444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
Blockchain technology has revolutionized various industries, including agriculture and the food supply chain. With its decentralized and transparent nature, blockchain provides a secure and efficient platform for recording, verifying, and tracking transactions, ensuring traceability, authenticity, and accountability throughout the agricultural and food supply chain. This technology has gained significant attention and adoption due to its potential to address key challenges such as food fraud, supply chain inefficiencies, and lack of trust among stakeholders.
Meaning
Blockchain, in the context of agriculture and the food supply chain, refers to a distributed ledger technology that enables the recording and tracking of transactions, contracts, and assets across multiple parties without the need for intermediaries. It provides a decentralized and transparent platform that ensures the integrity, security, and immutability of data, allowing participants to verify and trust the information exchanged within the ecosystem.
Executive Summary
The blockchain in agriculture and food supply chain market has witnessed substantial growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for transparency, traceability, and food safety. Blockchain technology offers several advantages, including improved supply chain efficiency, reduced costs, enhanced consumer trust, and the ability to mitigate fraud and counterfeit products. This report aims to provide key insights into the market, including drivers, restraints, opportunities, regional analysis, competitive landscape, segmentation, and future outlook.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
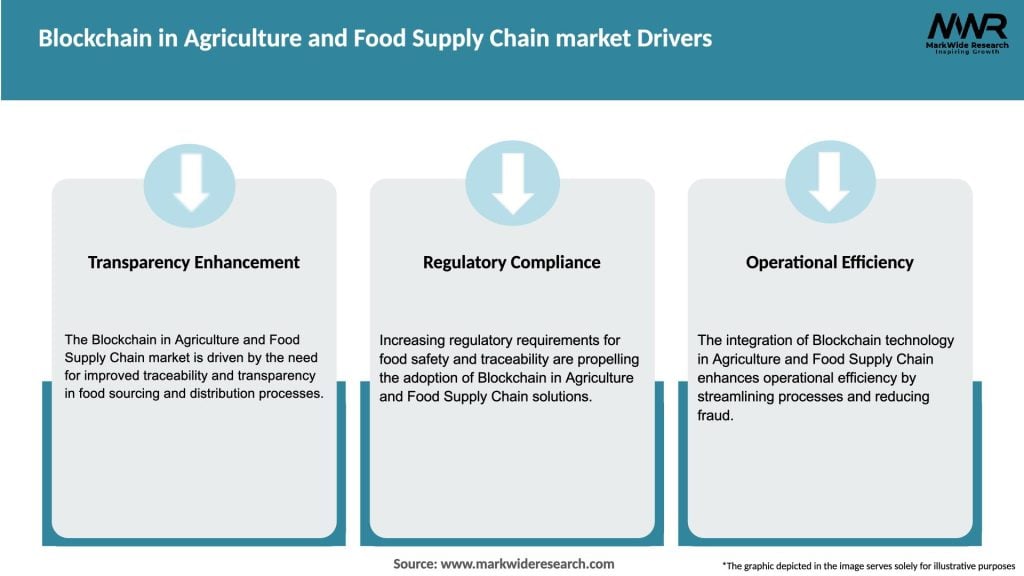
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities

Market Dynamics
The blockchain in agriculture and food supply chain market is driven by a combination of technological advancements, industry trends, regulatory changes, and consumer demands. The market dynamics include:
Regional Analysis
The adoption of blockchain technology in the agriculture and food supply chain varies across different regions. The key factors influencing regional dynamics include technological infrastructure, regulatory environment, industry maturity, and the level of awareness and acceptance among stakeholders.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Blockchain in Agriculture and Food Supply Chain Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
The blockchain in agriculture and food supply chain market can be segmented based on various factors, including:
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the agriculture and food supply chain, highlighting the need for resilient and transparent systems. The disruptions caused by the pandemic, such as supply chain disruptions, panic buying, and increased demand for e-commerce, have accelerated the adoption of blockchain technology. Blockchain’s ability to provide real-time visibility, track product provenance, and enable secure transactions has been instrumental in mitigating the challenges faced during the pandemic.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future of blockchain in the agriculture and food supply chain market looks promising. The increasing demand for transparency, traceability, and sustainability, coupled with advancements in blockchain technology, will drive further adoption. The integration of blockchain with emerging technologies, the expansion of blockchain applications beyond traceability, and the establishment of collaborative ecosystems will shape the future of the industry.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is transforming the agriculture and food supply chain industry by providing transparency, traceability, and enhanced efficiency. It addresses key challenges such as food fraud, supply chain inefficiencies, and lack of trust among stakeholders. The market is driven by the growing need for transparency and traceability, rising instances of foodborne illnesses, increasing consumer awareness and demand, and cost and efficiency benefits.
However, implementation challenges, scalability concerns, and lack of interoperability pose obstacles to widespread adoption. The market presents opportunities for integration with emerging technologies, adoption of smart contracts, and expansion of blockchain applications. Regional analysis reveals varying levels of adoption and regulatory support across different regions.
In conclusion, blockchain technology holds immense potential to revolutionize the agriculture and food supply chain market by providing transparency, traceability, and operational efficiencies. Its adoption is set to grow as industry stakeholders recognize the value it brings in addressing key challenges and meeting consumer demands for transparency and sustainability. By leveraging blockchain, the agriculture and food supply chain can ensure a safer, more reliable, and trustworthy ecosystem for all participants.
What is Blockchain in Agriculture and Food Supply Chain?
Blockchain in Agriculture and Food Supply Chain refers to the use of blockchain technology to enhance transparency, traceability, and efficiency in agricultural practices and food distribution. It enables secure and immutable record-keeping of transactions, which can improve food safety and reduce fraud.
What are the key companies in the Blockchain in Agriculture and Food Supply Chain market?
Key companies in the Blockchain in Agriculture and Food Supply Chain market include IBM, AgriDigital, VeChain, and Ripe.io, among others.
What are the drivers of growth in the Blockchain in Agriculture and Food Supply Chain market?
Drivers of growth in the Blockchain in Agriculture and Food Supply Chain market include the increasing demand for food safety, the need for supply chain transparency, and the rising adoption of digital technologies in agriculture. These factors are pushing stakeholders to seek innovative solutions to enhance operational efficiency.
What challenges does the Blockchain in Agriculture and Food Supply Chain market face?
Challenges in the Blockchain in Agriculture and Food Supply Chain market include the high initial implementation costs, the need for industry-wide standards, and resistance to change among traditional agricultural practices. These barriers can slow down the adoption of blockchain solutions.
What opportunities exist in the Blockchain in Agriculture and Food Supply Chain market?
Opportunities in the Blockchain in Agriculture and Food Supply Chain market include the potential for improved traceability of organic products, enhanced consumer trust through transparent sourcing, and the ability to streamline logistics and reduce waste. These factors can lead to more sustainable practices in agriculture.
What trends are shaping the Blockchain in Agriculture and Food Supply Chain market?
Trends shaping the Blockchain in Agriculture and Food Supply Chain market include the integration of IoT devices for real-time data collection, the rise of smart contracts for automating transactions, and increasing collaboration among stakeholders to create shared platforms. These innovations are driving the evolution of the sector.
Blockchain in Agriculture and Food Supply Chain market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Smart Contracts, Traceability Solutions, Supply Chain Management, Digital Ledger Technology |
| End User | Agricultural Producers, Food Processors, Retailers, Distributors |
| Technology | Distributed Ledger, IoT Integration, Cloud Computing, Data Analytics |
| Application | Food Safety, Inventory Management, Quality Assurance, Payment Processing |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Blockchain in Agriculture and Food Supply Chain Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at