444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
Market Overview
The post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) treatment market in Brazil is experiencing robust growth, fueled by heightened awareness of mental health issues, expanding treatment options, and government initiatives to improve mental health services. PTSD, a debilitating condition triggered by traumatic experiences, requires specialized interventions to alleviate symptoms and promote recovery.
Meaning
PTSD treatment encompasses a range of therapeutic modalities aimed at addressing the psychological and emotional ramifications of trauma. Evidence-based interventions, including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), pharmacotherapy, and psychosocial support, play a crucial role in managing PTSD symptoms and enhancing patients’ well-being.
Executive Summary
The PTSD treatment market in Brazil presents significant opportunities for growth and innovation, driven by increasing demand for mental health services, advancements in treatment modalities, and a supportive policy environment. While challenges such as stigma, treatment disparities, and workforce shortages persist, collaborative efforts from stakeholders across the healthcare continuum can address these barriers and improve access to quality PTSD care.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The PTSD treatment market in Brazil operates within a dynamic landscape shaped by various factors, including demographic trends, cultural norms, socioeconomic disparities, and policy interventions. Navigating these dynamics requires a nuanced understanding of local contexts and a tailored approach to treatment delivery.
Regional Analysis
Regional variations in mental health infrastructure, socioeconomic indicators, and cultural attitudes towards mental illness influence the distribution and accessibility of PTSD treatment services across Brazil. Urban centers typically offer greater access to specialized mental health care, while rural and remote regions may face significant barriers to treatment access.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in Brazil Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Treatment Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
The PTSD treatment market in Brazil can be segmented based on various factors, including treatment modalities, patient demographics, geographic regions, and healthcare settings. Segmenting the market enables a targeted approach to treatment delivery and resource allocation, ensuring that interventions are tailored to meet the unique needs of different patient populations.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic exacerbates mental health challenges, including PTSD, in Brazil, underscoring the need for expanded access to evidence-based treatment and support services. The pandemic’s psychological toll, coupled with disruptions to mental health service delivery, highlights the importance of innovative approaches to PTSD treatment, including telepsychiatry and digital therapeutics.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future of the PTSD treatment market in Brazil is promising, with continued expansion of treatment options, increased access to care, and greater awareness of mental health issues. However, addressing existing challenges, including stigma, treatment disparities, and workforce shortages, remains imperative for realizing the full potential of PTSD treatment interventions in Brazil.
Conclusion
The PTSD treatment market in Brazil is witnessing significant growth and evolution, driven by increasing recognition of mental health issues, expanding treatment options, and technological innovations in care delivery. While challenges such as stigma, treatment disparities, and workforce shortages persist, concerted efforts from stakeholders across the healthcare ecosystem can overcome these barriers and ensure equitable access to evidence-based PTSD treatment for all individuals in need.
What is Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Treatment?
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Treatment refers to the various therapeutic approaches and interventions designed to help individuals suffering from PTSD manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. This can include psychotherapy, medication, and support groups.
What are the key players in the Brazil Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Treatment Market?
Key players in the Brazil Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Treatment Market include companies such as Dasa, Apsen Farmacêutica, and Eurofarma, which provide a range of treatment options and support services for PTSD patients, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Brazil Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Treatment Market?
The Brazil Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Treatment Market is driven by increasing awareness of mental health issues, a rise in traumatic events leading to PTSD, and the growing availability of effective treatment options. Additionally, government initiatives to promote mental health care contribute to market growth.
What challenges does the Brazil Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Treatment Market face?
Challenges in the Brazil Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Treatment Market include stigma surrounding mental health, limited access to specialized care in rural areas, and a shortage of trained mental health professionals. These factors can hinder effective treatment and support for those affected by PTSD.
What opportunities exist in the Brazil Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Treatment Market?
Opportunities in the Brazil Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Treatment Market include the development of innovative therapies, increased investment in mental health services, and the potential for telehealth solutions to reach underserved populations. These advancements can enhance treatment accessibility and effectiveness.
What trends are shaping the Brazil Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Treatment Market?
Trends in the Brazil Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Treatment Market include a growing emphasis on personalized treatment plans, the integration of technology in therapy, and a focus on holistic approaches that address both psychological and physical health. These trends aim to improve patient outcomes and satisfaction.
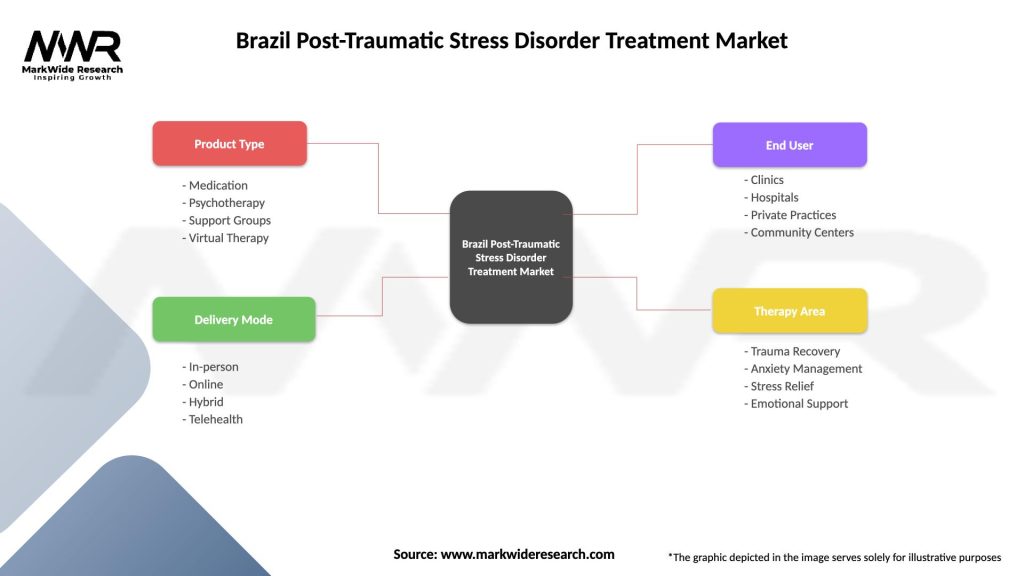
Brazil Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Treatment Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Medication, Psychotherapy, Support Groups, Virtual Therapy |
| Delivery Mode | In-person, Online, Hybrid, Telehealth |
| End User | Clinics, Hospitals, Private Practices, Community Centers |
| Therapy Area | Trauma Recovery, Anxiety Management, Stress Relief, Emotional Support |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in Brazil Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Treatment Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at