444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2750
The Asia-Pacific plastic waste management market represents one of the most critical environmental and economic sectors in the global sustainability landscape. This rapidly evolving market encompasses comprehensive solutions for collecting, sorting, processing, and recycling plastic waste across diverse economies including China, India, Japan, South Korea, Australia, and Southeast Asian nations. The region faces unprecedented challenges with plastic waste generation, driving innovative approaches to waste management infrastructure and circular economy initiatives.
Market dynamics indicate robust growth potential, with the sector expanding at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% through the forecast period. This growth trajectory reflects increasing environmental awareness, stringent regulatory frameworks, and rising investments in advanced waste processing technologies. The market encompasses various segments including mechanical recycling, chemical recycling, waste-to-energy conversion, and biodegradable plastic alternatives.
Regional variations significantly influence market development patterns. Developed economies like Japan and South Korea demonstrate advanced recycling infrastructure with recycling rates exceeding 85% for certain plastic categories. Meanwhile, emerging markets including India, Vietnam, and Indonesia present substantial growth opportunities despite infrastructure challenges. The market’s complexity stems from diverse regulatory environments, varying waste generation patterns, and different technological adoption rates across countries.
Technology integration plays a pivotal role in market evolution, with artificial intelligence, IoT sensors, and blockchain technology revolutionizing waste tracking and processing efficiency. These innovations enable better sorting accuracy, supply chain transparency, and optimized collection routes, contributing to overall system effectiveness and cost reduction.
The Asia-Pacific plastic waste management market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of services, technologies, and infrastructure dedicated to handling plastic waste throughout its lifecycle in the Asia-Pacific region. This market encompasses the collection, transportation, sorting, processing, recycling, and disposal of plastic materials, along with the development of alternative materials and circular economy solutions.
Core components include municipal waste management systems, industrial recycling facilities, waste-to-energy plants, and innovative processing technologies. The market addresses both post-consumer plastic waste from households and commercial establishments, as well as post-industrial plastic waste from manufacturing processes. It integrates traditional waste management approaches with cutting-edge technologies to maximize resource recovery and minimize environmental impact.
Stakeholder involvement spans government agencies, private waste management companies, recycling facilities, technology providers, and end-users across various industries. The market operates within complex regulatory frameworks that vary significantly across different countries, creating both challenges and opportunities for standardization and best practice implementation.
Strategic positioning of the Asia-Pacific plastic waste management market reflects its critical importance in addressing one of the region’s most pressing environmental challenges. The market demonstrates strong fundamentals driven by increasing plastic consumption, growing environmental consciousness, and supportive government policies promoting circular economy principles.
Key growth drivers include rapid urbanization, expanding middle-class populations, and increasing plastic consumption across various sectors. The region generates approximately 60% of global plastic waste, creating both significant challenges and substantial market opportunities. Government initiatives, including plastic waste import bans and extended producer responsibility programs, are reshaping market dynamics and driving investment in domestic processing capabilities.
Technology advancement represents a crucial differentiator, with innovations in chemical recycling, AI-powered sorting systems, and blockchain-based tracking solutions gaining traction. These technologies address traditional recycling limitations and enable processing of previously non-recyclable plastic types, expanding market potential significantly.
Market segmentation reveals diverse opportunities across collection services, mechanical recycling, chemical recycling, waste-to-energy conversion, and alternative material development. Each segment presents unique growth trajectories and investment requirements, with chemical recycling showing particularly strong potential for handling mixed and contaminated plastic waste streams.
Market intelligence reveals several critical insights shaping the Asia-Pacific plastic waste management landscape. The following key insights provide strategic direction for industry participants:
Market maturity varies significantly across the region, with developed markets focusing on efficiency improvements and emerging markets prioritizing infrastructure development. This diversity creates opportunities for technology transfer and knowledge sharing between countries at different development stages.
Environmental regulations serve as the primary catalyst driving market growth across the Asia-Pacific region. Governments are implementing comprehensive plastic waste management policies, including single-use plastic bans, extended producer responsibility programs, and mandatory recycling targets. These regulatory frameworks create compliance requirements that drive investment in waste management infrastructure and processing capabilities.
Urbanization trends significantly impact waste generation patterns and management requirements. Rapid urban population growth, particularly in developing countries, leads to increased plastic consumption and waste generation. Cities are investing in modern waste management systems to handle growing volumes while meeting environmental standards and public health requirements.
Corporate sustainability initiatives are becoming increasingly important market drivers. Major corporations are setting ambitious sustainability goals, including zero waste to landfill targets and increased use of recycled materials. These commitments create demand for reliable waste management services and high-quality recycled plastic materials, driving market expansion and innovation.
Technology advancement enables new market opportunities and improves operational efficiency. Innovations in sorting technology, chemical recycling processes, and waste-to-energy conversion are expanding the range of treatable plastic waste types and improving economic viability. Digital technologies including IoT, AI, and blockchain are optimizing collection routes, improving tracking capabilities, and enhancing overall system efficiency.
Consumer awareness and environmental consciousness are driving demand for sustainable packaging solutions and waste reduction initiatives. Growing public concern about plastic pollution, particularly marine plastic waste, is creating pressure on businesses and governments to implement effective waste management solutions.
Infrastructure limitations represent significant challenges across many Asia-Pacific markets, particularly in developing countries. Inadequate collection systems, limited sorting facilities, and insufficient processing capacity constrain market growth and effectiveness. The high capital requirements for modern waste management infrastructure create barriers to entry and limit expansion opportunities for smaller players.
Economic viability concerns affect market development, particularly for certain plastic types and contaminated waste streams. Low oil prices can make virgin plastic production more economical than recycling, reducing demand for recycled materials. Additionally, the economics of waste management vary significantly based on local labor costs, energy prices, and transportation infrastructure.
Technical challenges limit the effectiveness of current recycling technologies for certain plastic types and contaminated waste streams. Mixed plastic waste, multi-layer packaging, and contaminated materials present ongoing processing difficulties. Quality degradation during recycling processes also limits the number of recycling cycles possible for many plastic types.
Regulatory inconsistencies across different countries create operational complexities for regional players. Varying standards, classification systems, and compliance requirements increase operational costs and limit economies of scale. Trade restrictions and import/export regulations further complicate cross-border waste management operations.
Market fragmentation and lack of standardization create inefficiencies and limit technology adoption. The presence of numerous small-scale operators, informal waste collectors, and varying quality standards make it difficult to achieve consistent service levels and material quality across the region.
Chemical recycling technologies present substantial growth opportunities for handling previously non-recyclable plastic waste streams. These advanced processes can break down mixed plastics, contaminated materials, and complex packaging into basic chemical components for reuse. The technology addresses limitations of mechanical recycling and opens new revenue streams from waste materials previously destined for landfills or incineration.
Digital transformation opportunities include implementing smart waste management systems, IoT-enabled collection optimization, and blockchain-based tracking solutions. These technologies can significantly improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, and provide transparency throughout the waste management value chain. Data analytics and AI applications offer opportunities for predictive maintenance, route optimization, and quality control improvements.
Circular economy integration creates opportunities for developing closed-loop systems where waste materials become inputs for new product manufacturing. Partnerships between waste management companies, manufacturers, and retailers can create sustainable supply chains and new business models based on material recovery and reuse.
Regional cooperation initiatives offer opportunities for knowledge sharing, technology transfer, and coordinated policy development. Cross-border partnerships can address transboundary waste challenges and create economies of scale for technology deployment and infrastructure development.
Innovation ecosystems provide opportunities for developing breakthrough technologies, alternative materials, and novel business models. Collaboration between startups, research institutions, and established companies can accelerate innovation and create competitive advantages in emerging market segments.
Supply and demand dynamics in the Asia-Pacific plastic waste management market are influenced by multiple interconnected factors. The supply side is driven by increasing plastic waste generation from growing populations, urbanization, and economic development. Demand for waste management services is influenced by regulatory requirements, corporate sustainability commitments, and environmental awareness.
Competitive dynamics vary significantly across different market segments and geographic regions. Large international waste management companies compete with local players and government-operated facilities. Competition is intensifying as new technologies and business models emerge, creating opportunities for differentiation and market share gains.
Value chain dynamics encompass complex relationships between waste generators, collectors, processors, and end-users of recycled materials. Integration along the value chain is increasing as companies seek to control quality, reduce costs, and ensure reliable supply chains. Vertical integration and strategic partnerships are becoming more common as market participants seek competitive advantages.
Technology dynamics are rapidly evolving, with new innovations continuously emerging to address market challenges and opportunities. The adoption rate of new technologies varies across different markets, with developed countries typically leading in implementation while developing markets focus on proven, cost-effective solutions.
Policy dynamics significantly influence market development through regulatory changes, incentive programs, and international agreements. Government policies can rapidly reshape market conditions, creating new opportunities while potentially disrupting existing business models and competitive positions.
Comprehensive market analysis employs multiple research methodologies to ensure accuracy and reliability of findings. Primary research includes extensive interviews with industry executives, government officials, technology providers, and end-users across major Asia-Pacific markets. This approach provides insights into market trends, challenges, opportunities, and competitive dynamics from key stakeholders’ perspectives.
Secondary research encompasses analysis of government publications, industry reports, academic studies, and company financial statements. This research provides quantitative data on market size, growth rates, regulatory developments, and technology trends. Cross-referencing multiple sources ensures data accuracy and identifies potential discrepancies or biases.
Market modeling utilizes statistical analysis and forecasting techniques to project future market trends and growth patterns. Models incorporate various factors including economic indicators, demographic trends, regulatory changes, and technology adoption rates. Scenario analysis examines potential market developments under different assumptions and conditions.
Expert validation involves reviewing findings with industry experts, academic researchers, and policy makers to ensure accuracy and relevance. This process helps identify potential gaps in analysis and provides additional insights into market dynamics and future developments.
Data triangulation combines multiple research approaches and sources to validate findings and ensure comprehensive market coverage. This methodology helps identify consistent trends while highlighting areas of uncertainty or conflicting information that require additional investigation.
China dominates the regional market with the largest waste generation volumes and most extensive processing infrastructure. The country has implemented comprehensive plastic waste policies and invested heavily in recycling technology development. China’s market represents approximately 45% of regional processing capacity, though recent import restrictions have shifted focus toward domestic waste management capabilities.
Japan demonstrates advanced waste management practices with sophisticated sorting systems and high recycling rates. The country’s market is characterized by technological innovation, strict quality standards, and strong government support for circular economy initiatives. Japan serves as a technology leader and knowledge hub for the broader region.
India presents substantial growth opportunities driven by rapid economic development and increasing environmental awareness. The market faces infrastructure challenges but benefits from government initiatives promoting waste management and recycling. India’s large informal waste sector is gradually being integrated into formal waste management systems.
Southeast Asian markets including Indonesia, Thailand, Vietnam, and the Philippines show strong growth potential despite infrastructure limitations. These markets benefit from increasing foreign investment, technology transfer, and regional cooperation initiatives. Government policies are becoming more supportive of waste management development.
South Korea maintains advanced waste management infrastructure with high recycling rates and strong government support. The market focuses on technology innovation and efficiency improvements, serving as a model for other developing markets in the region.
Australia and New Zealand represent mature markets with well-established waste management systems and strong environmental regulations. These markets focus on technology advancement and circular economy implementation while addressing specific challenges related to remote populations and export dependencies.
Market leadership is distributed among various types of organizations including multinational waste management companies, regional specialists, government-operated facilities, and technology providers. The competitive landscape varies significantly across different countries and market segments.
Major international players include established waste management companies that have expanded into the Asia-Pacific region through acquisitions, partnerships, and greenfield investments. These companies bring advanced technologies, operational expertise, and financial resources to develop market opportunities.
Regional specialists play important roles in local markets, offering specialized services and local market knowledge. These companies often partner with international players or serve specific market niches where local expertise provides competitive advantages.
Technology providers are becoming increasingly important competitive players, offering innovative solutions for sorting, processing, and tracking plastic waste. These companies often work with waste management operators to implement advanced technologies and improve operational efficiency.
By waste type, the market encompasses various plastic categories including PET bottles, HDPE containers, PP packaging, PS products, and mixed plastic waste. Each category requires different processing approaches and has varying economic viability for recycling operations.
By processing technology, market segments include:
By end-use application, recycled materials serve various industries including packaging, textiles, automotive, construction, and consumer goods. Each application has specific quality requirements and pricing dynamics that influence processing approaches and market opportunities.
By service type, the market includes collection services, sorting and processing, transportation, and consulting services. Each segment has different competitive dynamics and growth patterns based on local market conditions and regulatory requirements.
By customer segment, the market serves municipal governments, commercial enterprises, industrial manufacturers, and residential communities. Each customer segment has different service requirements, pricing sensitivities, and growth patterns.
PET bottle recycling represents the most mature and economically viable segment, with well-established collection systems and strong demand for recycled materials. This category benefits from high consumer recognition, relatively simple processing requirements, and consistent quality standards. Market growth is driven by beverage industry commitments to increase recycled content usage.
Flexible packaging waste presents significant challenges due to multi-layer construction, contamination issues, and limited recycling infrastructure. However, this category offers substantial growth opportunities as new technologies enable processing of previously non-recyclable materials. Chemical recycling technologies are particularly relevant for this segment.
Industrial plastic waste typically offers higher quality materials and more predictable supply streams compared to post-consumer waste. This category benefits from direct relationships with waste generators and often requires specialized processing capabilities. Growth is driven by corporate sustainability initiatives and regulatory requirements.
Electronic waste plastics require specialized handling due to potential contamination with hazardous materials and complex material compositions. This category is growing rapidly due to increasing electronic device consumption and stricter e-waste regulations. Specialized processing facilities and certified handling procedures are essential for this segment.
Construction and demolition plastics represent an emerging opportunity as building codes increasingly require waste diversion and material recovery. This category requires different collection and processing approaches compared to packaging waste and often involves longer-term contracts with construction companies.
Waste management companies benefit from expanding market opportunities driven by regulatory requirements and corporate sustainability commitments. The market offers diversification opportunities across different waste types, processing technologies, and geographic regions. Companies can develop competitive advantages through technology adoption, operational efficiency improvements, and strategic partnerships.
Technology providers gain access to growing demand for innovative solutions addressing traditional recycling limitations. The market offers opportunities for licensing technologies, providing equipment and services, and developing long-term partnerships with waste management operators. Innovation in areas such as AI-powered sorting and chemical recycling creates significant value creation potential.
Government agencies benefit from improved environmental outcomes, job creation, and economic development opportunities. Effective waste management systems support public health goals, environmental protection objectives, and circular economy development. International cooperation and knowledge sharing help accelerate best practice implementation.
Manufacturing companies gain access to sustainable raw materials, cost savings opportunities, and enhanced brand reputation through circular economy participation. Using recycled materials can reduce supply chain risks, meet sustainability commitments, and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
Investors find opportunities in a growing market with strong regulatory support and increasing corporate demand. The sector offers various investment approaches including infrastructure development, technology companies, and integrated waste management operators. ESG investment trends support capital allocation to sustainable waste management solutions.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Digitalization and automation are transforming waste management operations through IoT sensors, AI-powered sorting systems, and blockchain tracking solutions. These technologies improve operational efficiency, reduce labor costs, and provide transparency throughout the waste management value chain. MarkWide Research indicates that digital technology adoption is accelerating across the region, with automation improving sorting accuracy by up to 35%.
Chemical recycling expansion represents a significant trend addressing limitations of traditional mechanical recycling. These advanced processes can handle mixed plastics, contaminated materials, and complex packaging previously destined for landfills. Investment in chemical recycling facilities is increasing rapidly as the technology becomes more economically viable.
Extended producer responsibility programs are expanding across the region, shifting waste management costs and responsibilities to product manufacturers and brand owners. These policies create incentives for sustainable packaging design and provide funding for waste management infrastructure development.
Circular economy integration is driving collaboration between waste management companies, manufacturers, and retailers to create closed-loop systems. These partnerships ensure reliable supply chains for recycled materials while reducing waste generation and environmental impact.
Cross-border cooperation initiatives are emerging to address transboundary plastic waste challenges and share best practices. Regional organizations and bilateral agreements facilitate technology transfer, capacity building, and coordinated policy development.
Alternative material development is accelerating as companies seek to reduce plastic waste generation through biodegradable alternatives, reusable packaging systems, and innovative material designs. These developments complement waste management efforts by reducing the volume of materials requiring processing.
Regulatory milestones include implementation of comprehensive plastic waste management policies across major Asia-Pacific markets. China’s National Sword policy restricting waste imports has reshaped global waste trade patterns and accelerated domestic processing capacity development. India’s Plastic Waste Management Rules and extended producer responsibility programs are driving infrastructure investment and industry consolidation.
Technology breakthroughs in chemical recycling have achieved commercial viability for processing mixed plastic waste streams. Several major facilities have commenced operations, demonstrating the scalability and economic potential of these advanced technologies. AI-powered sorting systems are achieving unprecedented accuracy levels, improving material recovery rates and reducing contamination.
Strategic partnerships between waste management companies, technology providers, and end-users are creating integrated value chains and ensuring reliable supply chains for recycled materials. Major consumer goods companies are signing long-term agreements for recycled plastic supply, providing revenue certainty for waste management operators.
Infrastructure investments include development of modern waste processing facilities, collection system upgrades, and technology deployment across the region. Government funding programs and private sector investment are supporting capacity expansion and technology adoption.
International cooperation initiatives include the ASEAN Framework of Action on Marine Debris and various bilateral agreements for technology sharing and capacity building. These programs facilitate knowledge transfer and coordinated approaches to regional waste management challenges.
Investment prioritization should focus on technologies and infrastructure that address the most pressing regional challenges. Chemical recycling technologies offer the greatest potential for handling problematic waste streams, while digital technologies can improve operational efficiency across all market segments. Investors should prioritize companies with strong technology capabilities and regional market presence.
Market entry strategies should consider local market conditions, regulatory requirements, and partnership opportunities. International companies should seek local partners with market knowledge and established relationships. Technology providers should focus on solutions that address specific regional challenges such as mixed waste processing and contamination management.
Policy engagement is essential for successful market participation, given the significant influence of government regulations on market conditions. Companies should actively participate in policy development processes and maintain strong relationships with regulatory agencies. Understanding and anticipating regulatory changes can provide competitive advantages and investment opportunities.
Technology development should focus on solutions that improve economic viability while addressing environmental challenges. Innovations that reduce processing costs, improve material quality, or enable processing of new waste types offer the greatest market potential. Collaboration with research institutions and technology partners can accelerate innovation and reduce development risks.
Operational excellence requires focus on efficiency, quality, and reliability to compete effectively in price-sensitive markets. Companies should invest in training, process optimization, and quality control systems to achieve consistent performance. Building strong customer relationships and service capabilities creates competitive advantages beyond price competition.
Market expansion is expected to continue at a robust pace, driven by increasing waste generation, regulatory support, and technology advancement. The market will likely see continued consolidation as larger players acquire smaller operators and technology companies. Regional integration and cooperation will increase, creating opportunities for companies with multi-country operations.
Technology evolution will focus on improving processing efficiency, expanding treatable waste types, and reducing operational costs. Chemical recycling technologies will achieve broader commercial deployment, while digital technologies become standard across the industry. Innovation in alternative materials and packaging design will complement waste management efforts.
Regulatory development will continue toward more comprehensive and stringent requirements, with increased focus on circular economy principles and extended producer responsibility. International cooperation and harmonization of standards will facilitate regional market integration and technology transfer.
Market maturation in developed countries will focus on efficiency improvements and technology advancement, while developing markets will prioritize infrastructure development and capacity building. MWR analysis suggests that emerging markets will experience the highest growth rates, with infrastructure investment increasing by over 50% in the next five years.
Sustainability integration will become increasingly important as companies and governments prioritize environmental outcomes alongside economic considerations. The market will evolve toward more comprehensive solutions that address the full lifecycle of plastic materials, from design through end-of-life management.
The Asia-Pacific plastic waste management market represents a critical component of the region’s environmental and economic future, offering substantial opportunities for growth and innovation while addressing pressing sustainability challenges. The market’s evolution reflects the complex interplay between environmental necessity, regulatory requirements, technological advancement, and economic viability.
Strategic positioning in this market requires understanding of diverse regional conditions, regulatory environments, and technology trends. Success depends on developing comprehensive solutions that address local market needs while leveraging advanced technologies and best practices from more developed markets. The market rewards companies that can navigate regulatory complexity, implement innovative technologies, and build strong stakeholder relationships.
Future success will increasingly depend on integration across the value chain, from waste generation through final material recovery and reuse. Companies that can develop circular economy solutions, leverage digital technologies, and adapt to evolving regulatory requirements will be best positioned for long-term growth and profitability in this dynamic and essential market sector.
What is Plastic Waste Management?
Plastic Waste Management refers to the processes involved in the collection, recycling, and disposal of plastic waste to minimize its impact on the environment. This includes various strategies such as waste segregation, recycling technologies, and public awareness initiatives.
What are the key players in the Asia-Pacific Plastic Waste Management Market?
Key players in the Asia-Pacific Plastic Waste Management Market include Veolia, SUEZ, and Waste Management, among others. These companies are involved in various aspects of waste management, including collection, recycling, and waste-to-energy solutions.
What are the main drivers of the Asia-Pacific Plastic Waste Management Market?
The main drivers of the Asia-Pacific Plastic Waste Management Market include increasing environmental regulations, rising public awareness about plastic pollution, and the growing demand for sustainable waste management solutions. These factors are pushing both governments and businesses to adopt more effective waste management practices.
What challenges does the Asia-Pacific Plastic Waste Management Market face?
The Asia-Pacific Plastic Waste Management Market faces challenges such as inadequate infrastructure for waste collection and recycling, lack of public participation, and the high costs associated with advanced recycling technologies. These issues can hinder effective waste management efforts in the region.
What opportunities exist in the Asia-Pacific Plastic Waste Management Market?
Opportunities in the Asia-Pacific Plastic Waste Management Market include the development of innovative recycling technologies, increased investment in waste management infrastructure, and the potential for public-private partnerships. These opportunities can enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of plastic waste management.
What trends are shaping the Asia-Pacific Plastic Waste Management Market?
Trends shaping the Asia-Pacific Plastic Waste Management Market include the rise of circular economy initiatives, advancements in biodegradable plastics, and increased collaboration between governments and private sectors. These trends are driving a shift towards more sustainable waste management practices.
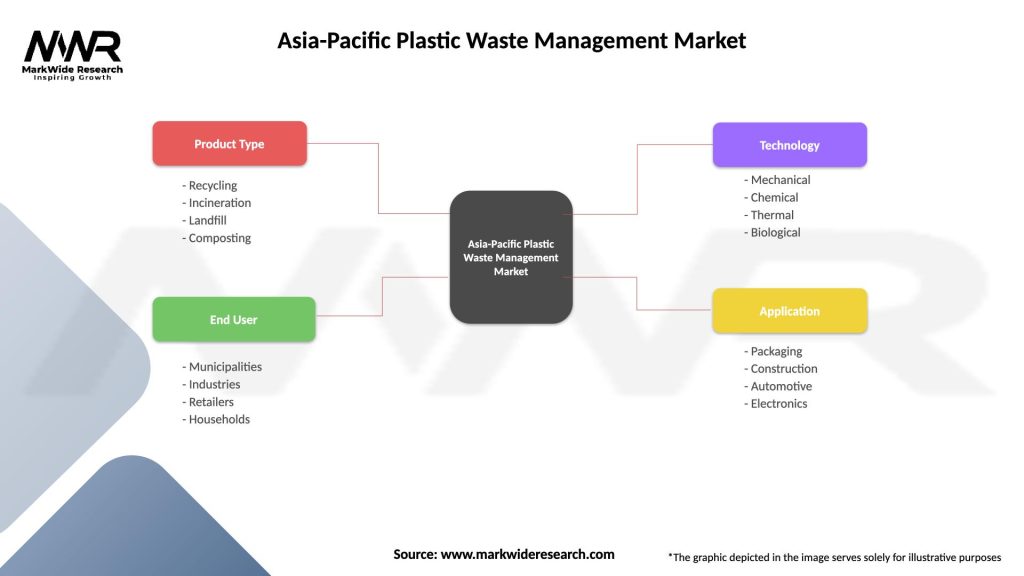
Asia-Pacific Plastic Waste Management Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Recycling, Incineration, Landfill, Composting |
| End User | Municipalities, Industries, Retailers, Households |
| Technology | Mechanical, Chemical, Thermal, Biological |
| Application | Packaging, Construction, Automotive, Electronics |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Asia-Pacific Plastic Waste Management Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at