444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
Asset management refers to the professional management of various types of assets, including financial assets, physical assets, and intellectual property, with the aim of maximizing their value over time. In today’s complex business environment, effective asset management has become crucial for organizations to optimize their resources, improve operational efficiency, and achieve sustainable growth.
Meaning
Asset management involves the systematic process of acquiring, operating, maintaining, upgrading, and disposing of assets in order to achieve the organization’s strategic objectives. It encompasses a wide range of assets, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, infrastructure, equipment, software, patents, and trademarks. The goal is to align the management of these assets with the organization’s overall business strategy, risk tolerance, and performance targets.
Executive Summary
The asset management market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing complexity of financial markets, the need for effective risk management, and the growing demand for investment products. With the rise of digital technologies, asset management firms have also embraced advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning to enhance their decision-making processes and improve investment performance.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The asset management market is characterized by intense competition, evolving investor preferences, changing regulatory landscape, and technological advancements. Asset managers need to adapt to these dynamics by continuously innovating, improving operational efficiency, and delivering superior investment performance.
Regional Analysis
The asset management market is geographically diverse, with major regions including North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and the rest of the world. North America is the largest market, driven by the presence of global financial hubs and a well-established asset management industry. Asia Pacific is experiencing significant growth, fueled by the rising middle class, economic development, and increasing institutional investments.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Asset Management Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
The asset management market can be segmented based on asset class, client type, and investment strategy. Asset classes include equities, fixed income, real estate, commodities, and alternative investments. Client types can range from individual investors to institutional investors, including pension funds, insurance companies, and sovereign wealth funds. Investment strategies can be categorized as active management, passive management, or a combination of both.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic had a significant impact on the asset management market. The initial market downturn and economic uncertainty led to heightened volatility and investor apprehension. However, asset managers demonstrated resilience by implementing risk mitigation measures, adapting investment strategies, and providing timely guidance to investors. The pandemic also accelerated the adoption of digital technologies, as remote work and virtual client interactions became the norm.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The asset management market is expected to continue growing in the coming years, driven by factors such as increasing wealth accumulation, retirement savings, and the adoption of advanced technologies. Asset managers that embrace digital transformation, sustainable investing, and client-centric strategies will be well-positioned to capture opportunities and deliver value to their clients.
Conclusion
The asset management market plays a vital role in optimizing the value of various types of assets, ranging from financial assets to physical assets and intellectual property. The industry is experiencing significant changes, driven by technological advancements, regulatory reforms, and evolving investor preferences. Asset managers need to adapt to these dynamics by leveraging technology, focusing on sustainable investing, and delivering personalized solutions. Despite challenges, the future outlook for the asset management market remains positive, with ample opportunities for growth and innovation.
What is asset management?
Asset management refers to the systematic process of developing, operating, maintaining, and selling assets in a cost-effective manner. It encompasses various financial services aimed at managing investments on behalf of clients, including individuals and institutions.
Who are the key players in the asset management market?
Key players in the asset management market include firms such as BlackRock, Vanguard, and Fidelity Investments, which provide a range of investment products and services. These companies manage large portfolios across various asset classes, including equities, fixed income, and alternative investments, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the asset management market?
The main drivers of growth in the asset management market include increasing global wealth, rising demand for retirement planning, and the growing popularity of passive investment strategies. Additionally, advancements in technology and data analytics are enhancing investment decision-making processes.
What challenges does the asset management market face?
The asset management market faces several challenges, including regulatory pressures, market volatility, and competition from low-cost investment options. These factors can impact profitability and require firms to adapt their strategies to maintain market share.
What opportunities exist in the asset management market?
Opportunities in the asset management market include the expansion of sustainable investing, the rise of fintech solutions, and the increasing demand for personalized investment strategies. Firms that leverage technology to enhance client engagement and offer innovative products may gain a competitive edge.
What trends are shaping the asset management market?
Trends shaping the asset management market include the shift towards environmental, social, and governance (ESG) investing, the integration of artificial intelligence in portfolio management, and the growth of digital platforms for investment access. These trends are influencing how firms operate and engage with clients.
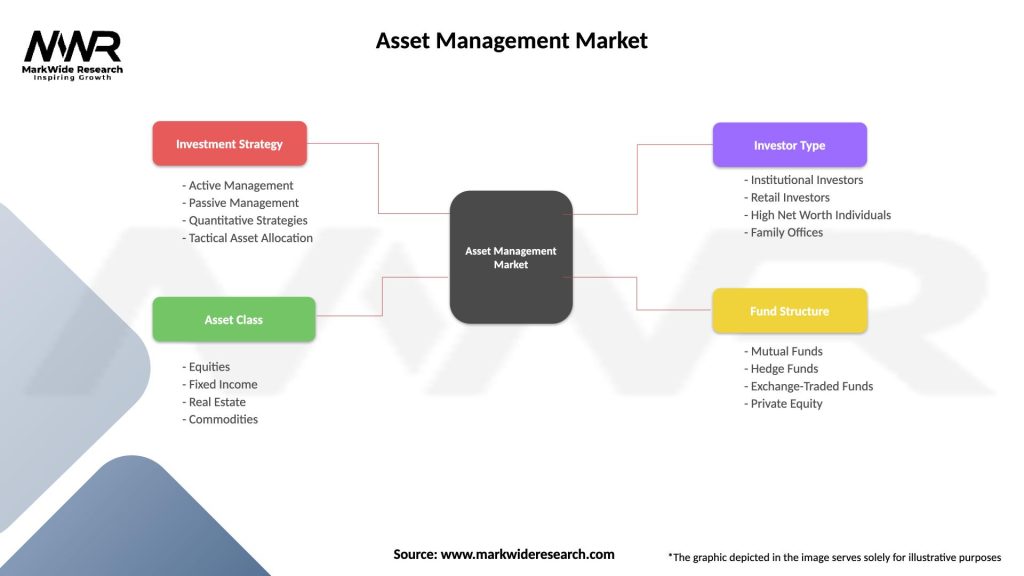
Asset Management Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Investment Strategy | Active Management, Passive Management, Quantitative Strategies, Tactical Asset Allocation |
| Asset Class | Equities, Fixed Income, Real Estate, Commodities |
| Investor Type | Institutional Investors, Retail Investors, High Net Worth Individuals, Family Offices |
| Fund Structure | Mutual Funds, Hedge Funds, Exchange-Traded Funds, Private Equity |
Leading Companies in the Asset Management Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at