444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2750
Market Overview
The Asia-Pacific Small Hydropower Market is a thriving sector that focuses on harnessing the potential of small-scale hydropower projects in the region. Small hydropower refers to the generation of electricity using hydropower technologies with a capacity of up to 10 MW. It offers a sustainable and renewable source of energy that can be harnessed from rivers, streams, and other water bodies.
Meaning
Small hydropower plants are designed to produce electricity by utilizing the energy from flowing or falling water. These plants typically consist of a dam or diversion structure, a water intake, a penstock, a turbine, and a generator. The water flow is used to rotate the turbine, which then drives the generator to produce electricity. The generated power can be used for various applications, including residential, commercial, and industrial purposes.
Executive Summary
The Asia-Pacific Small Hydropower Market is experiencing significant growth due to several factors, including increasing energy demand, favorable government regulations, and the need for sustainable and clean energy sources. The market has witnessed substantial investments in recent years, with many countries in the region focusing on expanding their small hydropower capacity.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The Asia-Pacific Small Hydropower Market is characterized by intense competition among key players, technological advancements, and a focus on sustainable development. The market is witnessing collaborations and partnerships between industry players, aiming to leverage each other’s expertise and resources for mutual growth.
Regional Analysis
The Asia-Pacific Small Hydropower Market can be segmented into various sub-regions, including East Asia, South Asia, Southeast Asia, and the Pacific. Each region has its unique characteristics, such as varying energy demand, government policies, and resource availability, influencing the growth of the small hydropower sector.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Asia-Pacific Small Hydropower Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
By Capacity:
By End-Use:
By Region:
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the Asia-Pacific Small Hydropower Market. While the initial phase of the pandemic led totemporary disruptions in project development and construction activities, the sector quickly recovered due to its essential nature as a source of reliable and clean energy. Governments in the region recognized the importance of maintaining energy security during the crisis, leading to continued support for small hydropower projects. The pandemic also highlighted the need for resilient and decentralized energy systems, further driving the demand for small hydropower as a reliable and locally available energy source.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the Asia-Pacific Small Hydropower Market is promising. The increasing energy demand, renewable energy targets, and favorable government policies are expected to drive continued growth in the sector. The market will witness further advancements in technology, project diversification, and collaborations between industry players. With the abundant water resources in the region, small hydropower will continue to play a significant role in the transition to a sustainable and low-carbon energy system.
Conclusion
The Asia-Pacific Small Hydropower Market presents lucrative opportunities for industry participants and stakeholders. With its sustainable and renewable nature, small hydropower offers a reliable and clean energy solution for the region. The market is driven by factors such as increasing energy demand, government support, and environmental benefits. Although there are challenges and environmental concerns associated with small hydropower, they can be mitigated through proper planning, technological advancements, and stakeholder collaboration. The market’s future outlook is positive, with a focus on technological innovations, project diversification, and partnerships to ensure a sustainable and resilient energy future for the Asia-Pacific region.
What is Small Hydropower?
Small hydropower refers to the generation of electricity using water flow in small-scale hydroelectric plants, typically with a capacity of up to ten megawatts. This renewable energy source is often utilized in rural areas for local power supply and can contribute to sustainable energy goals.
What are the key players in the Asia-Pacific Small Hydropower Market?
Key players in the Asia-Pacific Small Hydropower Market include companies like Andritz Hydro, Voith Hydro, and GE Renewable Energy, which are involved in the development and implementation of small hydropower projects, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Asia-Pacific Small Hydropower Market?
The growth of the Asia-Pacific Small Hydropower Market is driven by increasing energy demand, government incentives for renewable energy, and the need for sustainable energy solutions in remote areas. Additionally, advancements in technology are making small hydropower more efficient and accessible.
What challenges does the Asia-Pacific Small Hydropower Market face?
The Asia-Pacific Small Hydropower Market faces challenges such as regulatory hurdles, environmental concerns, and competition from other renewable energy sources. Additionally, the initial capital investment required for small hydropower projects can be a barrier to entry.
What opportunities exist in the Asia-Pacific Small Hydropower Market?
Opportunities in the Asia-Pacific Small Hydropower Market include the potential for off-grid power solutions, integration with other renewable energy sources, and the development of innovative technologies to enhance efficiency. There is also a growing interest in sustainable energy practices among local communities.
What trends are shaping the Asia-Pacific Small Hydropower Market?
Trends in the Asia-Pacific Small Hydropower Market include the increasing adoption of hybrid systems that combine small hydropower with solar and wind energy, as well as a focus on community-based projects. Additionally, there is a rising emphasis on environmental sustainability and minimizing ecological impacts.
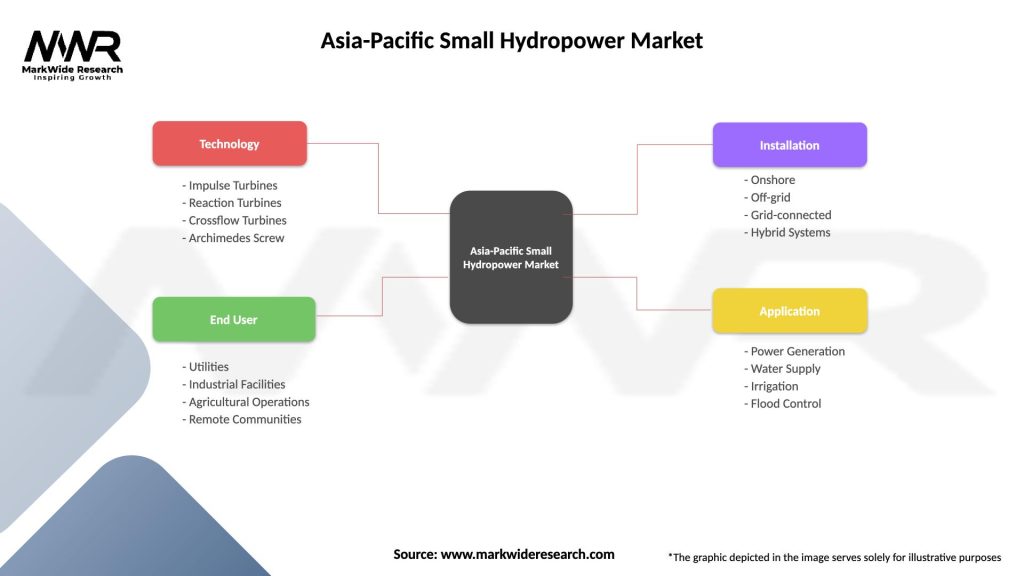
Asia-Pacific Small Hydropower Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Technology | Impulse Turbines, Reaction Turbines, Crossflow Turbines, Archimedes Screw |
| End User | Utilities, Industrial Facilities, Agricultural Operations, Remote Communities |
| Installation | Onshore, Off-grid, Grid-connected, Hybrid Systems |
| Application | Power Generation, Water Supply, Irrigation, Flood Control |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Asia-Pacific Small Hydropower Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at