444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
Blockchain technology has emerged as a revolutionary force across various industries, including agriculture. The application of blockchain in the agricultural sector has gained significant attention due to its potential to address numerous challenges faced by the industry. With its decentralized and transparent nature, blockchain has the power to transform the way agricultural processes are conducted, from farm to fork.
Meaning
Blockchain, in its essence, is a distributed ledger technology that enables secure and transparent transactions between multiple parties without the need for intermediaries. It operates through a network of computers, known as nodes, which collectively validate and record transactions in a sequential and immutable manner. Each transaction, or block, is linked to the previous one, forming a chain of blocks, hence the name blockchain.
Executive Summary
The blockchain in agriculture market is witnessing rapid growth as more and more industry participants recognize its potential to enhance efficiency, traceability, and trust within the agricultural supply chain. The technology offers numerous benefits, such as improved traceability, reduced fraud, enhanced food safety, and streamlined transactions. As a result, farmers, distributors, retailers, and consumers are increasingly adopting blockchain solutions to ensure the authenticity and quality of agricultural products.
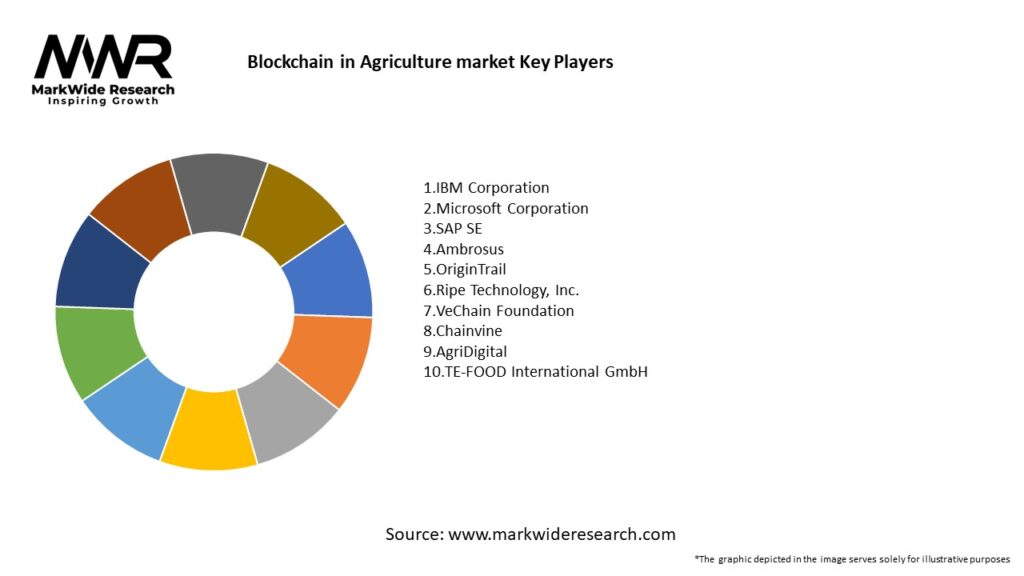
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
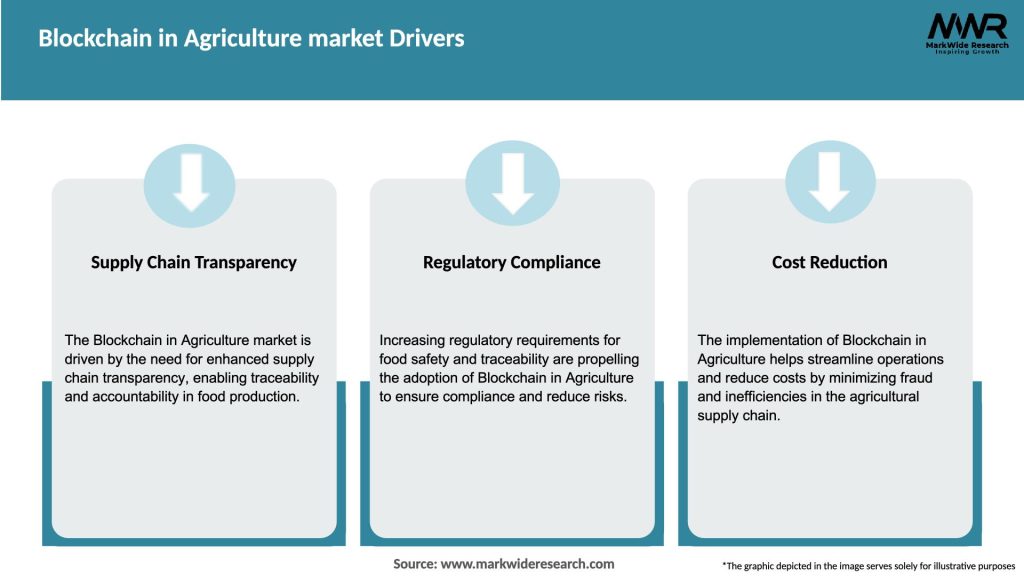
Market Drivers
Several key drivers are fueling the growth of the blockchain in agriculture market:
Market Restraints
While the blockchain in agriculture market holds immense potential, certain challenges and restraints must be addressed:
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The blockchain in agriculture market is characterized by the following dynamics:
Regional Analysis
The adoption of blockchain technology in agriculture varies across different regions. Here is a regional analysis of the blockchain in agriculture market:
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Blockchain in Agriculture Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
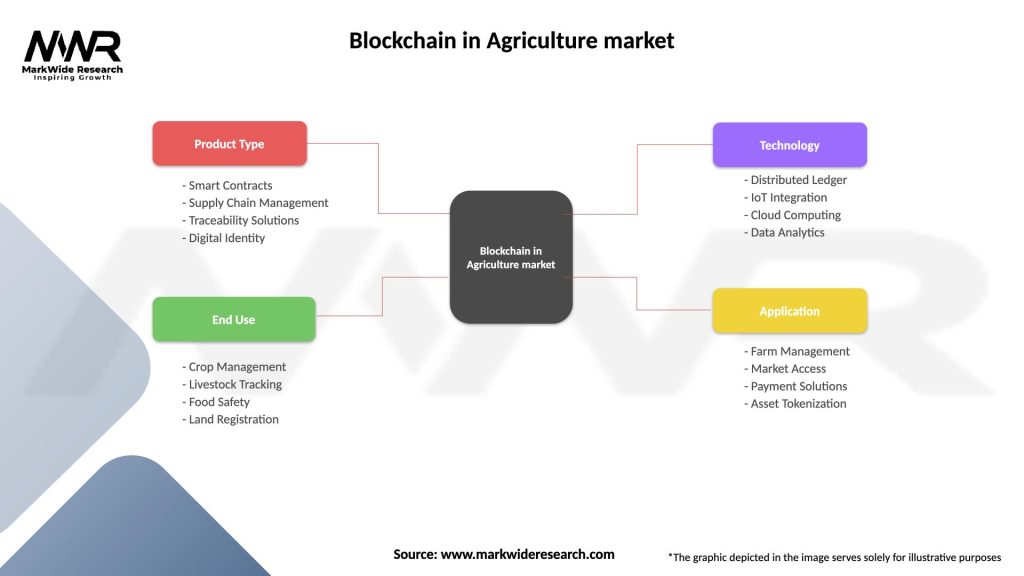
Segmentation
The blockchain in agriculture market can be segmented based on various factors:
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
The adoption of blockchain technology in agriculture offers several key benefits for industry participants and stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis of the blockchain in agriculture market provides a comprehensive understanding of its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the agriculture sector and has highlighted the importance of resilient and transparent supply chains. The adoption of blockchain technology in agriculture has been accelerated by the following factors:
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Based on market trends and developments, analysts suggest the following strategies for industry participants:
Future Outlook
The future of the blockchain in agriculture market looks promising, with significant growth potential. As awareness and understanding of blockchain technology continue to increase, more industry participants will recognize its benefits and adopt blockchain solutions. Key factors shaping the future of the market include:
Conclusion
In summary, the adoption of blockchain technology in the agriculture industry holds immense potential for improving transparency, traceability, and efficiency. With its decentralized and transparent nature, blockchain offers benefits such as enhanced supply chain management, reduced fraud, improved food safety, and increased consumer trust. Despite some challenges related to technology infrastructure, costs, and regulatory considerations, the market for blockchain in agriculture is expected to grow rapidly. The expansion of blockchain use cases, integration with emerging technologies, and government support will be key drivers of market growth.
Industry participants are advised to invest in research and development, foster collaborations, and educate their workforce to fully leverage the benefits of blockchain in agriculture. Addressing interoperability challenges and ensuring data security and privacy will be critical for successful implementation.
What is Blockchain in Agriculture?
Blockchain in Agriculture refers to the use of blockchain technology to enhance transparency, traceability, and efficiency in agricultural supply chains. It enables secure and immutable record-keeping of transactions related to farming, food production, and distribution.
What are the key players in the Blockchain in Agriculture market?
Key players in the Blockchain in Agriculture market include IBM, AgriDigital, and ChainPoint, which are known for their innovative solutions in supply chain management and traceability, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Blockchain in Agriculture market?
The main drivers of growth in the Blockchain in Agriculture market include the increasing demand for food safety, the need for supply chain transparency, and the rising adoption of digital technologies in farming practices.
What challenges does the Blockchain in Agriculture market face?
Challenges in the Blockchain in Agriculture market include the high initial implementation costs, the need for industry-wide standards, and resistance to change from traditional farming practices.
What opportunities exist in the Blockchain in Agriculture market?
Opportunities in the Blockchain in Agriculture market include the potential for improved traceability of organic products, enhanced efficiency in logistics, and the ability to create smart contracts for transactions between farmers and buyers.
What trends are shaping the Blockchain in Agriculture market?
Trends shaping the Blockchain in Agriculture market include the integration of IoT devices for real-time data collection, the rise of decentralized finance (DeFi) applications in agriculture, and increasing collaboration between tech companies and agricultural stakeholders.
Blockchain in Agriculture market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Smart Contracts, Supply Chain Management, Traceability Solutions, Digital Identity |
| End Use | Crop Management, Livestock Tracking, Food Safety, Land Registration |
| Technology | Distributed Ledger, IoT Integration, Cloud Computing, Data Analytics |
| Application | Farm Management, Market Access, Payment Solutions, Asset Tokenization |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Blockchain in Agriculture Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at