional trade is expected to grow substantially as cross-border infrastructure improves and trade barriers are reduced.
Sustainability focus will intensify with increasing adoption of climate-smart agriculture practices and environmental certification programs. Youth engagement in agriculture is projected to increase significantly through entrepreneurship programs and modern farming opportunities.
Investment flows into agricultural development are expected to increase from both public and private sources, supporting infrastructure development, technology adoption, and market expansion initiatives. Food security improvements will result from increased domestic production and reduced import dependency.
Cameroon’s agriculture market stands at a pivotal juncture with substantial opportunities for growth and transformation. The sector’s fundamental strengths including favorable natural conditions, crop diversity, and strategic location provide a solid foundation for sustainable development. Government commitment to agricultural modernization, combined with increasing private sector interest, creates favorable conditions for market expansion.
Key success factors will include continued investment in infrastructure development, technology adoption, and human capacity building. Market efficiency improvements through reduced post-harvest losses, better market information systems, and strengthened value chains will be crucial for realizing the sector’s full potential.
Strategic priorities must focus on balancing food security objectives with export market development while ensuring environmental sustainability and social inclusion. The Cameroon agriculture market has the potential to become a regional leader in agricultural production and agribusiness development through coordinated efforts among all stakeholders and sustained commitment to sector transformation.
What is Cameroon Agriculture?
Cameroon Agriculture refers to the cultivation of crops and livestock farming in Cameroon, which plays a crucial role in the country’s economy and food security. Key sectors include cocoa, coffee, and cassava production.
What are the major companies in the Cameroon Agriculture Market?
Major companies in the Cameroon Agriculture Market include SOCAPALM, which specializes in palm oil production, and Cameroon Development Corporation, known for its rubber and banana plantations, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Cameroon Agriculture Market?
The Cameroon Agriculture Market is driven by factors such as increasing domestic food demand, government support for agricultural initiatives, and the potential for export growth in cash crops like cocoa and coffee.
What challenges does the Cameroon Agriculture Market face?
Challenges in the Cameroon Agriculture Market include inadequate infrastructure, climate change impacts, and limited access to modern farming technologies, which hinder productivity and sustainability.
What opportunities exist in the Cameroon Agriculture Market?
Opportunities in the Cameroon Agriculture Market include the expansion of organic farming, investment in agro-processing industries, and the development of export markets for high-value crops.
What trends are shaping the Cameroon Agriculture Market?
Trends in the Cameroon Agriculture Market include the adoption of sustainable farming practices, increased use of digital technologies for farming management, and a growing focus on food security and nutrition.
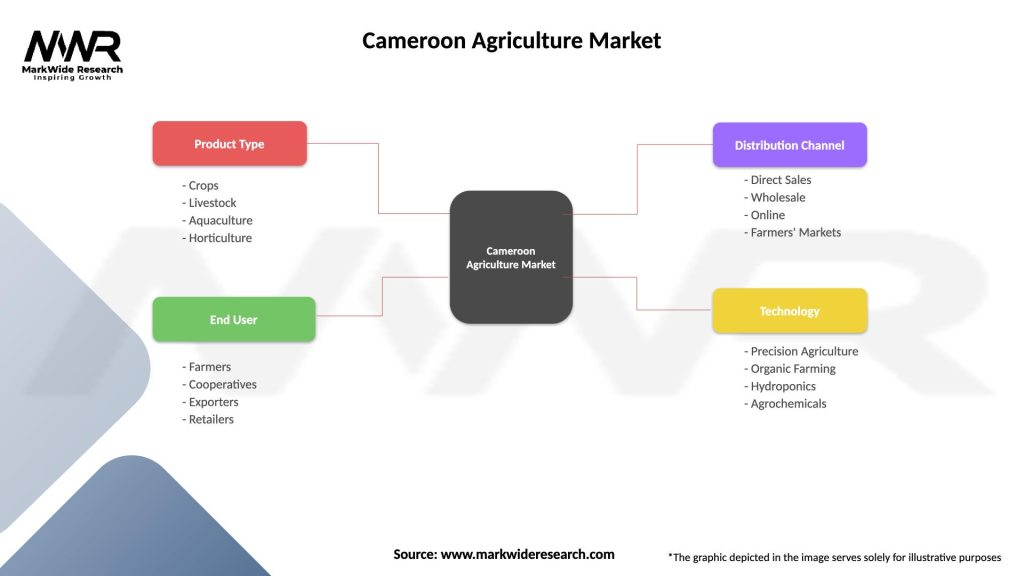
Cameroon Agriculture Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Crops, Livestock, Aquaculture, Horticulture |
| End User | Farmers, Cooperatives, Exporters, Retailers |
| Distribution Channel | Direct Sales, Wholesale, Online, Farmers’ Markets |
| Technology | Precision Agriculture, Organic Farming, Hydroponics, Agrochemicals |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Cameroon Agriculture Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at