444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The blood and organ bank market plays a crucial role in healthcare by providing life-saving resources to individuals in need. Blood and organ banks serve as repositories for donated blood, tissues, organs, and other biological materials. These facilities ensure the safe collection, storage, testing, and distribution of these vital resources, which are essential for various medical procedures, including transfusions, transplants, and research purposes.
Meaning
Blood and organ banks are specialized establishments that facilitate the collection, processing, and distribution of blood, organs, tissues, and other biological materials. These banks adhere to strict quality standards and regulations to ensure the safety and efficacy of the collected resources. By providing a centralized system for acquiring and distributing these materials, blood and organ banks help save lives, improve patient outcomes, and contribute to advancements in medical research.
Executive Summary
The blood and organ bank market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by factors such as increasing awareness about organ donation, advancements in transplant technologies, rising prevalence of chronic diseases, and growing demand for blood transfusions. This market encompasses both public and private entities that operate blood banks, organ procurement organizations (OPOs), and tissue banks. The key focus areas of these establishments include efficient collection processes, robust testing and screening procedures, safe storage practices, and prompt distribution of blood and organs to meet the needs of patients and healthcare providers.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The blood and organ bank market is dynamic and influenced by various factors such as advancements in medical technology, changes in government regulations, demographic trends, and public awareness campaigns. Collaboration between stakeholders, ongoing research and development activities, and strategic investments play key roles in shaping the market landscape. The market is also impacted by geopolitical factors, socioeconomic disparities, and cultural attitudes towards organ donation and transplantation.
Regional Analysis
The blood and organ bank market exhibits regional variations based on factors such as healthcare infrastructure, regulatory frameworks, cultural norms, and socioeconomic conditions. Developed regions with well-established healthcare systems often have sophisticated blood and organ banking facilities. In contrast, developing regions may face challenges related to infrastructure, resource availability, and regulatory compliance.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Blood and Organ Bank Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
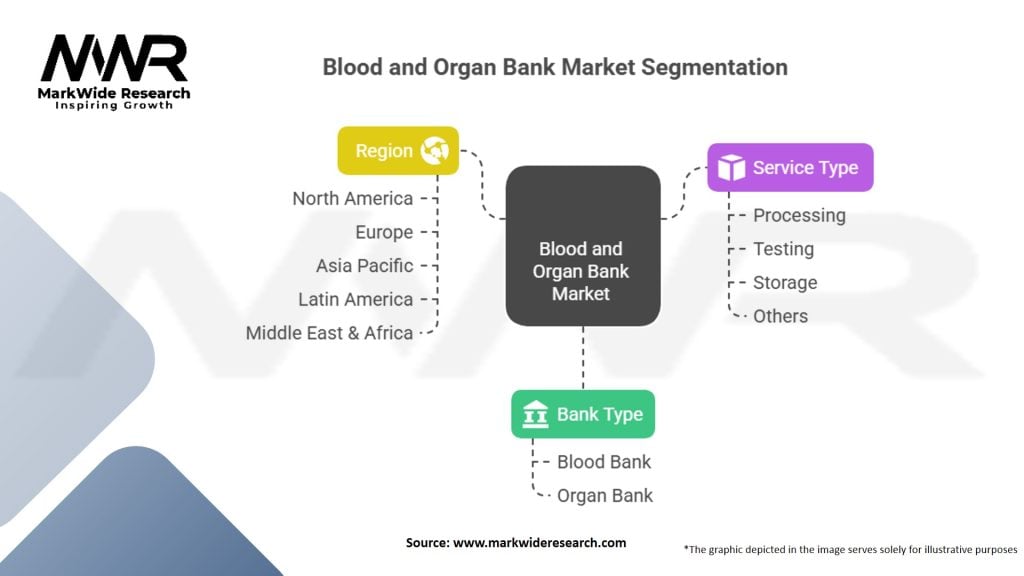
Segmentation
The blood and organ bank market can be segmented based on the type of services offered, including blood banking, organ procurement, tissue banking, and cell banking. Additionally, segmentation based on the end-users such as hospitals, transplant centers, research institutions, and biotechnology companies provides insights into the specific needs and requirements of different customer groups.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic had a significant impact on the blood and organ bank market. The pandemic disrupted the availability of donated blood, organs, and tissues due to restrictions on social gatherings, reduced mobility, and fear of infection. Blood banks faced challenges in maintaining an adequate supply, leading to shortages in certain regions. Organ transplantation procedures were also affected, with a decrease in transplant surgeries due to resource reallocation and prioritization of critical care.
However, the pandemic also highlighted the importance of preparedness and resilience in the blood and organ banking sector. Enhanced safety protocols, rigorous testing measures, and the development of strategies to manage potential outbreaks ensured the continued provision of safe blood and organs. The crisis prompted innovative approaches, such as the use of virtual platforms for donor registrations and telemedicine consultations for pre-transplant evaluations.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The blood and organ bank market is expected to witness sustained growth in the coming years. Advancements in medical technology, increasing public awareness about organ donation, and collaborative efforts among stakeholders are likely to drive the market. However, challenges such as organ shortage, ethical considerations, and regulatory complexities will require ongoing attention and innovative solutions. The continued focus on patient safety, technological advancements, and global collaboration can pave the way for a more efficient and sustainable blood and organ banking ecosystem.
Conclusion
The blood and organ bank market plays a critical role in healthcare by ensuring the availability of life-saving resources for patients in need. It encompasses blood banks, organ procurement organizations, tissue banks, and cell banks. Factors such as increasing awareness about organ donation, technological advancements, and the rising prevalence of chronic diseases drive the market. While challenges related to organ shortage, ethical considerations, and infrastructure constraints exist, opportunities lie in advances in stem cell research, collaborations, and technology adoption. The market is dynamic, influenced by regional variations, and requires continuous efforts to optimize operations, enhance safety, and address societal and healthcare needs.
What is Blood and Organ Bank?
Blood and Organ Bank refers to facilities that collect, store, and distribute blood and organ donations for medical use. These banks play a crucial role in healthcare by ensuring the availability of vital resources for transfusions and transplants.
What are the key players in the Blood and Organ Bank Market?
Key players in the Blood and Organ Bank Market include organizations such as the American Red Cross, NHS Blood and Transplant, and Vitalant, among others. These companies are involved in the collection, testing, and distribution of blood and organ products.
What are the growth factors driving the Blood and Organ Bank Market?
The Blood and Organ Bank Market is driven by factors such as the increasing demand for blood transfusions, advancements in medical technology, and a growing awareness of the importance of organ donation. Additionally, rising incidences of chronic diseases contribute to the need for these services.
What challenges does the Blood and Organ Bank Market face?
The Blood and Organ Bank Market faces challenges such as regulatory compliance issues, the risk of contamination, and a shortage of donors. These factors can hinder the efficiency and effectiveness of blood and organ collection and distribution.
What opportunities exist in the Blood and Organ Bank Market?
Opportunities in the Blood and Organ Bank Market include the potential for technological innovations in storage and transportation, increased public awareness campaigns, and partnerships with healthcare providers to enhance donation rates. These factors can help improve service delivery and expand access.
What trends are shaping the Blood and Organ Bank Market?
Trends in the Blood and Organ Bank Market include the integration of digital technologies for donor management, the use of artificial intelligence for matching donors with recipients, and a focus on personalized medicine. These innovations aim to improve operational efficiency and patient outcomes.
Blood and Organ Bank Market
| Segmentation Details | Details |
|---|---|
| Bank Type | Blood Bank, Organ Bank |
| Service Type | Processing, Testing, Storage, Others |
| Region | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Blood and Organ Bank Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at